- Hemorrhoids: From Basic Pathophysiology to Clinical Management - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3342598/)
- Internal and External Hemorrhoids - (http://ddc.musc.edu/public/symptoms/hemorrhoids.html)
- Enlarged Hemorrhoids: How can You Relieve the Symptoms Yourself? - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk279466/)
- Definition & Facts of Hemorrhoids - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids/definition-facts)
- Hemorrhoids - Overview - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/0715/p204.html#sec-2)
- About Hemorrhoids - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3140328/)
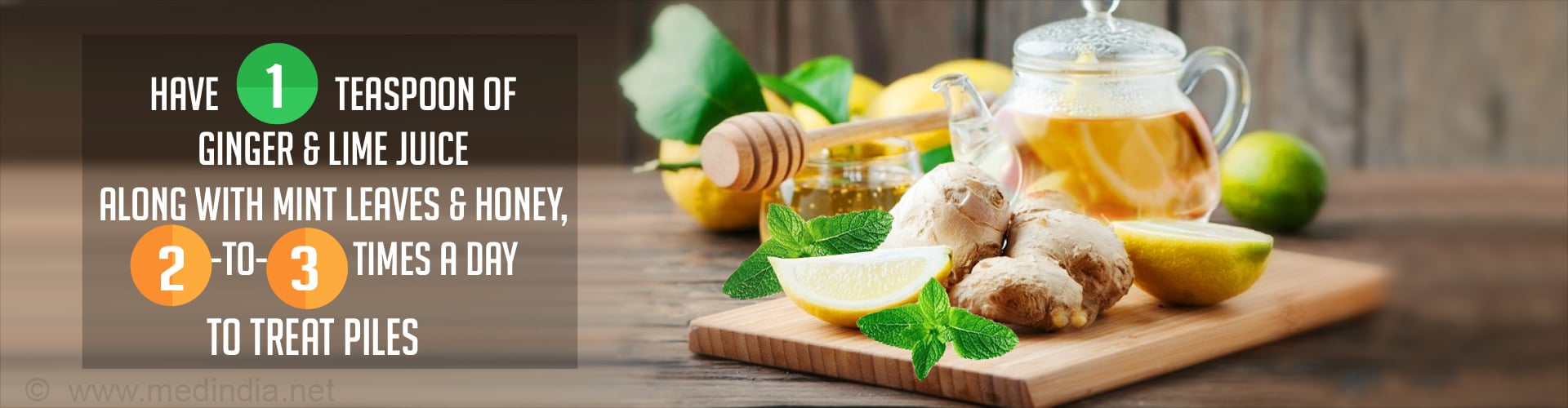
- Home Remedies for Piles - (https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/health-fitness/health-news/home-remedies-for-piles/articleshow/7347423.cms)
- Hemorrhoids and What to do About Them - (https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/hemorrhoids_and_what_to_do_about_them)
Information About Hemorrhoids / Piles
Hemorrhoids or piles are abnormally enlarged and dilated blood vessels (mainly veins) near the anus.
They occur in both men and women, most often between the ages of 20 and 50 years. Several factors like Age, Heredity factors, Diet and fluid intake are responsible for the development of piles.
In many cases, hemorrhoids are very small and the symptoms usually settle down without treatment.
Hemorrhoids are effectively treated with over-the-counter medications, good fluid intake, and by following a diet rich in fiber to avoid constipation. In severe cases, the piles may require surgical intervention.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Hemorrhoids
Go to source)
What are the Types of Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can be of two types and are classified as external or internal.
External Hemorrhoids occur on the outside edge of the anus. They are often painful. They are dilated veins forming swellings at the outer side of the external sphincter are known as external piles or perianal hematoma.
They are less common than internal hemorrhoids. External hemorrhoids are very itchy and cause intense pain if a blood clot forms inside the hemorrhoid (thrombosed external hemorrhoid). A thrombosed external hemorrhoid often requires surgical. It may heal with scarring and leave a skin tag protruding from the anus.
Internal hemorrhoids - are much more common that external hemorrhoids. Internal are dilated veins beneath the mucous membrane and occur 2 to 4 cm above the opening of the anus within the anal sphincter. They are above a line called the dentate line in the anus.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Internal and External Hemorrhoids
Go to source)
They are usually painless because there are few pain-sensing nerves in the rectum. Bleeding may be the only sign of internal piles.
Internal hemorrhoids are classified into four grades:
Grade 1 - Hemorrhoids are small swellings inside the lining of the anus. They are not visible externally. They may bleed but do not protrude through the anus.
Grade 2 - Hemorrhoids are larger than Grade 1 hemorrhoids. They extend inside the anus and may get pushed out when passing a stool, but soon return back inside the anus.
Grade 3 - Hemorrhoids are often called 'prolapsed hemorrhoids’. They appear outside the anus and can be pushed back on pressing with the finger.
Grade 4 - Hemorrhoids cannot be pushed back and remain outside the anus all the time. They are large and generally require a surgical treatment for their correction.
What are the Causes of Hemorrhoids?
Several factors are responsible for the development of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids commonly occur due to weakness of the tissues that support the blood vessels in the anal region and are commonly associated with the following:
- Heredity - They can be hereditary due to congenital weakness of the vein walls.
- Sitting posture - Sitting for long hours can predispose to piles.
- Lifting heavy weights regularly.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea - Straining by constipation and over purgation can cause hemorrhoid. Dysentery may aggravate latent hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy - Hemorrhoids are common among pregnant women. The pressure of the fetus in the abdomen, as well as hormonal changes causes the hemorrhoidal vessels to enlarge.
- Diseases like liver cirrhosis.
- Obesity.
- Improper diet- Eating junk food and a diet lacking in fiber contribute towards Hemorrhoids.
- Age - generally seen in the age group from 30 to 50 years.
- Persistent cough and sneeze.
- An obstruction or abnormal growth on the way to the anal canal.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hemorrhoids and What to do About Them
Go to source)

What are the Symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
Many people with hemorrhoids do not experience any symptoms and do not even know they have them.
In majority of the cases, Hemorrhoids are not serious and go away on their own within a few days.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids include:
- Bleeding from the anus, which is more common with internal than external hemorrhoids. It can occur before, during, or after defecation.
- Anus appears red and swollen.
- Itching, burning, swelling or pain is present near the anus.
- Itching may be present due to swelling and irritation produced by the hemorrhoids.
- Inflammation of the hemorrhoidal tissue
- Mucus discharge may appear during bowel movement.
- Protrusion of the hemorrhoids from the anus occurs frequently. This usually occurs after defecation, prolonged standing, or unusual physical exertion.
- Sense of fullness in the anus and straining while passing stools may be present.
- Anemia - If bleeding is profuse or long term, the patient may have anemia.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Definition & Facts of Hemorrhoids
Go to source)

How can we Diagnose Hemorrhoids?
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids is made on the basis of history and rectal examination.
History
The doctor usually questions the patient regarding any family history of piles, appearance of stools and bowel movements. The patient is also asked to explain the type of bleeding they experience. If it is fresh blood or dark blood. In piles generally the blood is fresh and bright red mixed with stools.
Physical examination - The examination includes:
Digital rectal examination, where the doctor examines the piles with a gloved finger.
Proctoscopy (Anoscopy) - A hollow, lighted tube, known as a proctoscope, is used to look at hemorrhoids and examine the lining of the rectum. The doctor may ask the person to strain during this examination to see the protrusion.
Laboratory investigations
Blood test is done to check the hemoglobin to rule out anemia.
The doctor may recommend a colonoscopy if the signs and symptoms are suggestive of another digestive system disease.