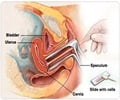
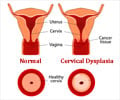
Health groups issue new guidelines for prevention and early detection of cervical cancer.
- Women should not be screened before age 21
- Women 21 to 29 should be screened with the Pap test alone (conventional or liquid-based) every three years. HPV testing should NOT be used for screening in this age group.
- For women 30 and over, the preferred approach is the Pap test plus HPV testing ("co-testing") every five years. Continued screening with the Pap test alone (without HPV testing) every three years is an acceptable alternative. While screening with HPV testing alone is promising, at this time it is not recommended for most clinical settings.
- Screening is not recommended for women over age 65 who have had at least three consecutive negative Pap tests or at least two negative HPV tests the last 10 years, with the most recent test in the last 5 years. Women in this age group who have a history of pre-cancer (CIN2 or a more severe diagnosis) should continue routine screening for at least 20 years.
- Women who have undergone a hysterectomy (with removal of the cervix) for reasons not related to cervical cancer or pre-cancer should not be screened.
- Women who have been vaccinated against HPV should follow the age-specific recommendations in these guidelines (for unvaccinated women).
The new guidelines are not intended for women with a history of cervical cancer, exposure to DES in utero, or women who are immunosuppressed (e.g. HIV positive). Costs and other financial issues were not considered in creating the guidelines.
"Pap tests have been done yearly in the past, but we now know that annual screening is not needed and in fact can lead to harm from treatment of cell changes that would never go on to cause cancer," said Debbie Saslow, PhD, director of breast and gynecologic cancer for the American Cancer Society. "Since 1980, organizations including the ACS have recommended less frequent screening. With the addition of the HPV test, we can test even less frequently, as the risk of pre-cancer and cancer when both tests are negative is so low. With these recommendations, our groups are helping to make sure women get the full lifesaving benefits of screening while minimizing its known harms."
Other new recommendations included in the guideline:
- Women at any age should NOT be screened annually by any screening method.
- Women with a slightly abnormal Pap test result (called "ASC-US") and a negative HPV test can be screened again with co-testing in 5 years or with the Pap test alone in 3 years.
- Women with a negative Pap result but a positive HPV test can either be rescreened with co-testing in one year, or tested with a test for specific types of HPV (HPV16 and HPV 18).
Advertisement
"Our process resulted in guidelines that are focused on collectively presenting the best patient-centered cervical cancer screening strategies," said Mark Stoler, MD, past-president of the American Society for Clinical Pathology. "These final recommendations are based on a broad and emerging body of literature, and meld the very latest knowledge on the interplay between new molecular tests and traditional cytology."
Advertisement
The guidelines are being published jointly in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians (ACS), Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease (ASCCP), and American Journal of Clinical Pathology (ASCP).
Source-Eurekalert