In 90% of women with female genital tuberculosis condition, the fallopian tubes are affected. In around 70% uterine endometrium is affected.
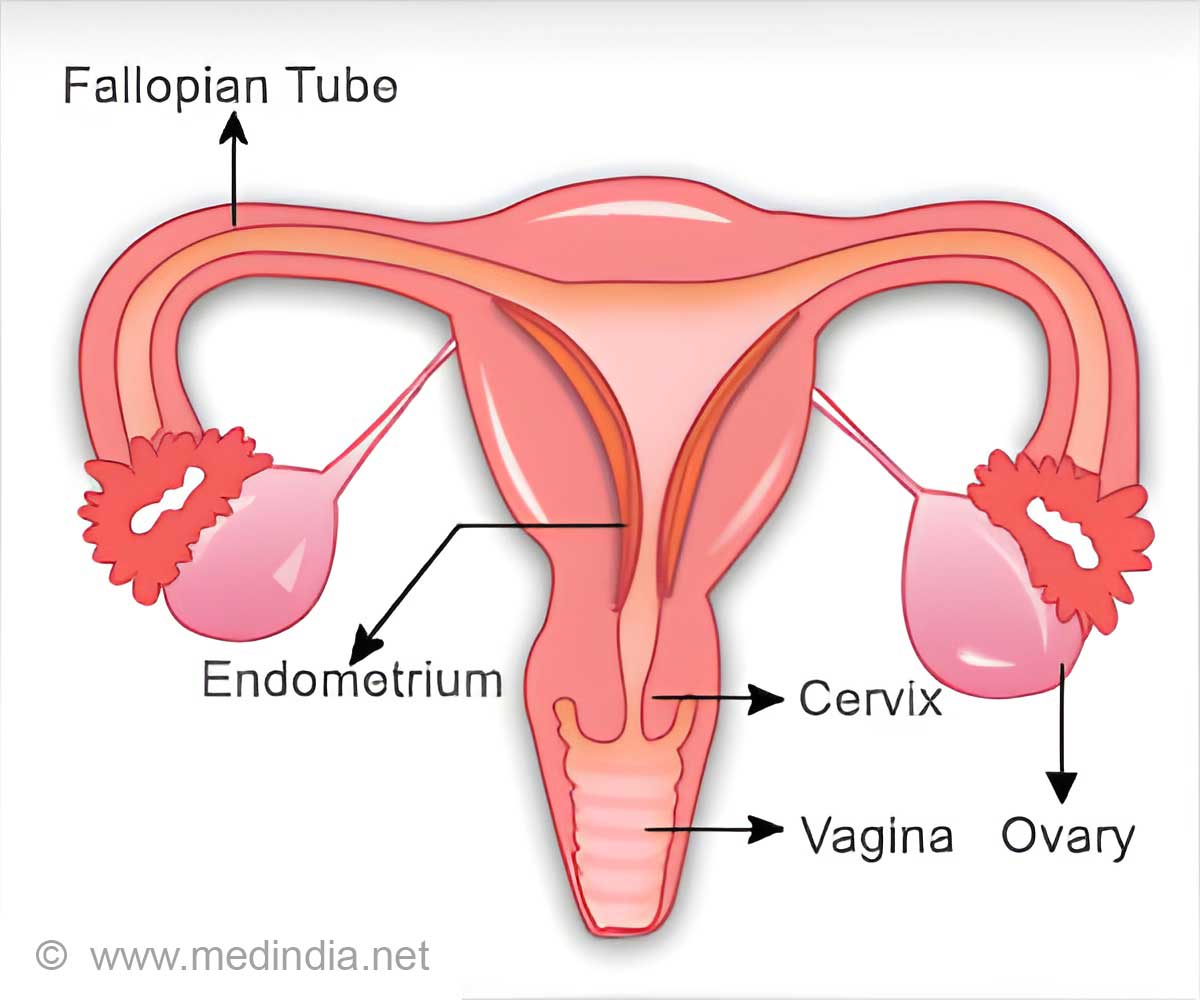
What is Female Genital Tuberculosis
"Female Genital Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection of the female reproductive system that is known to cause infertility in women. This type of TB can take a toll on the fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries, cervix, and vagina," said Dr. Surabhi Siddhartha, Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist, Motherhood Hospital, Mumbai. It causes menstrual dysfunction and infertility through the damage of genital organs.‘Female Genital Tuberculosis (FGTB) affects the female reproductive system and requires immediate attention. The condition is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (rarely Mycobacterium bovis and/or atypical mycobacteria).’





Women suffering from female genital TB generally develop no symptoms at all, especially in the early stages. Often, infertility is the only presenting symptom. "If the fallopian tube is infected the egg which gets fertilised will fail to pass via the tube and reach its destination which is the uterus. Hence, the woman will not be able to conceive," Siddhartha said.
TB is the world's deadliest infectious disease, which afflicts more than 10 million people each year. India contributes to over 30 percent of the global TB burden.
In 2021, India had estimated 30 lakh new TB cases. About 38 percent of TB deaths globally took place in India.
"Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious airborne disease leading to high morbidity and mortality rates not only in India but globally too. TB can have severe consequences for women, especially during their reproductive years and during pregnancy. TB most commonly affects the lungs, but it may affect multiple organ systems in the body and it may lead to infection in the fallopian tubes as well. It can also have a lasting impact on the endometrium, leading to infertility among females," said Dr. Sulbha Arora, Clinical Director, Nova IVF Fertility, Mumbai.
Advertisement
According to the doctors, one of the ways to keep genital TB at bay, is to treat pulmonary TB effectively without fail. Doing so can stop it from spreading to the reproductive system. Also, practicing safe sex methods, and getting immunized as per the doctor's advice, they suggested.
Advertisement
Source-IANS