Chemotherapy-induced weight gain in early-stage breast cancer
Go to source). The chemo patients also exhibited signs of inflammation and significant changes to the number and variety of bacteria in their guts.
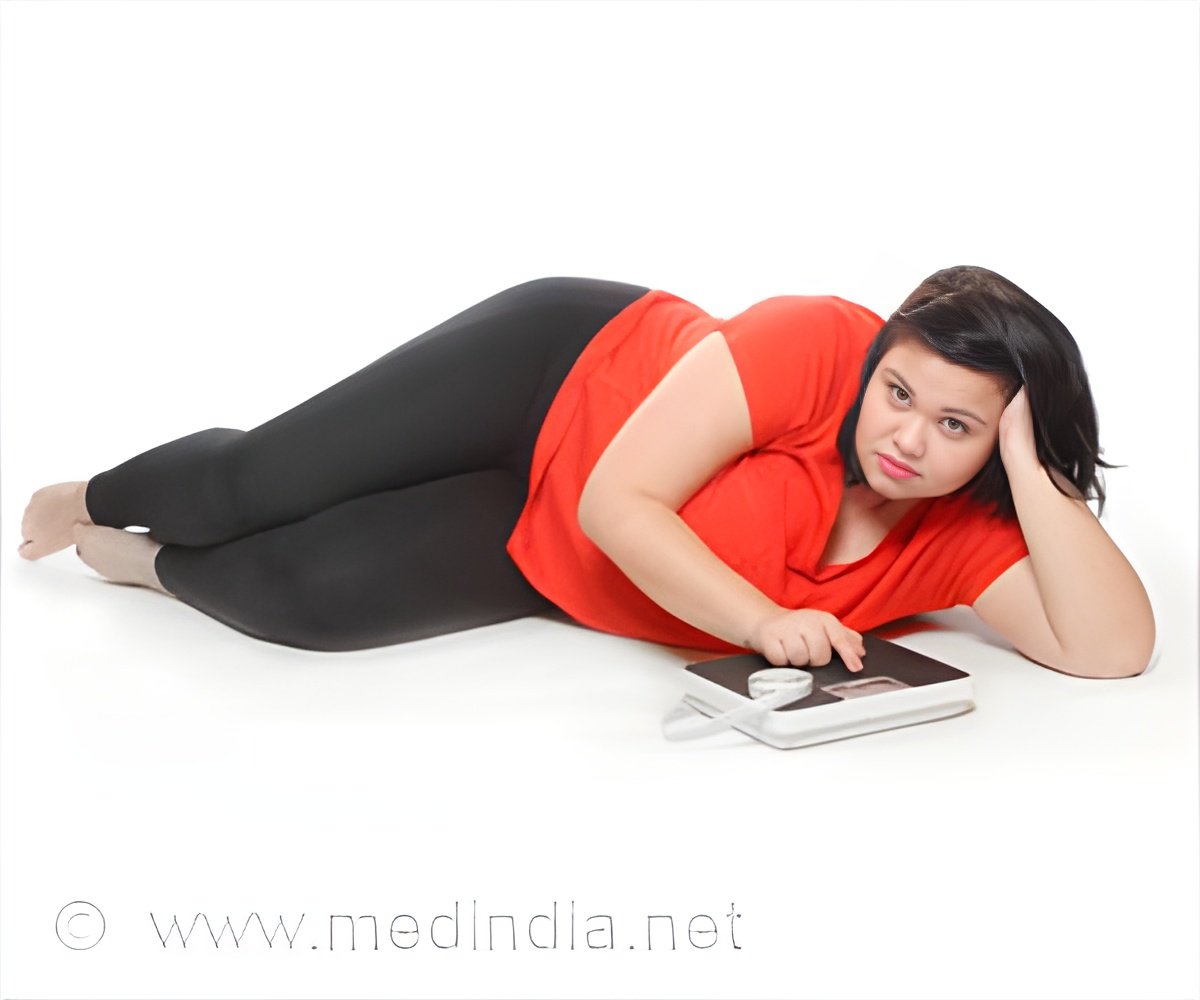
‘Individuals undergoing chemotherapy experienced a decline in muscle mass while simultaneously accumulating abdominal fat, a condition associated with increased risks of heart disease, diabetes, and even cancer recurrence. #obesity #weightgain #gutbacteria #cancer’





“Changes in the bacterial populations within the gut directly correlate with unhealthy weight gain and increased body fat composition in breast cancer patients who were treated with chemotherapy,” says John Walker, professor in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry and head of medical oncology for northern Alberta at the Cross Cancer Institute, who co-led the study with Gane Ka-Shu Wong, professor in the departments of medicine and biological sciences.
Exploring the Link: Gut Microbiota Damage and Chemo-Induced Weight Gain
Obesity has been linked with several kinds of cancer, including breast cancer, and oncologists have long observed that cancer treatment seems to make it worse. Many people lose weight after a cancer diagnosis, but that trend is reversed in breast cancer patients who undergo chemotherapy. Studies have shown that while 50 percent of breast cancer patients are overweight or obese before their diagnosis, that rate goes up to 67 percent after treatment.Changes to diet or exercise patterns during treatment are simply not significant enough to explain that difference, since they affect all patients who are treated for cancer, Walker notes.
”There's something unique about this modulation of the gut microbiome for breast cancer patients who receive chemotherapy.”
Walker notes it is not surprising that chemotherapy drugs have bacteria-killing effects, since some are derived from antibiotics and all are metabolized through the liver and then the gut.
“Breast cancer is an unparalleled success story in medicine. We see cure rates over 90 percent today, so survivorship is now equally important. We want to ensure that in survival, our patients aren’t then dealing with the metabolic consequences of weight gain during treatment.”
Advertisement
- Chemotherapy-induced weight gain in early-stage breast cancer - (https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-023-02751-8)