“Keep the pressure down is the slogan for the World Kidney Day 2009. It points to the importance of high blood pressure as a primary cause of kidney disease.
March 12th 2009
World Kidney Day (WKD) is a campaign to increase awareness on the importance of kidneys, and to reduce the occurrence of kidney disease, globally. It is celebrated in more than 100 countries on the second Thursday of March every year.“Keep the pressure down” is the slogan for the year 2009 -- a clear pointer to the importance of high blood pressure as one of the chief causes of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
Agenda 2009
The campaign will strive to inform the public about the ‘amazing kidneys’ besides creating awareness on the importance of screening, by encouraging people to undergo simple tests that will help to diagnose kidney disease. To achieve this the World Kidney Day (WKD) has formed an official partnership with the World Hypertension Day, which occurs on the 17th of May.
The organizers of the World Kidney Day-- the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) and the International Federation of Kidney Foundations (IFKF) hope to achieve the following by pressurizing governments and the healthcare organizations and personnel-
• Routine measurement of BP and urine examinations
• Compulsory screening of high risk patients for CKD
• Informing patients with CKD and teaching them self help techniques.Chronic Kidney Disease
Ten percent of the world’s population i.e., about 500 million people suffer from kidney damage of some sort. A good number of them die from heart diseases that develop as a result of CKD, which is condition associated with progressive decline in kidney functions.
CKD is strongly associated with other health problems such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). The common factor that binds these conditions is high blood pressure. A person suffering a combination of these conditions has a poor prognosis.
Earlier inflammatory diseases of the kidney, urinary tract obstructions or hereditary disorders like polycystic kidneys caused CKD. Now hypertension and diabetes top the list.
Blood and urine samples to test for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and creatinine level of blood serumcan help to diagnose the condition.
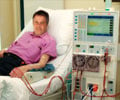
CKD always results in irreversible kidney damage -- requiring dialysis or kidney transplant -- or death. The risk of dying from heart problem is more in these individuals than the risk of end stage renal disease (ESRD).
This disease is treatable and its progression can curtailed if timely detection is enabled. To actualize this, regular screening must be carried out. Compulsive tests must be carried out on high risk individuals such as--
• Diabetics
• Those with hypertension
• Obese people
• Individuals above the age of 50
• Those who smoke
• Those with a family history of kidney disease
Some of the Most Alarming Facts About Kidney Disease
The recent global increase in kidney disease is cause of worry for many countries especially in Asia. Some of the facts include
1. The incidence kidney failure (or chronic Kidney disease) has doubled the last 15 years.
2. Diabetes is an important cause of kidney failure and diabetes is five times more common in the Asians when compared to the white population
3. Another lifestyle related disorder – hypertension or blood pressure is an important cause of kidney failure and it too has seen a global increase in its incidence. Asians again are twice more prone to develop this condition in comparison to the white population.
4. There are approximately 7.85 million people suffering from chronic kidney failure in India.
5. In the United States the cost of treating patients with renal replacement therapy will be US $28 billion by the year 2010. It is estimated that over 600 000 patients will require treatment.
Almost 80% of patients with CKD have elevated BP. On the other hand , increased blood pressure can be the consequence CKD.
High BP stresses the blood vessels in the kidneys and reduces their ability to filter wastes from the blood.
Therefore normalizing high BP is the main tenet of managing CKD and patients with high BP need to be closely monitored. Proper lifestyle changes and medications can help to control BP, which in turn will help to reduce the need for dialysis and decrease the risk for heart attack and stroke.
Controlling Blood Pressure
Some of the steps to control blood pressure include lifestyle changes and these have a profound impact in normalizing BP. They are-
• Regular exercise for 30-40 minutes, 5-6 days /week
• Balanced low fat, low salt diet- A healthy diet with salt consumption less than five grams helps to lower BP substantially
• Meditation helps to calm an agitated mind
• Abstinence from smoking and alcohol is an integral part of BP control
• Maintaining normal weight is absolutely vital in controlling BP
• Periodic BP monitoring is necessary to monitor the body’s progress
• BP medications must be taken as prescribed by your physician
• Aging is the most common risk factor for diabetes, high BP, and CKD.
• Nearly one billion people all over the world have high BP.
• By 2025, the number is expected to rise to 1.56 billion.
• The prevalence of high blood pressure is predicted to escalate by 24 percent in developed countries and by 80 percent in developing regions.
• 333 million adults in North America and Europe had high blood pressure in the year 2000, while there were 639 million affected people in the developing countries.
• High blood pressure must be treated as a global problem as it affects people in the developed and developing nations.
Transplant vs. Dialysis
According to long-term Scottish data, a successful kidney transplant has been shown to triple the life expectancy in patients suffering end-stage renal failure in comparison with the life expectancy in patients who continued with dialysis.
The life expectancy in patients who received a kidney donation from a cadaver was 17.19 years while those who continued on dialysis had a life expectancy of 5.84 years.
Irrespective of age the risk of death reduced remarkably following transplantation in comparison to dialysis.
This revelation based on solid research should encourage people to donate their kidneys .The fact that their kidneys would be put to good use should enable them to truly ‘rest in peace’!
Dr Reeja Tharu/S