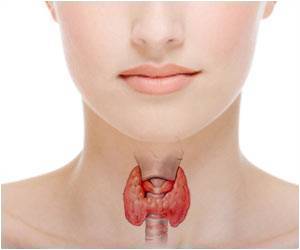
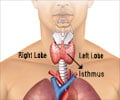
Vandetanib delays progression of locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer.
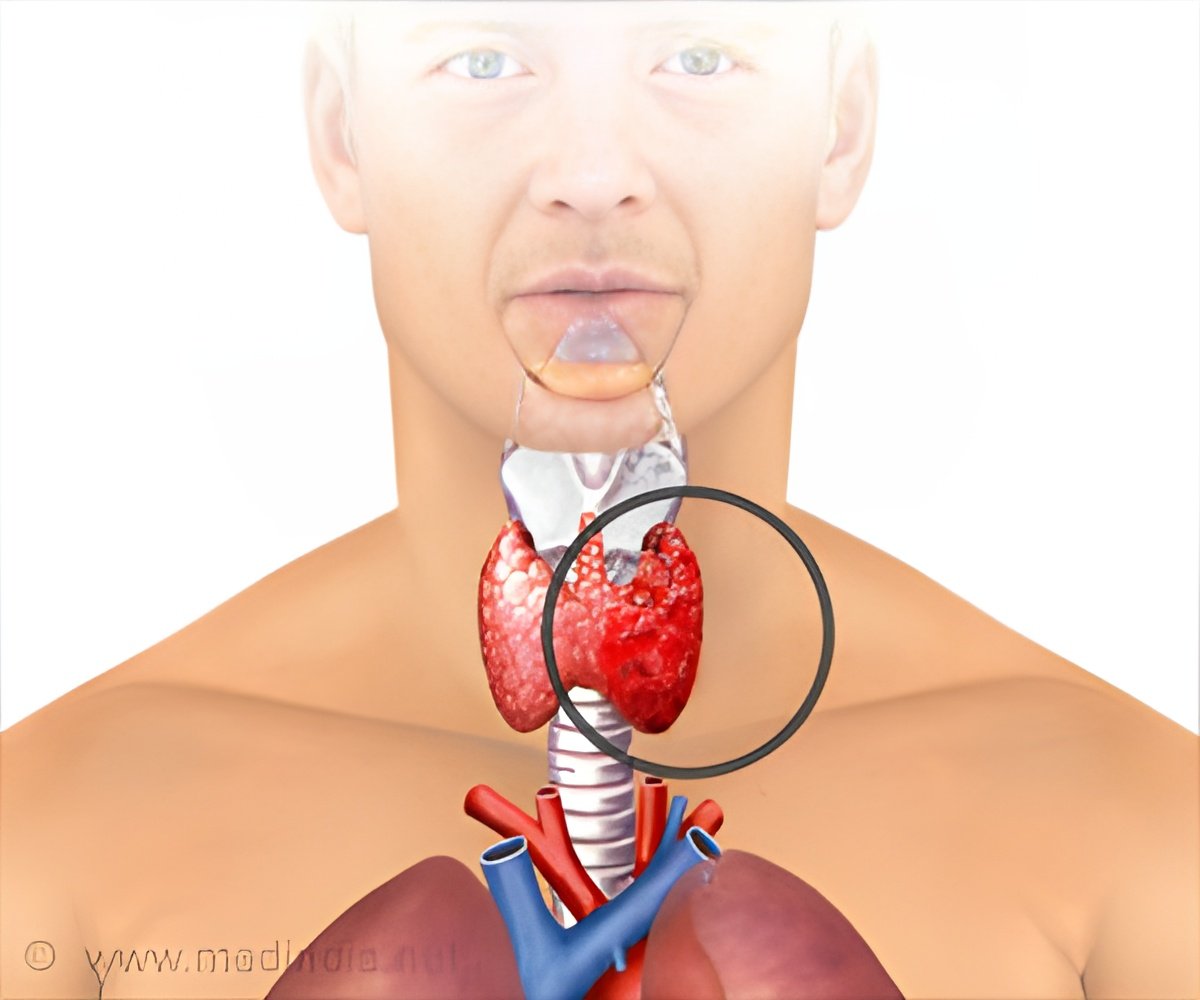
Vandetanib is a novel anticancer drug already approved for the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer that has advanced locally or spread to distant sites. It follows the principle of targeted therapy, that is, it attacks cancer cells without affecting normal cells.
A small study evaluated the efficacy and safety of vandetanib in the treatment of advanced differentiated thyroid cancer that did not respond to radiotherapy. The study was conducted in 145 patients equal or over the age of 18 years with thyroid cancer (papillary, follicular or poorly differentiated) in Europe. The patients received either 300 mg of vandetanib per day (72 patients) or a placebo (73 patients).
At the end of the study, it was observed that 52 patients in the vandetanib group and 61 patients in the placebo group showed disease progression. The deaths reported at the end of the study were 19 in the vandetanib group and 21 in the placebo group. Patients in the vandetanib group had a significantly longer progression-free survival as compared to those who did not.
Vandetanib is known to be associated with a serious cardiac side effect called QTc prolongation. This is an abnormality in the cardiac rhythm, which can even lead to death. QTc prolongation was observed in 10 patients receiving vandetanib in the study. Other complications like diarrhea, asthenia and fatigue were also more common in patients receiving vandetanib.
Three deaths in the study were attributed to treatment. Among these, the two deaths in the vandetanib group were due to bleeding from skin metastases and pneumonia, whereas the death in the placebo group was due to pneumonia.
Reference:
Source-Medindia