Studies in rats show that Ginkgo Biloba extract could prevent atherosclerosis in diabetes patients.

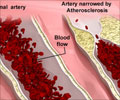
Recently, researchers conducted a study to see the effect of this extract on atherosclerosis in diabetes. Atherosclerosis causes buildup of plaques in the inner lining of blood vessels. It can lead to thickening of the arteries and decreases blood supply to various organs supplied by the arteries.
The study was conducted on rats with obese type 2 diabetes. The rats were divided into three groups of 12 rats each. One group served as a control whereas the other two were administered 100mg/kg and 200 mg/kg of EGb761 per day for 6 weeks’ duration. At the three-week mark, the carotid arteries of the rats were damaged using standard techniques. Damage to a portion of an artery favors the deposition of cholesterol and formation of a plaque. The plaque then continues to grow and occludes the artery.
The researchers found that rats treated with EGb761 showed a decrease in plaque formation following the injury. This was more significant in rats on a higher dose of EGb761 i.e. 200 mg/kg/day. Cell proliferation was lower and apoptosis of the muscles of the blood vessels was higher in the EGb761 groups. Inflammation was also lower in the EGb761 groups. Other parameters were also tested, the results of which reinforced the antiatherogenic properties of EGb761.
The study thus indicates that EGb761 may play an important role in reducing atherosclerosis and risks for heart diseases in diabetics. Further studies in humans are required to establish their use for this purpose.
Reference:
http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0020301#s1
Source-Medindia