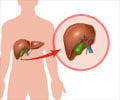
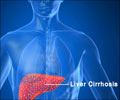
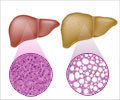
Overdoses from prescription products containing acetaminophen may cay cause severe liver damage that ends in liver transplant or death.
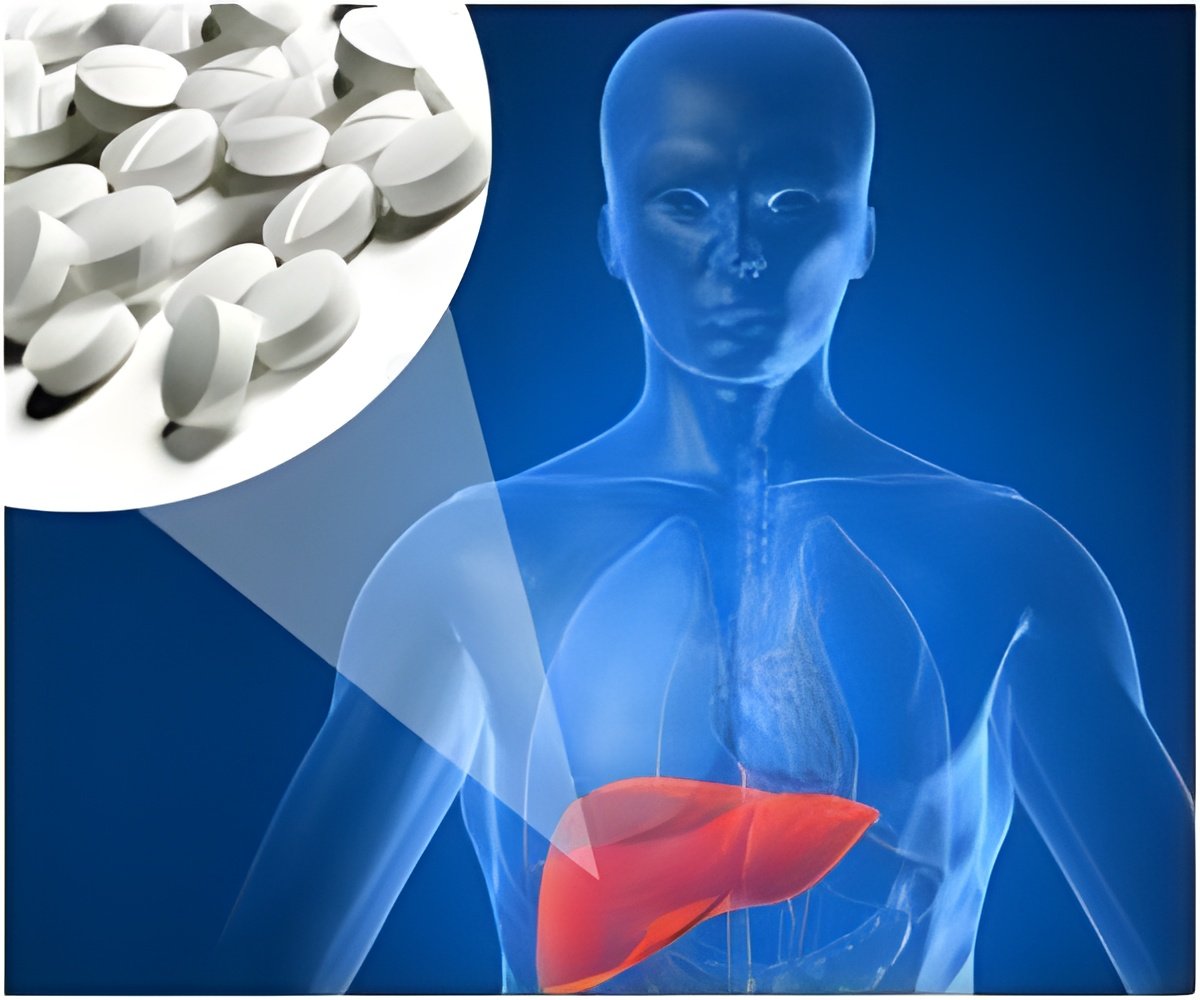
The three commonest causes for acetaminophen induced liver injury are:
• Taking the drug in doses exceeding the recommended limits in a 24 hour period
• Taking more than one acetaminophen-containing product at the same time
• Drinking alcohol while taking the drug
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has taken new steps to reduce the risk of severe liver injury associated with acetaminophen. All makers of prescription products that contain acetaminophen have been asked to limit the amount of the drug to 325 milligrams per tablet or capsule. It is also required to have a ‘Boxed Warning’ on all acetaminophen prescription products that highlights the potential risk for severe liver injury. FDA is also requiring a warning on labels of all prescription products that contain acetaminophen that highlights the potential for allergic reactions (swelling of the face, mouth, and throat; difficulty breathing; itching; and rash).
The FDA has the following advice for consumers:
• Take not more of an acetaminophen-containing medicine than directed
• Take not more than one product that contains acetaminophen at any given time
• Read all labels for prescription and OTC medicines and asking the pharmacist if your prescription pain medicine contains acetaminophen
• Do not drink alcohol when taking acetaminophen
• Stop your medicine and seek medical help immediately if you-
a) experience allergic reactions such as swelling of the face, mouth, and throat; difficulty breathing; itching; or rash
b) think you have taken more acetaminophen than directed
• Do not take more acetaminophen than the maximum daily dose of 4,000 milligrams or 4 grams.
Reference: Food and Drug Administration (FDA) -Consumer Updates
Source-Medindia