In children, warning signs include cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin), rapid breathing, poor feeding, and slow growth.
- Warning signs of congenital heart disease in children include cyanosis (bluish skin discoloration), rapid breathing, poor feeding, and slow growth
- Other symptoms may include fatigue, respiratory infections, swelling, sweating, clubbing of fingers and toes, and fainting
- Parents and caregivers should seek medical attention promptly if they notice these signs
What is Congenital Heart Disease?
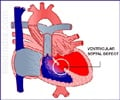
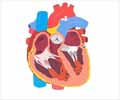
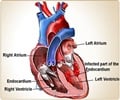
Congenital heart disease (CHD) in children refers to a group of heart abnormalities or defects that are present at birth. These defects can affect the structure and function of the heart, leading to various health issues (1✔ ✔Trusted SourceCongenital heart defects in children
Go to source). Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a condition that affects the structure and function of the heart present at birth. It can range from mild to severe, and some children may not show any symptoms until later in life.
The symptoms and severity of CHD can vary from child to child. Some children may have mild symptoms, while others may experience severe complications that require surgery or other medical interventions. Regular check-ups with a pediatrician and, if needed, a pediatric cardiologist are essential for diagnosing and managing CHD in children.
Treatment options can include medication, catheter-based procedures, or open-heart surgery, depending on the specific defect and its severity. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical care can greatly improve the long-term outlook for children with CHD.
What are the Signs of Congenital Heart Disease in Children?
However, there are several warning signs and symptoms that parents and caregivers should be aware of in children with congenital heart disease.These signs can vary depending on the specific type and severity of the heart defect, but common warning signs may include:
Cyanosis
: Bluish or grayish discoloration of the skin, lips, or nails, especially when the child is active or crying. This can be a sign of reduced oxygen levels in the bloodRapid breathing
: Fast or labored breathing, especially during feedings or while at restPoor feeding
: Difficulty with feeding, sweating during feeds, or becoming tired easily while eatingSlow growth
: Failing to gain weight or grow at the expected rate for their ageFatigue and irritability
: Unexplained tiredness, excessive sleepiness, or crankiness, which can be due to the heart having to work harder to pump bloodRespiratory infections
: Frequent respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, can be a sign of weakened heart functionSwelling
: Swelling or puffiness in the legs, ankles, feet, abdomen, or around the eyes, which can be caused by fluid retention due to heart problemsSweating
: Excessive sweating, especially on the head while feeding or during sleepClubbing of fingers and toes
: Abnormal, rounded enlargement of the fingertips and toes, which can occur when the heart is not pumping enough oxygen-rich bloodFainting or dizziness
: Sudden loss of consciousness or feeling lightheaded can be signs of insufficient blood flow to the brain
Regular check-ups with a pediatrician and, if needed, a pediatric cardiologist are crucial for the early detection and management of congenital heart disease. If you suspect that your child may have CHD or if you observe any of these warning signs, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical care can significantly improve the outcome for children with congenital heart disease.
- Congenital heart defects in children - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/congenital-heart-defects-children/symptoms-causes/syc-20350074)
Source-Medindia