Researchers formed a consortium to explore the genetic roots of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders, focusing on high-risk genes.

Scaled and efficient derivation of loss-of-function alleles in risk genes for neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders in human iPSCs
Go to source).
‘Did You Know?
Schizophrenia affects roughly 20 million people worldwide, and many still lack access to effective treatments. #neurodevelopmentaldisorder #psychiatriccondition #genes’





It’s becoming more and more clear that genetic mutations in certain genes can increase the likelihood of developing NPD, and several hundreds of those “risk genes” have been identified to date, but their role related to NPD remains a mystery. Schizophrenia affects roughly 20 million people worldwide, and many still lack access to effective treatments. #neurodevelopmentaldisorder #psychiatriccondition #genes’
Uniting Global Experts to Tackle NPDs
“Very little is known about the basic function of most of these genes, and what we do know often comes from work in cancer cell lines rather than brain cell types,” says David Panchision, Chief of the Developmental and Genomic Neuroscience Research Branch at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), who spearheaded the SSPsyGene program aiming to tackle this challenge.“As such, we still don’t have a clear understanding of how alterations in these genes may work individually or in combination to contribute to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders.”
To get to the bottom of this, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) initiated a consortium called SSPsyGene (sspsygene.ucsc.edu) in 2023, uniting research teams from renowned US universities with the joint goal of characterizing the genetic origins of NPD, focusing on 250 selected high-risk genes.
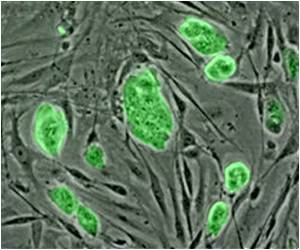
Among the contributors are Jubao Duan, Endeavor Health (formerly NorthShore University Health System) and University of Chicago, USA, and Zhiping Pang, Rutgers University, USA with their teams, who developed a method for mutating NPD risk genes in human stem cells at large scale.
Advertisement
The modified stem cells can subsequently be turned into neurons and other brain cells to model the consequences of risk gene mutations in a simplified, lab-based version of the human brain.
The resulting stem cell lines will be made available to other researchers worldwide to facilitate research on those risk genes and their contribution to NPD.
In future works, Pang, Duan, and the other members of the consortium will join forces to generate mutated stem cell lines for a much larger number of risk genes, with the ultimate goal of understanding the genetic causes for NPD and for generating better treatments.
“The hope is that this collaborative work will generate a highly impactful resource for the neuroscience and psychiatric research community,” Panchision says.
Reference:
- Scaled and efficient derivation of loss-of-function alleles in risk genes for neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders in human iPSCs - (https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(24)00241-8)
Source-Eurekalert