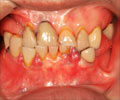
Soft gums tend to show high susceptibility to the disruption of gum health because of mechanotransduction-mediated proinflammatory responses in gingival fibroblasts.
‘Fibroblasts present in gums may sense mechanical stress to influence supporting bone resorption along with immune cells.’





The gingiva is home to fibroblasts - cells that contribute to the formation of connective tissue. Now, they have discovered that soft gingiva results in inflammation and hinders the development of gingival fibers.What Does it Mean if Your Gums are Soft?
It has long been known that individuals with thick or stiff gingiva are less susceptible to gingival recessions. This is where the gingiva begins to recede and expose a tooth's root. Many factors can lead to gingival recession, such as gum disease, over-brushing, and chewing tobacco. But this is the first time that gingival stiffness has been attributed to biological reactions.Although fibroblasts play an important role in the maintenance, repair, and healing of the gingiva, they also produce various inflammatory and tissue-degrading biomolecules which degrade the gingival fibers. In addition, fibroblasts are associated with immune responses too.
Researchers from Tohoku University's Graduate School of Dentistry created an artificial culture environment that simulated soft or hard gingiva and cultured human gingival fibroblasts on them.
They discovered that hard gingiva-simulated stiffness activated an intracellular anti-inflammatory system in the gingival fibroblasts that prevented inflammation. Yet, soft gingiva-simulated stiffness suppressed the fibroblastic anti-inflammatory system. This increased the likelihood of inflammation and resulted in less collagen synthesis.
This research is the first to demonstrate the biological mechanisms at play regarding a patient's gingival properties. The results are expected to accelerate the development of advanced biomaterials to control local inflammation or microdevices that simulate the microenvironment of inflammatory conditions.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert