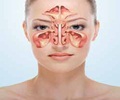
For cases of chronic sinusitis that are unresponsive to treatment, it is crucial to conduct a comprehensive patient history and thorough clinical examination.
Think outside the box – atypical infections in chronic sinusitis
Go to source).
Understanding the Prevalence and Complexity of Chronic Sinusitis
Inflammations of the paranasal sinuses represent a common clinical picture. The annual prevalence of chronic sinusitis in Europe is up to 10% (2✔ ✔Trusted SourcePrevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in the general population based on sinus radiology and symptomatology
Go to source). Sinusitis can be divided into acute and chronic forms. In particular, the chronic forms (>12 weeks duration) are often challenging in the context of therapy. Generally, all ventilation disorders of the paranasal sinuses (concha bullosa, nasal septal deviations, etc.,) represent risk factors (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk factors for chronic rhinosinusitis
Go to source) for the development of any form of sinusitis. In addition, an immune deficiency or systemic diseases relevant to the immune system predispose to infections with atypical pathogens. Most sinusitis are caused by (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factors and Comorbidities in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Go to source) viruses, sometimes bacteria and, in rare cases, fungal infections. Furthermore, sinusitis can be differentiated with regard to the affected paranasal sinuses.
In addition to conservative treatment options for chronic sinusitis (glucocorticoid nasal sprays, antibiotics, antimycotics, immunotherapy), surgical procedures (functional endoscopic sinus surgery) can also be considered. However, chronic sinusitis tends towards a high rate of recurrences. Therefore, in many cases only symptom control is achieved.
“It is also important to consider atypical causes and disease connections (root canal treatment, aspergilloma) when dealing with chronic sinusitis. Interdisciplinary diagnostics and therapy are crucial for the successful treatment of this rare entity.”
References:
- Think outside the box – atypical infections in chronic sinusitis - (https://www.oncoscience.us/article/576/text/)
- Prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in the general population based on sinus radiology and symptomatology - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30578880/)
- Risk factors for chronic rhinosinusitis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25479315/)
- Risk Factors and Comorbidities in Chronic Rhinosinusitis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26800681/)