- The chronic asthenia syndrome: a clinical approach - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20529781)
- Asthenic symptoms in a rural family practice. Epidemiologic characteristics and a proposed classification - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2391456)
- Diagnosis and treatment of asthenic syndrome in elderly people after acute respiratory viral infection - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25403306)
- Depression or asthenia related to metabolic disturbances in obese patients after intestinal bypass surgery - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/463585)
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0024898/)
- Evaluation of the Patient with Muscle Weakness - (http://www.aafp.org/afp/2005/0401/p1327.html)
- Lack of Energy During Pregnancy - (http://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/lack-energy-pregnancy/)
What is Asthenia?
The term asthenia refers to extreme muscle weakness and lack of energy. It is described as unusual fatigue without or before any effort. Reports state that it is a frequent cause occurring in almost 30% of ambulatory settings. And, 0.2-0.7% of these cases belong to the chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) or systemic exercise intolerance disease (SEID). CFS is a serious debilitating disorder that may seriously affect the quality of one’s life causing long-term illness.
What are the Causes of Asthenia?
Asthenia may be caused by a number of factors and the most common ones are listed below:
- Anxiety or depression - It is the main cause of fatigue and counts for almost half of the cases of Asthenia. In fact, in most of the cases it goes unrecognized and undiagnosed. It is mostly experienced by the individuals suffering from life-limiting illness. It interferes with a patient’s functional status and quality of life.
- Sedentary lifestyle - According to WHO, 60-85% of people in the world lack necessary amount of physical activity in their life. This state of inertia makes their muscles weaker.
- Aging - With increasing age there is reduction in the ability of cells and tissues in the body to maintain homeostasis, and particularly when the person is under stress, symptoms of Asthenia are seen more often.
- Infections - Prolonged infection in the body such as tuberculosis, hepatitis, or infective endocarditis can cause this condition and have a debilitating effect on muscles.
- Chronic diseases - Diseases like myasthenia gravis involves rapid, generalized weakness, and other chronic conditions like insomnia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease and cancer can also affect the quality of life.
- Pregnancy - Pregnancy is associated with fatigue and low energy levels in many cases and is most common during the third trimester. Reduction in the energy levels is due to the altered progesterone levels.
- Drug-induced myopathies - They are very usual complications of drug therapy. The common symptoms are proximal muscle weakness, increased muscle enzyme levels, and electromyographic changes. For example combinations of a fibrate and a statin or cyclosporin and colchicine can induce severe myopathies.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy - Certain chemotherapy drugs may also affect the overall health and mobility of the individual. Some of them are as follows:
- Cisplatin and carboplatin - Affect vestibular system of the inner ear.
- High dose of cytosine arabinoside and fluorouracil - May affect the cerebellum leading to imbalance.
- Vitamin deficiencies - Lack of Vitamins in the body can make the person feel dizzy, tired and unable to perform daily activities.

What are the Symptoms and Signs of Asthenia?
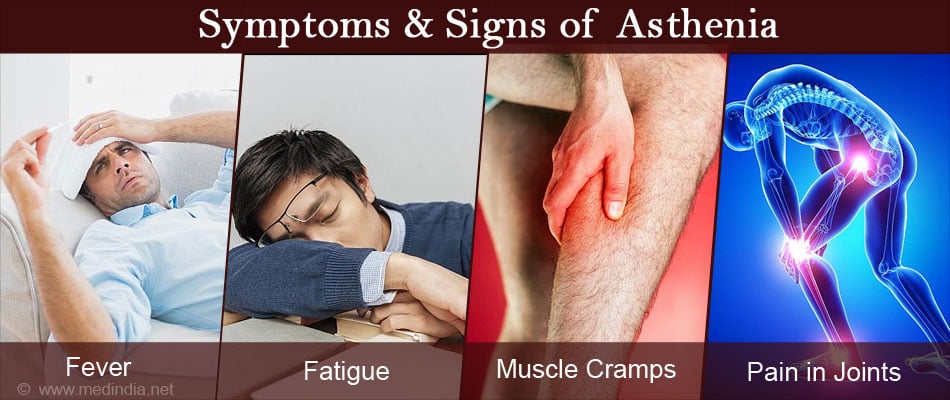
The common symptoms and signs of Asthenia include the following:
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Loss or lack of energy
- Muscle cramps
- Absence or loss of muscle strength
- Episodes of tremors
- Wobbly sensation
- Pain in joints
- Deteriorating attentiveness
- Excruciating pain
- Restless sleep
- Sudden loss of consciousness
How Do You Diagnose Asthenia?
In the presence of the above mentioned symptoms the doctor should be consulted for proper diagnosis and evaluation of the condition of the patient and to rule out any serious underlying disease.
Blood tests:
- Complete blood count including vitamin B12, folate and ferritin levels
- Inflammatory markers such as ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) and CRP (C-Reactive Protein) to rule out underlying chronic inflammatory disease
- Biochemical tests such as blood glucose, serum electrolytes, liver function tests, renal function tests, thyroid function tests and vitamin D levels.
- Autoantibody screen to rule out autoimmune disease

Urine tests:
An urinalysis is performed to rule out diabetes, renal or liver disease and pregnancy, especially recent onset chronic fatigue in women in the reproductive age.
Other tests:
If there an index of suspicion, the following tests may be carried out which may include HIV testing, electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram to rule out heart disease, tuberculin testing and chest x-ray to rule out tuberculosis. Urine toxicology screen may be indicated in certain cases, especially if substance abuse is suspected.
How Do You Treat Asthenia?
Treatment for asthenia depends on the underlying cause for it. In many cases, supportive therapy and counseling may help. The various treatments include the following:
Symptomatic pain relief may be necessary with NSAIDs and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Management of sleep disorders under a specialist
Asthenia due to stress-related neurotic disorders: Individuals suffering from generalized anxiety disorders, panic attacks and adjustment disorders, may be treated by therapists, general practitioners, or psychiatrists.
- Antidepressants are given to treat prolonged weakness linked to depression.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy has also been shown to be useful.
Asthenia due to Infections: Weakness or loss of energy and strength caused due to infections may be treated by using antibiotics depending on the causative agent of that infection.
Asthenia due to auto-immune disorders: Treatments for asthenia due to autoimmune disorders such as myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis or gestational diabetes include corticosteroids and other medications that are used to suppress the immune system. For example, azathioprine and cyclosporine in case of myasthenia gravis.

Correction of any underlying deficiency such as iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
Some other techniques may also help to treat asthenia such as:
Physical therapy: It may be opted to evaluate for safety concerns, optimize mobility and for assistance regarding the involvement of muscle strengthening exercises or use of assistive devices.
Occupational therapy: After chemotherapy or surgery people might experience imbalance or problems with mobility, so in general, this therapy guides as to how to do many tasks that one normally does, in a more effective manner.
How to Prevent Asthenia?
- Maintain an active lifestyle- Making proper schedules of the day including free leisure time and some physical exercises can help prevent asthenia.
- Try to spend at least 30 minutes outdoors. It relaxes mind and body, reduces stress and has positive effect on mental health.
- Take a proper healthy diet full of nutrients. It keeps the body recharged with energy and reduces fatigue. Foods rich in calcium, protein and less in fats can be incorporated in diet.

- Avoid caffeine and alcohol.
- Consult a doctor immediately in case of persistent fatigue or energy loss and weak muscles.
- Excessive and strenuous exercises or dieting should be avoided.
- Get a good night’s sleep