- Epiglottis - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/imagepages/19595.htm)
- Definition - Epiglottis - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/epiglottitis/basics/definition/con-20027854)
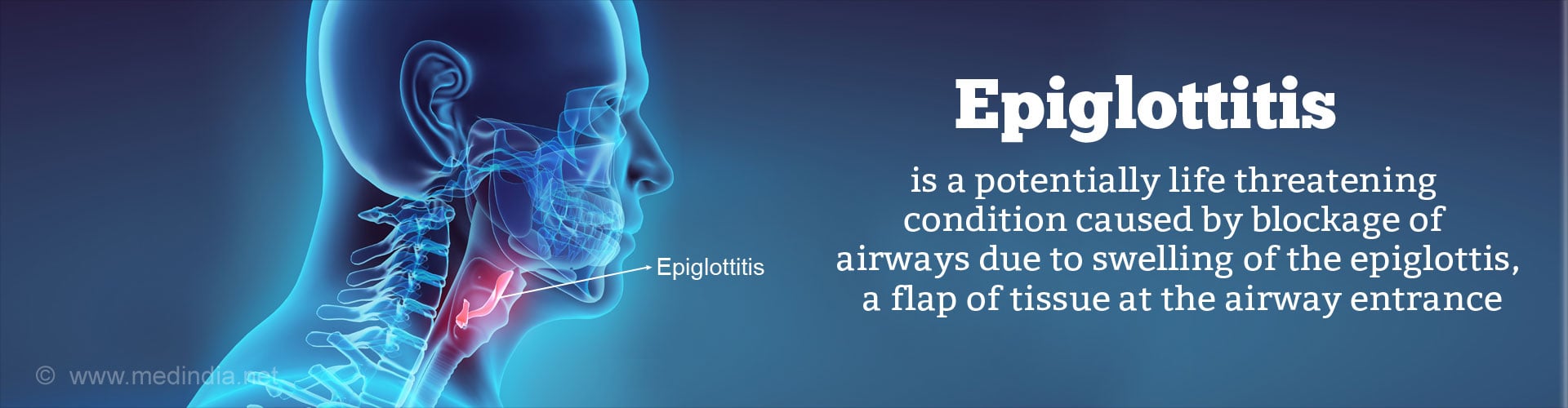
What is Epiglottitis?
Epiglottitis is a condition which occurs due to the swelling or inflammation of the epiglottis. It occurs more commonly in children between 2-6 years and rarely in adults.
Structure and Function of the Epiglottis
The epiglottis is an anatomical cartilage flap that has a leaf like shape. It is located in the throat between the tongue and the larynx but can be seen popping just above the tongue when you open the mouth and say ah in front of a lighted mirror. The term “Epi” denotes what is above and the term “glottis” means the tongue. This describes its location well.
The epiglottis at rest assumes an upright position allowing the air to pass through the larynx and into the lungs. At the time of swallowing, food or liquids, the epiglottis folds over the entrance of the larynx and acts like a trap-door to seal it. This mechanism prevent food from spilling into the air passages and causing obstruction to breathing. If by some chance food or liquid does get spilled over into the windpipe, the body further protects this passage through a cough reflex that sometimes can be quite violent. Most of us have experienced such a violent cough particularly while enjoying a hearty meal.
What are the Causes for Epiglottitis?
Most often, epiglottitis occurs due to infectious causes and less often due to injury.
- The most common infectious agent implicated is Hemophilus Influenzae type B. The other infectious causes are viral agents like herpes or varicella-zoster or bacterial agents like Streptococcus pneumonia.
- Other causes that could result in the swelling of the epiglottis are due to burns from swallowing hot liquids, smoke or foreign objects and any injury to the area.
- In adults, higher chances of this condition is seen when the immune system is weak and affected by either some other disease or has been reduced by immunosuppressing agents like steroids.
- Routine Hib vaccination (against Hemophilus influenza B ) in children has reduced the occurrence of this condition in children.
What are the Symptoms of Epiglottitis?
Symptoms of epiglottitis in children develop within a matter of a few hours while the evolution of symptoms is slower in adults and occurs over a few days rather than hours. These include
- High fever, cyanosis
- Abnormally high pitched or hoarse voice (stridor)
- Breathing difficulties and abnormal breathing sounds
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Pain and difficulty in swallowing which results in drooling of saliva.
- An upright and forward leaning posture is required with tongue protruding out to allow more air entry into airway. Further blocking of airway due to the epiglottal swelling can result in cardiac arrest and death.
If such symptoms are seen then immediate medical consultation is advised.

What are the Complications of Epiglottitis?
Complications seen in epiglottitis include
- Respiratory failure – When the airway is obstructed due to swelling and inflammation of the epiglottis, oxygen entry into the lungs is seriously affected and levels of oxygen in the blood become dangerously low, while accumulation of carbondioxide occurs. This can lead to respiratory failure, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Spread of infection – Infection can spread to other sites in the body leading to lung infection (pneumonia), infection of the membranes covering the brain (meningitis) and entry of bacteria into the bloodstream (septicemia).
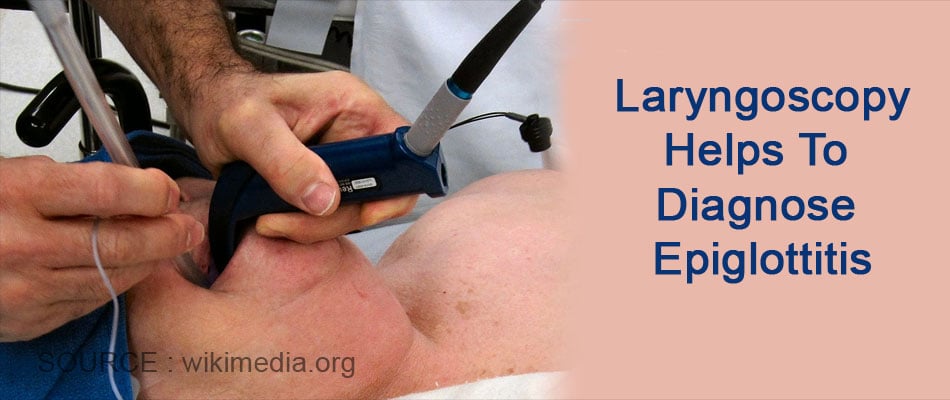
How is Epiglottitis Diagnosed?
- This condition requires to be diagnosed at emergency care facility and no attempt should be made at home to open the mouth forcefully and view the throat.
- Oxygen levels of the patient need to be monitored to rule out any hypoxia in the patient.
- Throat examination – A special device (laryngoscope) is used to view the throat and look for evidence of epiglottic swelling or any obstruction by a foreign body.
- Other tests done include routine blood investigations and cultures of throat and blood to find out the causative agent of infection.
- X ray of the neck – Imaging should be done only after airway is protected. A swollen epiglottis appears as a ‘thumb’ sign.
How is Epiglottitis Treated?
Maintaining the oxygen levels in the body is one of the most important measures in treatment to prevent further complication.
- This is done by providing oxygen support with moistened humidified oxygen with a mask.
- Intubation may be required which involves passing a tube through the nose or mouth into the windpipe till the swelling decreases.
- In some cases, ventilator support may be required.
- If the epiglottis is blocking the airway, then an opening is made into the windpipe or trachea (tracheostomy) might be required to permit airflow into the lungs. This is an emergency airway flow created, which bypasses the larynx and allows air entry directly into the lungs.
- Antibiotics that are broad spectrum will be administered for treatment of any infections that may be responsible for the epiglottic swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory agents like corticosteroids are used to reduce the swelling of the Epiglottis.

- Intravenous fluids are started to keep the patient in a stable condition.
How can we Prevent Epiglottitis?
Prevention of a life-threatening condition like epiglottitis requires:
- Vaccination against Hemophilus Influenza B is effective in preventing epiglottis in children less than 5 years of age. This vaccination is given as 3 dosage or 4 dosage vaccines.
- For older children and adults that have a weak immune system due to Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy, Spleen removal, Sickle cell anemia and other conditions also vaccination is advised.
- Hygienic practices like not sharing personal items, washing of hands, use of a hand sanitizer are other measures that will prevent the spread of infection.
- Close contacts of the patient may require to be treated with antibiotic medication to prevent the condition.
Health Tips
- Being up to date in vaccination is a must to prevent infections of this nature.
- In case you are traveling with your child to a place that may be endemic to this condition then required vaccinations should be taken before travel.
- Good hand hygiene practices should be followed.
- Covering your mouth while coughing or sneezing with your hand or handkerchief can help in preventing transmission.

- Washing of hands with soap after coughing or sneezing. If water is not available then a hand sanitizer should be kept close by.
- In case you suspect your child to have an infection, immediate consultation is required and the child should not be sent to school to prevent transmission of the infection.