About
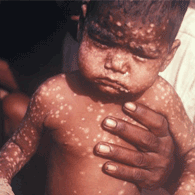
Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized by the complete or partial absence of pigment called melanin in the skin, hair and eyes. It is also known as hypopigmentation, oculocutaneous albinism or ocular albinism.
This is an autosomal recessive type of inherited disorder, which means that the chance of the disorder being passed from one generation to the next is low. Statistics show that about 1 in 17,000 people suffer from some form of albinism.
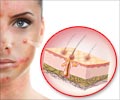
Albinism is an inherited defect affecting melanin production and metabolism. Melanin is a naturally occurring pigment, which is responsible for the color of our skin, hair and eyes. It protects the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet light. Therefore, people in the tropics are darker as their sun exposure is more, in comparison to the people who live in temperate climates. If the gene encrypting this pigment is defective, the body becomes pale and white.
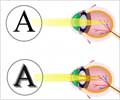
People who are affected by albinism are called albinos. They have absence of color in the hair, skin, or iris of the eye; or lighter than normal skin and hair. Lack of skin pigmentation makes albinos more susceptible to sunburn and skin cancers. Vision problems like extreme far-sightedness or near-sightedness, nystagmus, strabismus, photophobia and astigmatism are common in people with albinism.
Albinism can be diagnosed merely by observation of major or total absence of pigmentation of the skin, hair and eyes. Genetic testing, electroretinogram, chemical testing of hair and blood tests aid in diagnosing albinism.
There is no cure for albinism. Treatment is aimed to ease the symptoms. Treatment of the eye conditions consists of visual rehabilitation. It is important that albinos use sunscreen before sun exposure to prevent premature skin aging or skin cancer.
Albinos can live a normal life span, however, some forms of albinism can be life-threatening. The lives of people with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome can be shortened by lung disease. People in tropical countries who do not use skin protection may develop life-threatening skin cancers.
Albinism may cause social problems, because people with albinism look different from their families, peers, and other members of their ethnic group. There is no known way to prevent albinism. Genetic counseling should be considered for individuals with a family history of albinism or hypopigmentation.