- Computed Tomography (CT) - (http://www.fda.gov/radiation-emittingproducts/radiationemittingproductsandprocedures/medicalimaging/medicalx-rays/ucm115317.htm)
- Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) - (http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pet)
- CT scan - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003330.htm)
- About Computed Tomography (CT) - (http://www.nibib.nih.gov/science-education/science-topics/computed-tomography-ct)
What is Computed Tomography?
Computed Tomography or Computerized tomography (CT) is a type of medical examination that makes use of X-rays and computer processing to create cross sectional images of the body.
CT scan has also been known as Computerized Axial Tomography scan (CAT scan). The word Tomography is derived from the Greek words tomos, meaning “slice”or “section” and graphia, meaning “to describe” or “to write”. 3-D imaging and additional visualization can be performed with multiple tomographic images. CT procedure can scan nearly every part of the body and provide much more efficient results when compared to X-rays.
How does CT scanner operate?
A motorized X-ray source rotates around the circular opening called the gantry, of a donut-shaped structure in the Computed Tomography scanner. During a CT scan, the subject lies on a surface that slowly moves through the gantry while the X-ray source rotates around in the structure, shooting narrow beams of X-rays through a section of the subject’s body. Digital X-ray detectors are used in the CT scanners, which are located directly opposite to the X-ray source. The detectors pick up the X-rays on their way out of the subject. Many images taken at different angles are collected during one complete rotation and are transmitted to a computer. For each rotation, the CT computer reconstructs the image data collected into one or multiple cross-sectional images of the internal organs or tissues using complex mathematical formulae.
Types of CT scan
Computed Tomographic scans can be differentiated based on the part of the body being examined. These scans often use a contrast material to enhance the visibility of certain tissues. The different types are Abdominal CT, Head CT, CTAngiography, Chest CT, Spinal cord CT, Urinal tract CT etc.
Types of CT scanners
The CT scanners can be sortedinto types based on the technology used in the machine. They include:
- X-ray Computed Tomography: This is the conventional CT scanner that scans a particular section of the subject at a time and sends it across to a computer for further processing
- Spiral or Helical Computed Tomography: These provide accurate information on the internal organs. In spiral CT, the X-ray beam is emitted on a continuous basis and rotates around the subject, as the subject is moved through.
- Micro Computed Tomography: In micro CT, the pixel size of the images is in micrometer. It is used in cases involving small animals, biomedical samples and other studies where minute detailing is desired.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography: The Cone Beam CT is a recent addition, where the X-ray source is cone shaped and the resultant image is in 3-D. It has major uses in the field of implant dentistry, interventional radiology etc.
Uses and Advantages
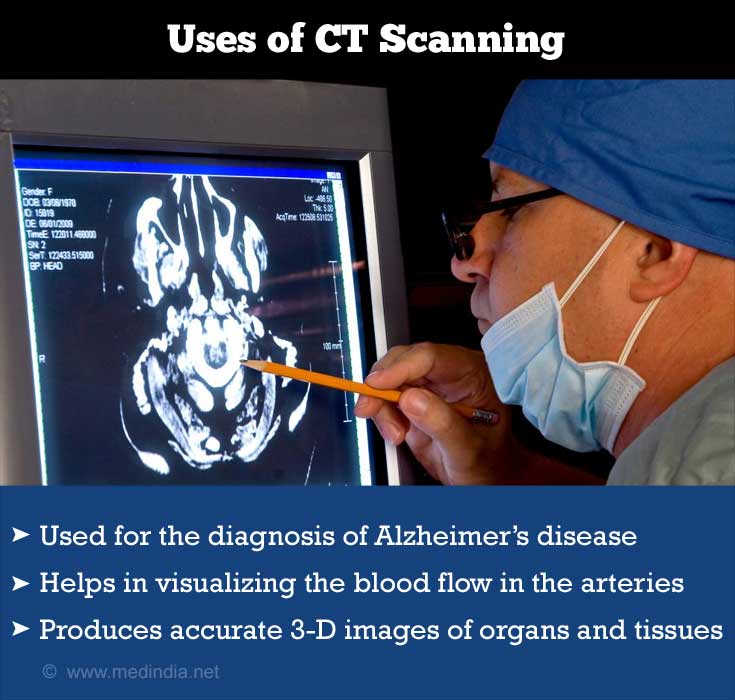
Uses of CT scanning
- Organs such as stomach, gall bladder, liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the colon and rectum can be visualized with great clarity using CT imaging of the abdomen. They are used for the diagnosis of appendicitis, stage of cancer, tumours and gangrene.
- Head CT scan is used for the
diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease , brain tumours, bleeds, injuries to the brain and other major brain diseases. It is also used for CT guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of intracranial tumors, arteriovenous malformations etc. - Computed Tomography Angiography helps in the visualization of blood flow in the arteries throughout the body. It is used in the diagnosis of aneurysms (bulging), stenosis (narrowing) of the arteries, dissection of the aorta etc.
- Chest CT scan uses special equipment to visualize organs and tissues of the chest which provides images of multiple tissues such as lungs, heart, bones, muscles, blood vessels, soft tissues etc. These images are used to detect acute and chronic changes in lung parenchyma, diagnose tumours, emphysema, inflammations etc.
- Micro CT scans are in the micrometres range and have a variety of uses in the biomedical field, electronics, microdevices, food technology, geology, microfossils etc.
- Industrial Computed Tomography is mainly used for internal inspection of components in industries. Its varied uses include flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications.
- Recently, CT scanners have been superimposed with a Nuclear Medicine procedure such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET scan) . This produces much more accurate 3-D images of organs and tissues.
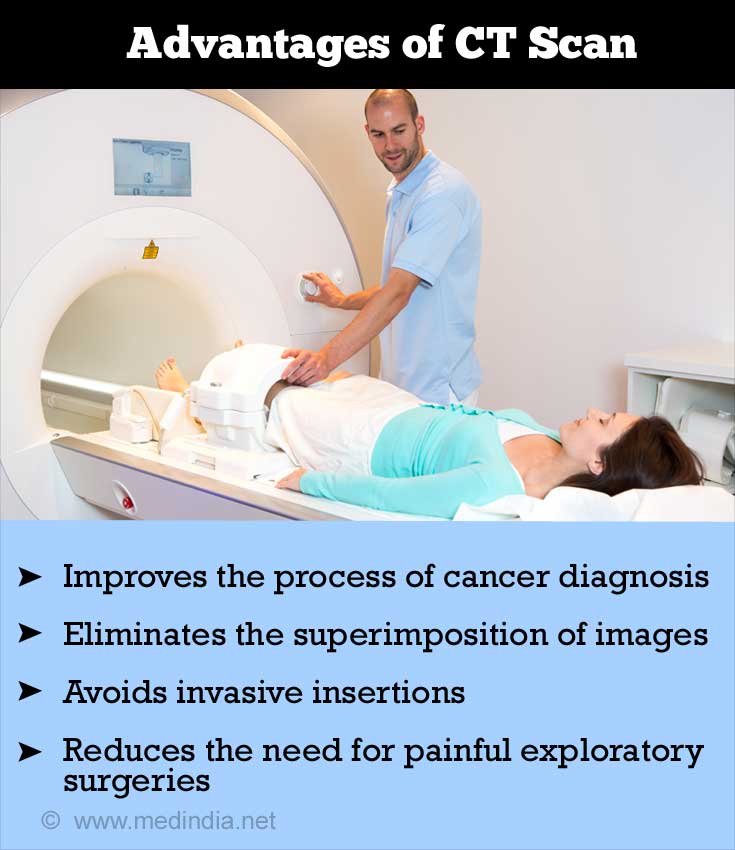
Advantages of CT scanning
- CT scanning is often used in the final stage of diagnosis and additional work up will not be necessary. It helps to determine if and when surgery is required.
- Usage of CT scans reduces the need for painful exploratory surgeries
- The inherent high-contrast resolution of CT helps in differentiating between tissues that differ in physical density by less than 1%
- It has the ability to eliminate the superimposition of images of structures outside the area of interest
- CT scans greatly improve the process of cancer diagnosis and detection of the stage of cancer
- Using CT scanning helps in placing the patient into appropriate areas of hospital care
- In the case of CT angiography or CT colonography, invasive insertions into the patient’s body can be avoided
Complications involved in CT scan
CT scan involves exposure to radiation, which has its own added risks stated as follows:
- Ionizing radiation is produced by X-rays, which may cause biological effects like increased lifetime risk of cancer.
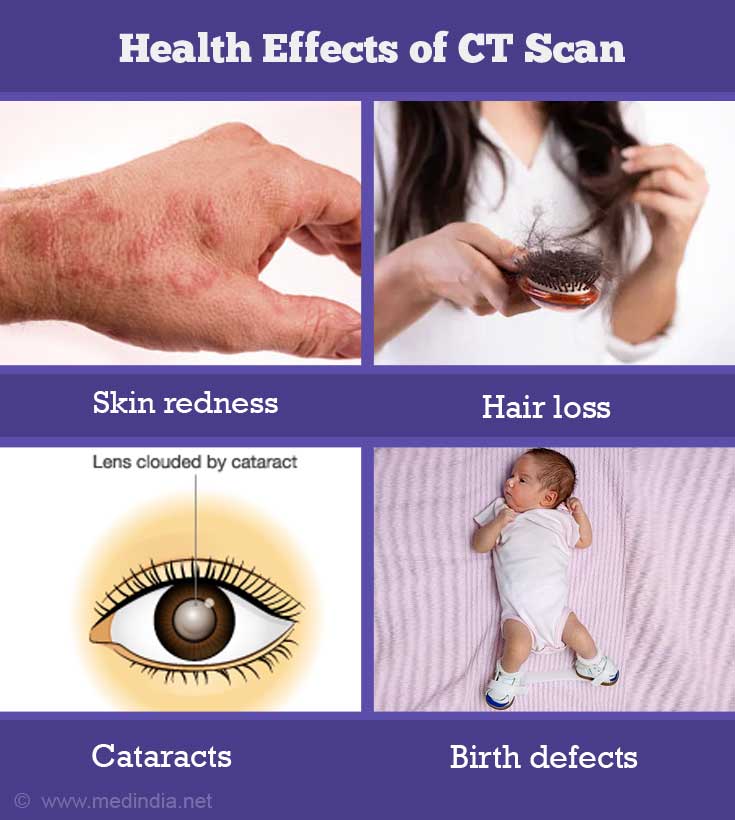
- X-rays can cause adverse health effects such as skin redness, skin tissue injury, hair loss, cataracts or birth defects in case of prolonged high dose exposure. Hence, women are asked to inform the CT scan technician if they are pregnant before the CT examination.
- Allergic reaction to the contrast material being injected may also occur. In such cases, the patient is advised to take special medication 24 hours before the exam. It can also harm kidney function.
- Since the radiation exposure is much larger for a CT scan than a traditional X-ray, the American College of Radiology advises that CT exams should be limited only to those cases where the benefit to be gained greatly outweighs the risk involved.
- As children are more sensitive to ionizing radiation and the amount of radiation received increases due to their smaller size, they have a relatively higher risk for developing cancer. Hence, the scanners are to be adjusted to reduce the level of radiation.