- Sinusitis - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sinusitis)
- Sinus Infection - (http://acaai.org/allergies/types/sinus-infection)
- About Sinusitis - (https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/sinusitis.html)
- More on Sinusitis - (http://www.entnet.org/content/sinusitis)
What is Sinusitis?
Sinusitis, the infection or inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, causes distress like blocked nose, and fullness or pain in the face. Infection, allergies and air pollution are the most common causes of sinusitis.
Sinusitis is one of the most common conditions, affecting about 10% to 30% of population in the United States and Europe, each year.
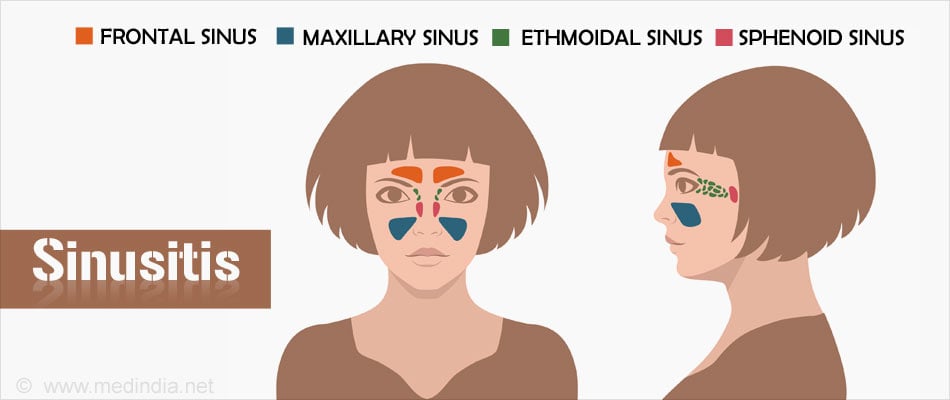
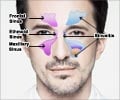
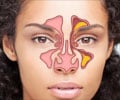
The human skull hollows out in several places, which appear as air-filled cavities. Each of these hollows is called sinus. These sinuses are located around the nasal cavity and each of them has an opening that can drain its mucus into the nasal cavity. Sinuses are found symmetrically in pairs and are named according to where they are located.
- Maxillary Sinus: Large air cavities located inside the bony structure of the cheeks, on either side of the nose.
- Frontal Sinus: Small air cavities located at the base of the nose in the forehead between the eyebrows.
- Ethmoid Sinus: Tiny air cavities located between the eyes at the nasal bridge.
- Sphenoid Sinus: A pair of air cavities located in the bones that lie behind the nasal cavity.
All these sinuses are lined with mucosal tissues and produce a thin layer of mucus to keep the cavities moist. Excess mucus drains out into the openings connected to the nasal cavity at various places. This is the reason that sinuses found in the skull are called paranasal sinuses.
Viral or bacterial infections and allergies can cause inflammation of the sinuses and their mucosal lining. This results in excessive production of mucus which can be thick or thin. The mucus gets accumulated in the sinuses and facilitates the growth of bacteria, resulting in infection. Excessive mucus blocks openings, resulting in a feeling of heavy-headedness.
Types of Sinusitis
The infection of the paranasal sinuses is categorized according to the duration and frequency for which it occurs.
- Acute Rhinosinusitis: A new or sudden infection in the sinuses that lasts for one to four weeks is acute rhinosinusitis.
- Recurrent acute Rhinosinusitis: When four or more separate episodes of acute rhinosinusitis occur within one year, with an interim period of healthy mucosal tissues, the condition is categorized as recurrent acute rhinosinusitis.
- Subacute Rhinosinusitis: Rhinosinusitis that lasts between 4 to 12 weeks duration is called subacute rhinosinusitis.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis: When a single attack of rhinosinusitis infection lasts for more than 12 weeks, it is called chronic rhinosinusitis.
- Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Sinusitis: This condition is characterized by the exacerbation of infection that is already a chronic sinusitis. After the period of acute exacerbation of the symptoms, the condition returns to the baseline chronic condition.
What are the Causes of Sinusitis?
Common causes of sinusitis include:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral and fungal infections can cause acute sinusitis or can aggravate the symptoms in a person with chronic sinus infection. The infections usually subside with necessary antibacterial or antifungal treatments. Viral infections need to be managed symptomatically.
Bacterial, fungal and viral infections cause acute sinusitis, usually following upper respiratory tract infection. The following are some of the causal organisms of respiratory infections and sinusitis.
| Bacteria | Virus |
|
|
- Allergic Reactions: Allergens, like pollen and dust, which trigger the mucosal lining of the nasal cavity, can cause inflammation in the sinuses also. This results in thickening of mucus membranes within the sinuses, blocking the mucus drainage and further leads to bacterial growth.
- Deviated Nasal Septum: Septum is the wall between the two nostrils. When the nasal septum is shifted to one side, one nasal cavity becomes smaller than the other. This can also cause blockage of the opening of the sinus thereby affecting drainage into the nose and causing recurrent or chronic sinusitis.
- Nasal Polyps: Nasal polyps are tissue growths that usually occur inside or at the back of the nasal cavity. These tissues may block the outlets of mucus and cause infections.
- Trauma to the Face: A fractured facial bone may cause obstruction of the sinus opening, causing accumulation and infection of the mucosal cavity of the sinus.
Some people are more prone to getting chronic or recurrent sinusitis than others if they have any of the following risk factors:
- Asthma
- Poor immunity
- Exposure to air pollution
- Cystic fibrosis
- Aspirin sensitivity
- Allergic conditions such as hay fever
- Exposure to passive smoking
- Exposure to chemicals
What are the Symptoms of Sinusitis?
Some of the common symptoms of sinus infection are:
- Facial fullness, pressure or pain
- Headache
- Stuffy nose
- Running nose with thick or thin discharge
- Cough or chest congestion
- Loss of smell
- Bad breath
In addition to the above symptoms, acute sinusitis may present with:
- Fever
- Body ache and tiredness
- Pressure or pain on the sides of the nose and cheeks
- Associated ear infection
Chronic sinusitis also presents with most of the above symptoms and is characterized by:
- Associated dental pain
- Pus in the nasal cavity
- Frequent headaches

How is Sinusitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of sinusitis can be done based on presenting symptom and examination of the patient. Viral sinusitis typically lasts for less than 10 days. If the symptoms of a sudden attack of sinusitis last for more than 10 days, it could be considered as bacterial sinusitis.
Acute sinusitis that presents as pain in the upper teeth can be distinguished from a toothache by tilting the head forward. Pain increases with the forward tilt in the case of sinusitis.
Diagnostic procedures that may be recommended for sinusitis include:
- X-Ray of the skull
- Blood tests
Diagnostic procedures for chronic sinusitis may include:
- CT Scan
- MRI Scan
- Nasal endoscopy, where the inner lining of the nose is examined
- Biopsy of tissue sample from the nasal cavity
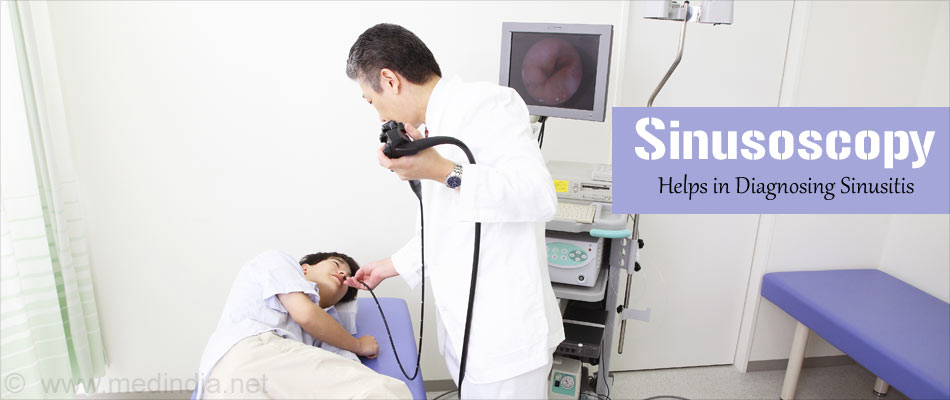
- Sinusoscopy, where the inner linings of the sinuses are examined
What are the Complications of Sinusitis?
Sinusitis may be a localized infection. But the location of the sinuses makes the surrounding structures prone to infection. Sinusitis must be treated and managed effectively so that it does not lead to complications.
- Eyes: There is a possibility of infection of the eye socket, accompanied by fever and severe illness. It may also result in the loss of sight. Spread of the infection can result in periorbital cellulitis, inflammation of the eyelid and skin around the eye. Orbital cellulitis may occur affecting the eye tissues. Abscess (collection of pus) may occur in and around the eye tissues.
- Ears: The nasal cavity is connected to the middle ear via the auditory tube (Eustachian tube). This enables the infections of the nasal cavity and the sinuses to spread to the middle ear. Ear ache and dizziness are common symptoms in such cases. Sinusitis can also spread to the mastoid bones (bony part of the skull behind the ear) and cause abscess and infection.
- Bad Breath: Halitosis, or bad breath, is the result of the by-products of the bacteria, which cause infection. It is a common symptom of chronic sinusitis.
- Brain: Infection of the frontal and sphenoid sinuses can spread to the surrounding meninges, the three layers of membranes protecting the brain. Abscess, or pus formation is another possibility that results from the spread of infection from the sinus to the brain.
- Dental Problems: Chronic sinusitis may cause the pain that radiates to the upper molar teeth. As the sinus is closely situated just above the upper jaw (maxilla), the upper teeth can get infected.
- Osteomyelitis: The term osteomyelitis is a generally used for infection in a bone. Since sinuses are cavities inside the bone, the infection there can reach the bony tissues by contact and can cause bone death or osteomyelitis.
How is Sinusitis Treated?
Different types of sinusitis involve different treatments. Some of the sinus infection treatments provide absolute cure while others may only provide symptomatic relief.
| Type of treatment | Indication | Effectiveness |
| Symptomatic | Viral infections | Provides temporary relief of symptoms like congestion |
| Antibiotics(Amoxicillin, Fluoroquinolones) | Bacterial infections | Destroy bacteria that cause infection and cure the infection and the resulting symptoms. |
| Corticosteroids | Sinusitis with nasal polyps | Very rarely used, usually in combination with antibiotics. |
| Nasal irrigation | Nasal congestion or stuffy nose | Washing down the nasal cavity with water using neti pot helps in providing relief from congestion. |
| Antihistamines | Allergic reactions of nose and sinus | If sinusitis is caused by allergic reactions, then antihistamines can help. |
| Decongestant nasal spray | Congestion or stuffy nose | Temporary relief from congestion, but does not treat the cause of the sinusitis. |
| Breathing in low-temperature steam or gargling | Congestion or stuffy nose | Relieves symptoms for a while, until the next lot of mucus is produced. It also provides a soothing effect by moistening the mucus lining. |
| Surgical procedure of puncturing the sinus to flush with saline water. | Chronic sinusitis that causes severe congestion | Done by an ENT surgeon. Provides relief from chronic conditions |
| Balloon Sinusoplasty – balloon used to unclog the openings of the sinuses | Chronic sinusitis that does not respond to any other treatment procedures. | Opens up the sinus drainage enabling the mucus to flow more easily. |
| Caldwell-Luc radical antrostomy | Chronic sinusitis that cannot be drained out | Surgery involves opening the front wall of the maxillary sinus through an incision in the upper gum, and draining out the mucosa completely. |
Some simple home remedies for sinusitis can help in relieving the symptoms.
- Breathe in the steam of medium-hot water. Adding Eucalyptus oil or peppermint oil to the water is sometimes recommended.

- Use a warm compress on your face, like placing a towel dipped in warm water and squeezed out. This will help ease the mucus flow and relieve pain.
- Sleep with your head in an elevated position to help sinuses drain out the excess mucus.
- Flush out the nasal passages using the neti pot. Neti pot is a specially designed pot that helps in putting saline water into one nostril. The head is tilted in such a way that the water comes out through the other nostril.
- Certain spices like turmeric, pepper and ginger root help relieve congestion. These can be mixed with milk and consumed at frequent intervals.
Prevention of Sinusitis
Sinusitis is one of the conditions that can cause a lot of distress. Luckily, simple measures help in preventing sinusitis.
- Wash hands regularly, especially after a contact with a person who is infected.
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids during an acute or chronic attack of sinusitis. This will keep the mucus lining moist.
- Avoid cigarette smoke and air pollution.
- Manage your allergies carefully before they turn into infections.
- Avoid swimming in unclean water.
Health tips
- Keep your body well hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Use air humidifier indoors if the climate is arid.
- Avoid cleaning products that can give rise to excessive fumes. For example, bleaching powder.
- Avoid air pollution and passive smoking. Use face masks when at risk of exposure to pollution.