About
Nomenclature: Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Acute Myelogenous Leukemia, AML.
Acute myeloid Leukemia, more popularly known by its abbreviated form - AML, is a fast- evolving leukemia that affects both children and adults alike.
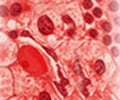
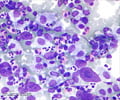
Acute Myeloid Leukemic cells under Microscope
The word 'leukemia' means 'white blood,' and is used to indicate the high white blood cell counts of the disease.
Leukemia is a cancer that begins in the inner part of the bone marrow and moves quickly into the blood from where it spreads to other parts such as the spleen, lymph nodes, liver, central nervous system and to the other organs of the body. There are two forms of myeloid leukemia – chronic and acute. The term 'Chronic' refers to slowly – evolving form of myeloid leukemia that may take years to progress. The 'acute' variety, on the other hand, advances in a quick manner. 'Myeloid' refers to the type of WBC that is affected. Leukemia was first recognized 150 years ago, and since then has been intensely researched and studied. The treatment of leukemia over the years has seen remarkable triumphs, frustrations and failures. Dr.Donald Pinkel, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, USA, sums it up as follows:
"The value of history is not just in savoring the past, but in appreciating how it illuminates the present and guides us into the future. Several lessons can be learned from the study of the history of leukemia, particularly childhood leukemia. One is the importance of heeding new facts and listening to new ideas and hypotheses. At each point in the history of leukemia there have been instances of lost time and opportunity because of unreasoned resistance to innovation. It is important for physicians and scientists to be open to new thinking that challenges conventional wisdom and ways.”
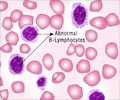
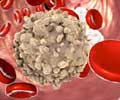
Normally the bone marrow produces immature stem cells that grow and differentiate into the three blood cells type – the Red Blood Cells (RBC), the White Blood Cells (WBC) and Platelets. These blood cells vary in their morphology and function. The RBCs carry oxygen and other nutrients to the different body tissues; the WBCs fight off infections and diseases while the platelets are responsible for blood coagulation.
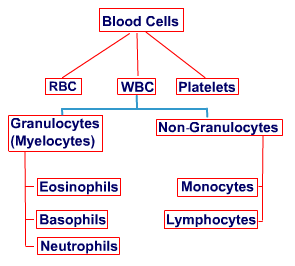
In leukemia, a single WBC stem cell becomes abnormal and undergoes uncontrolled proliferation. These leukemic cells can be found in the blood and they course through the body, causing enlargement of the spleen, liver and other organs.