About
“It is easier to stay out than get out.” - Mark Twain (American Author)
Alcohol is a time-tested curse that has wrecked countless lives. Addiction to alcohol has left several brilliant lives desolate and destroyed many a promising career.
Since time immemorial, man has been hooked to substances that lend him a “high” and, alcohol is just one of the many intoxicants available to him.
Serving alcohol has been an important part of many social occasions and rituals. In fact alcohol consumption has become a social norm in various communities. The transition of an occasional drinker becoming an excessive drinker, and then eventually becoming an alcohol-dependent can be gradual. It is precisely for all these reasons that the ill effects of alcohol are ignored until the symptoms get too overwhelming.
Today alcohol consumption is one of the most serious public health issues, not just in the developed and affluent countries but also poorer nations.
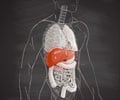
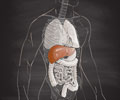
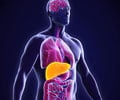
Liver is a vital organ and performs several roles. Two important functions include producing proteins that help the blood to clot and removing body wastes. The liver also regulates the supply of substances such as glucose throughout the body. In order to perform these functions the liver cells must function normally.
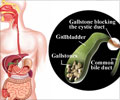
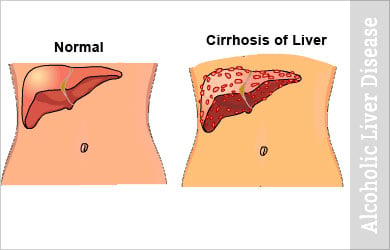
Alcohol abuse or alcohol addiction is distinctively linked to alcoholic liver disease, a condition in which the liver is permanently damaged due to excessive drinking.
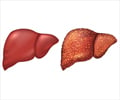
Initial changes to the liver include swelling and inflammation (hepatitis). This may soon be followed by cirrhosis, when the morphology of the liver cells becomes abnormal--they become scarred and fibrosed. Most abnormal cells begin to die and the remaining abnormal ones multiply in order to overcome the shortage. This results in nodules. The scarring of the abnormal liver interferes severely with the liver’s basic function.
Alcohol abuse may not cause liver disease in all alcoholics but it certainly predisposes them to the condition. Non-alcoholics too may develop chronic liver disease. Women appear to be more susceptible to the condition than men.
Alcoholism is also associated with a series of other illnesses, medical conditions or problems that can be physical, psychological, social, criminal or economical in nature.