- Bailey and Love Short Practice of Surgery 25th edition.
About
Incidence - Basal cell cancer or basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of
Spread- The cancer grows slowly and spreads locally damaging and eroding the surrounding tissues like a rodent or a mouse, hence it is also called a ‘Rodent Ulcer.’
Origin- The origin of the cancer is from the deepest layer of the skin that is also called the basal layer ( i.e at the base). UV light and BCC - Damage to skin following chronic exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun is the main cause for the development of basal cell cancer. UV light is the light that tans the skin and the cancer affects the white or pale skin more and hence the incidence of these cancers is higher among people living away from the equator in the temperate climates. Lower radiation levels from ultraviolet rays are required to stimulate the development of basal cell cancer as compared to squamous cell cancer.
Risk Factors that predispose an individual to developing basal cell cancer - are similar to for squamous cell cancer and include:
- Chronic sun exposure
- Male gender
- White skin
- Blue or green eyes
- Blond or red hair
- Older age and exposure to carcinogenic chemicals and radiation
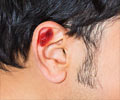
Basal cell cancer usually appears on the face, often in the area above a line joining the angle of the mouth and ear lobe. As this cancer occurs in the line following the track of the tears it is called "tear cancer."
Symptom and Signs - It may appear as bright pink, shiny well defined red spots, small pearly swellings, a nodule or a pale scar. As it grows, the center ulcerates. The cancer can invade and destroy deeper tissues leading to disfigurement. It usually grows locally and rarely spreads to distant organs.
Treatment - Basal cell cancer is usually treated with microscopic surgery. Radiotherapy, local injection of chemotherapeutic drugs and cryotherapy are other options in its treatment.
Prognosis or outcome - is bad for larger cancers, recurrent cancers and those located near the eyes, nose or ears. It is also bad in patients with decreased immunity.
Prevention - Excessive exposure to the sun especially around noon should be avoided to prevent the development of basal cell cancer. When unavoidable, adequate measures should be adopted to protect the skin from solar damage. Regular skin examinations and awareness about the changes caused by basal cell cancer helps in early detection and treatment of the condition.