- Ectopic Heartbeat - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001100.htm)
- Heart Palpitations - Causes, Symptoms and Treatments - (https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/conditions/palpitations)
- Symptoms, Diagnosis and Monitoring of Arrhythmia - (https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/symptoms-diagnosis--monitoring-of-arrhythmia)
- About Ectopic Heartbeat - (http://sifaka.cs.uiuc.edu/~yuelu2/opinionintegration/health/Ectopic_heartbeat.html)
What is Ectopic Heartbeat?
Ectopic heartbeats are small changes in regular, normal heartbeats. These changes cause either a skipped or extra heartbeat. There usually is no clear cause for these changes and they are usually harmless. The two common types of ectopic heartbeat are: premature ventricular contractions (PVC) and premature atrial contractions (PAC).
There is no clear cause for these changes which are usually harmless. The two common types of ectopic heartbeat are:
- premature ventricular contractions (PVC) – are extra, abnormal heartbeats beginning in either of the heart’s two ventricular chambers.
- Premature atrial contractions (PAC) – are common forms of arrhythmias due to premature discharge of electrical impulse into the atrium thereby causing a premature contraction.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Ectopic Heartbeat
Go to source)
What Causes Ectopic Heartbeat?
Ectopic heartbeats are rare in children without congenital heart disorders. Adult ectopic heartbeats are common and usually the result of PVC or PAC.
Some of the causes for ectopic heartbeat include conditions like low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia), decrease in blood supply to the heart (ischemia) or heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy).
Factors that cause or worsen ectopic heartbeat include smoking, excess use of alcohol, caffeine and certain non-pharmaceutical drugs and stimulants(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Heart Palpitations - Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
Go to source).

What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Heartbeat?
Since ectopic heartbeats disrupt the normal electrical activity in the heart, patients may experience dizzy spells, light-headedness, breathlessness and fatigue during the ectopic beat.
Most ectopic heartbeat cases usually present with the common symptom of palpitations. However, not all cases of palpitation are due to ectopic heartbeat. In some cases, patients have no symptoms and ectopic heartbeat is detected during an ECG or physical examination.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Symptoms, Diagnosis and Monitoring of Arrhythmia
Go to source)
How is Ectopic Heartbeat Diagnosed?
Doctors are usually able to diagnose ectopic heartbeats with a physical examination if the pulse is erratic. In most cases, the blood pressure is normal and the ectopic heartbeat is infrequent. The doctor may order the following tests in order to diagnose ectopic heartbeat:
- Continuous ambulatory cardiac monitoring (Holter monitor) – also known as ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG), this technique records the electrical activity of the heart as the patient goes about his/her normal, daily activities. Many heart conditions are detected only during activity and this method is useful to detect ectopic heartbeat and arrhythmias.
- Coronary angiography – is a procedure using a contrast dye and x-rays to examine the blood flow through the arteries in the heart.
- Echocardiogram – uses sound waves to create images of the heart. This image provides greater detail than an x-ray.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) – records electrical activity in the heart in a supine position.
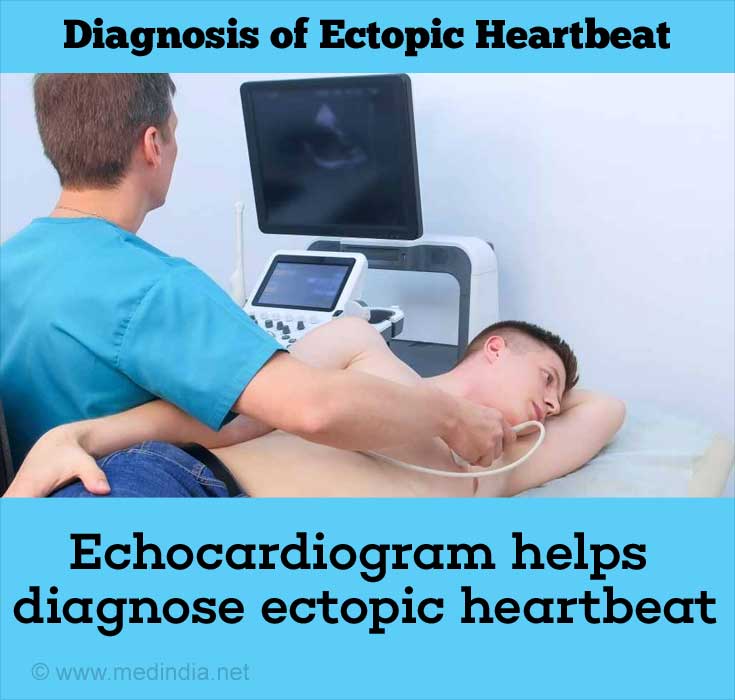
All the above diagnostic imaging tests are non-invasive and do not require anesthesia.
What are the Treatments for Ectopic Heartbeat?
Doctors generally prescribe simple medications like beta-blockers to alleviate the ectopic heartbeat. In patients with respiratory issues like asthma or chronic bronchitis, beta-blockers cannot be used and hence alternatives like calcium-channel blockers are used.
In cases where the ectopic heartbeat is worsening the heart function, the doctor may recommend a procedure known as catheter ablation. Catheter ablation is a procedure used to modify the abnormal heart muscle to prevent it from transmitting electric signals. Catheters or thin wires are passed into the heart via the blood vessels. The wires are threaded through punctures in the groin and the catheter ends reach the heart muscle. The ablation (heat or freezing) is applied to the abnormal muscle for about 30 seconds. Since this is an invasive procedure, sedatives and
Complications
Call your doctor if you experience a sudden racing of the heart, severe palpitations along with chest pain or excessive sweating and breathlessness.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Ectopic Heartbeat
Go to source)