- Cancer Facts and Statistics - (https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics.html)
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2009) Comparative Effectiveness of Therapies for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. AHRQ: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality [online]. - (http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pros_cancer)
- Prostate Cancer Treatment - (http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pros_cancer)
- Lee BH, Kibel AS, Ciezki JP, Klein EA, Reddy CA, Yu C, et al. (2014) Are Biochemical Recurrence Outcomes Similar After Radical Prostatectomy and Radiation Therapy? Analysis of Prostate Cancer-Specific Mortality by Nomogram-predicted Risks of Biochemical Recurrence. Eur Urol. - (http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pros_cancer)
What is External Beam Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer?
Radiotherapy for prostate cancer is an alternative to surgical treatment such as Radical prostatectomy and over the years the results of this treatment have improved and currently the results seem to be comparable to surgery.
New era of medical research and treatment with radiations began, following the ground-breaking discovery of radioactive elements radium and polonium by Madam Marie Curie. Radiation therapy is now an essential part of Cancer therapy around the world. The Treatment modality is now highly developed and sophisticated for cancers like Prostate cancer.
Two Main Types of Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer:
- External beam Radiotherapy
- Internal Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy)
External Beam Radiation Therapy (ERBT) utilises high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells by disrupting their DNA structure.
Radiotherapy for Prostate cancer is used for different stages of the cancer and is indicated as follows:
- As a first line treatment for localised cancer or the cancer which is not spread outside the prostate gland. Success rate for curing cancer with radiotherapy at this stage is similar to Radical prostatectomy surgery.
- First line therapy along with hormonal therapy for the cancer, which has spread outside the prostate gland but in nearby tissues only.
- In case of incomplete removal of prostate gland during surgery or in Cancer recurrence.
- As a palliative treatment in Advanced cancer with purpose of reducing the tumor size and providing pain relief due to bone metastasis.
When is External Beam Radiation Therapy (ERBT) Not Used?
ERBT is contraindicated in patients with history of gastrointestinal problems like ulcerative colitis and diverticulitis as well as in patients with poorly controlled Diabetes, because EBRT in these patients will carry high risk of Intestinal Obstruction, Perforation, Colitis and Proctitis.
When is External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) for Prostate Cancer?
EBRT is used for treating prostate cancer in its early stages and also for prostate cancer that has spread outside the gland to bones. The Radiation is applied from outside the body in form of focused beams of radiation.
Imaging evaluations like X-ray, CT scan or MRI of pelvis area is done before initiation of the therapy to identify the exact location of prostate cancer. Once the tumor size and location is known, physicians put some ink marks on the skin of patient which are then used to focus radiation beams on affected area.
Mostly the patient is treated 5 days a week as an out-patient up to 7-9 weeks. The procedure is painless and is completed within few minutes.
Observational research suggests that when patients with localised cancer are treated with EBRT, 60-65% of them have disease-free survival up to five years. However, 10 year disease free survival rate is observed in only 30-40% and disease recur in 70-80% patients at 15 years after therapy. The long term results of radical prostatectomy are considered better than EBRT.
What are Different Types of EBRT?
With advancement in technology, newer EBRT techniques have been developed which can administer higher dose of radiation which are more focused to the tumor to reduce radiation to adjoining structures and hence lower the side effects of the treatment.
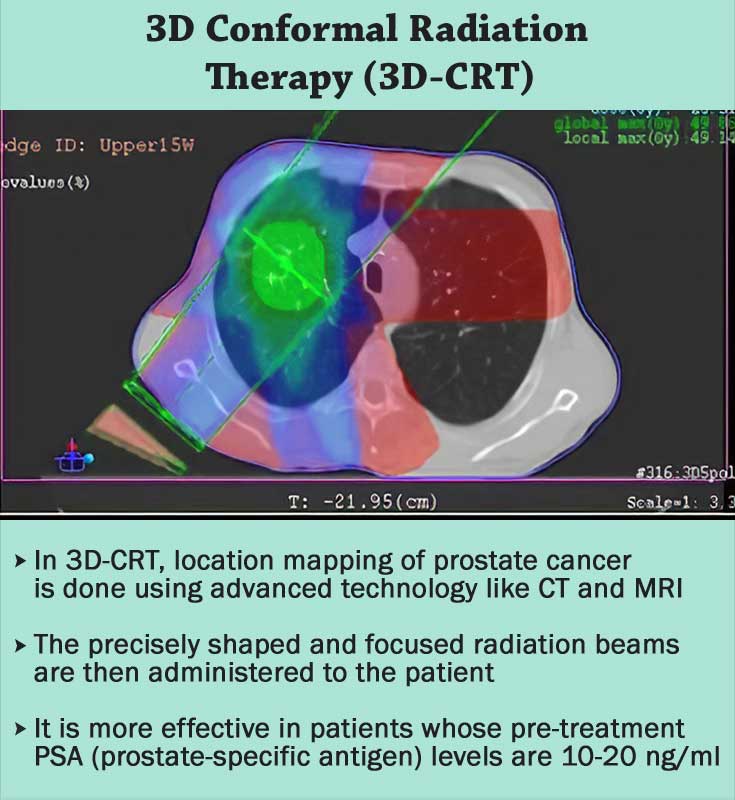
Three Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT)
In 3D-CRT, location mapping of prostate tumor is done using advanced technology like CT and MRI, after which precisely shaped and focused radiation beams are administered to the patient. During the course of therapy, the patient is confined in a Plastic body cast to reduce movement and increase accuracy of the treatment.
Research suggests that 3D-CRT is more effective in the patients whose pre-treatment PSA (prostate specific antigen) level are 10-20 ng/ml. Also the therapy is 30% more effective as compared to the EBRT in providing disease free survival up to five years.
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for Prostate Cancer Treatment
IMRT is an advanced form of 3 Dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Currently, it is the most common method of EBRT used for treating prostate cancer. A movable unit of the machine moves around the affected area to deliver focused radiation beams from different angles. The main advantage of this method is that the radiation dose can be adjusted and reduced during the course of treatment so that normal surrounding tissues are less affected and hence it lowers the side effects of radiation.
Recent IMRT machines carry an in-built imaging scanner. This advanced technique is known as Image guided radiation therapy (IGRT). Imaging scanners in IGRT allow the Radiologist to capture picture of prostate tumor during the procedure and allows him to make necessary Radiation dose adjustments in order to enhance effectiveness and reduce radiation toxicity to normal surrounding tissues. However, further research is warranted to verify the safety and efficacy of this method.
In another form of IGRT, minute implants are placed in the prostate tumor which emits radio waves which act as the guide to Radiation machine for delivering more focused radiation. The main advantage of this technique is that it guides the radiation machine to make even the minutest movement adjustment even if the patient moves during normal breathing. The machines that use this are known as Calypso®.
A Major Meta-Analysis of 23 studies among 9556 Prostate patients, by Yu et Al in 2016 has found out that IMRT produces less toxicity has shown significant reduction in Morbidity and gastro-intestinal toxicity when compared to 3D CRT.
Further sophisticated variation of IMRT is known as Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT). The VMAT technique administers radiation to affected area in focused by highly rapid manner and therefore allows the procedure to complete within few minutes.
While VMAT technique is more convenient for the patient, so far no research has been identified to prove it superior to IMRT.
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Prostate Cancer Treatment
SBRT is another form of advanced technology used for delivery high intensity radiation to the prostate cancer tumor with extreme precision (i.e. stereostatically). The technique utilises sophisticated imaging techniques like 3 dimensional CT scans to develop precise map of prostate tumor.
The entire course of treatment is completed within few days with SBRT as compared to few months with other forms of External beam radiation therapy and therefore reduces the overall cost of prostate cancer treatment.
However, recent clinical trial performed at Yale School of Medicine suggested that patient taking SBRT are at higher risk of developing genitourinary and gastrointestinal radiation toxicity as compared to the conventional IMRT.
Proton Beam Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Treatment
Proton beam Radiation therapy utilises protons for generating radiations unlike X-rays used in other types of EBRT. X-rays emit radiation energy both before and after hitting the target and therefore affects the surrounding normal tissues. On the other hand, protons first travel up to particular distance and then release energy. This characteristic of Proton beams allows them to deliver higher energy to prostate tumor in a more precise manner. Techniques similar to those used in 3D-CRT and IMRT are also used for Proton beam radiation therapy.
Although early results are promising, so far studies have not shown that proton beam therapy is safer or more effective than other types of EBRT for treating prostate cancer.
Right now, proton beam therapy is not widely available. The machines needed to make protons are very expensive, and they aren’t available in many centres or countries. Proton beam radiation might not be covered by all insurance companies at this time.
Combining Radiotherapy with Other modes of Treatment for Prostate Cancer
Radiotherapy can be combined with hormonal therapy or surgery to improve treatment outcomes. There are various terms used for this combination
What is Combined Radiotherapy and Androgen Ablation?
The combined radiotherapy and androgen ablation are gaining significance in treating Prostate cancer with Intermediate grade cancers such as Gleason scores of 7 or more, which suggests bi-lobar and more severe cancer, which is moderately curable or very unlikely to be cured. The Treatment modality uses both the androgen ablation using hormone therapy and External beam radiation together or in alternative stages.
Research by Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (USA) has found that 4 months of hormonal ablation therapy along with EBRT is more effective in producing disease-free survival (identified by low levels of PSA) at 5 years as compared to EBRT alone for patients with Gleason score of more than 6.
In case of more curable early stages of prostate cancer, the European Organisation for Research and treatment has found that primary total hormonal ablation therapy for reducing the size of tumor increases the effectiveness and outcome of 3D-CRT in producing disease free survival at 5 years.
What is Adjunctive EBRT?
When External beam radiation therapy is given in addition after prostate surgery or in addition to Brachytherapy, it is known as adjunctive EBRT.
As per the findings of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (USA), combination of EBRT and permanent implant brachytherapy provides higher rate of disease free survival at 5 years for high-risk patient as compared to brachytherapy alone or surgery alone.
In many cases, higher PSA levels are detected even after Radical prostatectomy, which suggests incomplete removal of prostate tumor. Adjunctive EBRT is applied in such cases. American Society of Therapeutic Radiation Oncology suggest that post-operative EBRT reduces the PSA levels by 70% and therefore provides more effective destruction of prostate tumor.
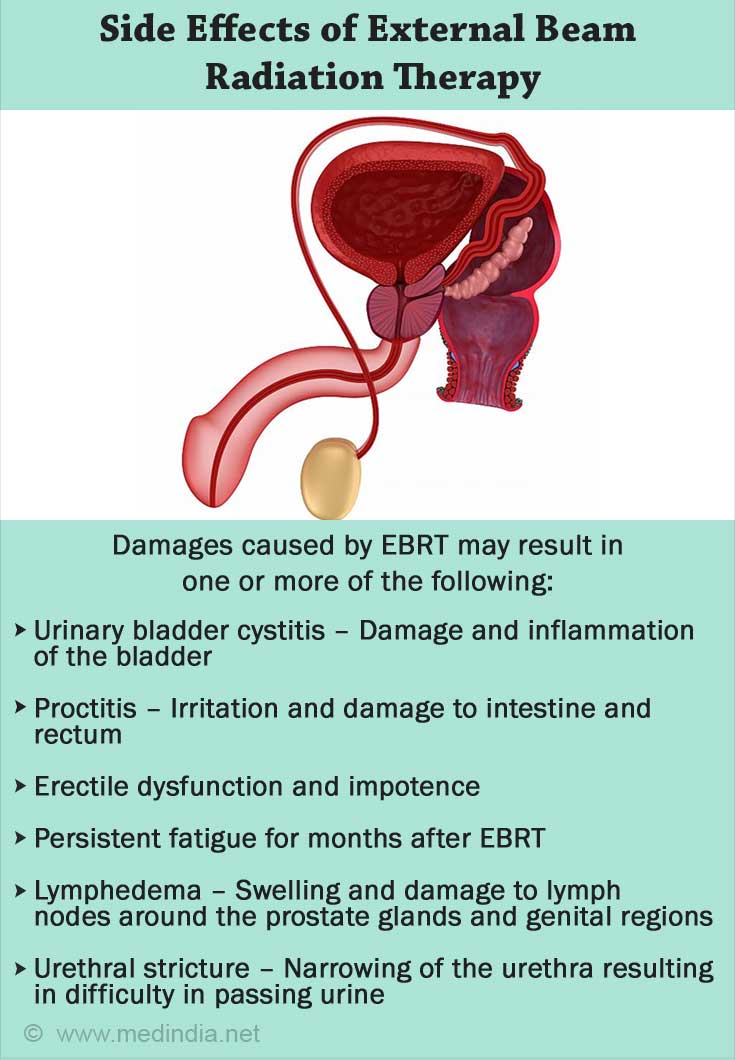
What are the Possible Side Effects of EBRT?
- Bowel disturbances: Irritation and damage caused to intestine and rectum by radiations lead to development of medical condition called Proctitis. The condition is characterised by frequent diarrhoea, bloody stool, stool leakage, and incontinence of gas.
- Urinary bladder cystitis: Damage to urinary bladder and cystitis causes urine frequency, Urinary incontinence, burning sensation and often bloody urine.
- Erectile dysfunction and Impotence: Erection problems and impotence gradually develop over years after EBRT.
- Fatigue: Very common side effect. Feeling of tiredness continues for months after taking EBRT.
- Lymphedema: If the lymph nodes around the prostate glands are damaged during EBRT, lymph fluid becomes stagnant in legs and genital region causing swelling and pain.
- Urethral Stricture: Rarely the urethra (tube which allows to pass urine out of body) is damaged by radiation which causes difficulty in urination.
It should be noted that with advancement in EBRT techniques which administer focused radiations, the rates of these adverse effects are decreasing.






