About
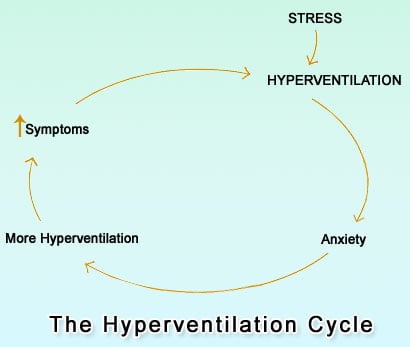
Hyperventilation is a state of over breathing that usually occurs due to anxiety or panic. The person breathes in excess to the body’s requirement and this causes symptoms of lightheadedness, followed by numbness and tingling sensation. It however can also occur in more serious situations like – following a heart attack, lung infection or shock.
Hyperventilation raises the pH value of the blood by lowering the carbon-di-oxide concentration in the blood. This makes the blood more alkaline. It also brings about constriction of the blood vessels that supply the brain thereby restricting the transport of vital electrolytes that are required for the functioning of the nervous system.
Low concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood is known as hypocapnia – a condition that causes the blood pH to rise and is referred to as a respiratory alkalosis. This high pH also causes lowering of calcium (called hypocalcemia) being available in the blood. Low calcium affects the nerves and muscles and causes tingling sensation in fingers and light headedness.
The body also has a habit of producing an acute shortage of carbon dioxide naturally. This situation is controlled by a centre in lower section of the brain which ensures that the normal level of carbon- di- oxide and oxygen remains balanced in the blood.
Although it may contradict earlier belief, excessive breathing can be counter productive and can result in a reduced oxygen supply to the brain. For this reason doctors sometimes artificially induce
Rapid or deep breathing may be observed in serious conditions including heart attacks or even rapid loss of blood that leads to a state of shock.
Hyperventilation lasts longer (few hours) than a heart attack and improves with exercise but does not improve with heart medications. Unlike heart attack, hyperventilation is more common in younger people.
Hyperventilation syndrome, on the other hand, is more specific and produces a group of symptoms. It also emerges in an individual under certain conditions. Although the symptoms closely resembles those of panic attacks, the two conditions are entirely different. Panic disorders are usually a result of an emotional problem while the symptoms of hyperventilation syndrome occurs even if no emotional complaint is present.
There are the two forms of hyperventilation syndrome – that which occurs everyday and those that occur suddenly! The excessive breathing may be difficult to detect in the everyday form while in the sudden form the symptoms are more intense and manifests rapidly.