About
What is Temporal Arteritis / Giant Cell Arteritis?
Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) or Temporal Arteritis or Cranial Arteritis is a condition where medium and large arteries especially those supplying the head region get inflamed.
Giant Cell Arteritis (artery – blood vessel supplying blood from the heart to different parts of the body, itis - inflammation) is a condition where certain arteries show inflammatory changes. It belongs to a group of disorders called vasculitis (vascular – relating to blood vessels, it is - inflammation). It is also called cranial arteritis since arteries supplying to the head region are usually affected. Another term used for this condition is temporal arteritis since the superficial temporal arteries are often inflamed. These are arteries located near the temples or the sides of the forehead just above the ears. Besides affecting the arteries supplying to the head, giant cell arteritis may also involve other medium and large arteries including the aorta.
Causes of Temporal Arteritis
The reason for the inflammation is not known. It could be inherited through genes as well as it could appear de novo. It is more common in Scandinavian population than in blacks or Asians. People above the age of 50 years, females compared to males and patients with a condition called polymyalgia rheumatica are at a particular risk of suffering from this condition.
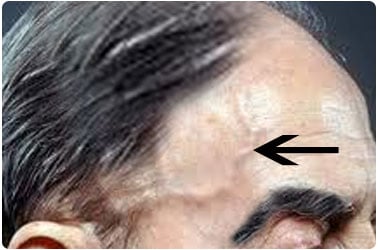
Symptoms vary from headaches, jaw pain and scalp pain to blurring of vision and blindness. Early diagnosis and treatment is necessary to prevent the patient from losing his sight.
A number of tests like ESR and C Reactive protein assist in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Imaging studies like color doppler sonography, PET scan and MRI are also useful. A biopsy of the temporal artery and examination of the specimen for inflammatory changes confirms the diagnosis.
Drugs belonging to the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid group are used to treat giant cell arteritis. Treatment usually lasts for one to two years. The patient should undergo frequent checkups during treatment to adjust the dose of the drug and make sure that he does not suffer from side effects of the treatment.