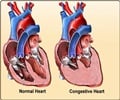
The number of new cases of heart failure in Ontario decreased 33% over a decade.

Researchers looked at trends in heart failure in Ontario from 1997 to 2007 in a large group representative of the population. There were 419 551 incident cases of heart failure, with 216 190 requiring admission to hospital and the remaining 203 361 managed as outpatients at the time of initial diagnosis. Most studies of heart failure trends have not included outpatients.
Patients aged 65 years or older represented 80% of the total number of cases. Patients who were admitted to hospital were older and had more health issues, such as heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure, compared with those not requiring admission. One-year mortality rates declined slightly, from 35.7% to 33.8% for inpatients and from 17.7% to 16.2% for outpatients.
"We saw a 32.7% decline in the incidence of heart failure cases in Ontario between 1997 and 2007, which translates to a 3% average annual decline; this is similar to the rates of decline previously observed in overall cardiovascular disease mortality and incidence of ischemic heart disease events in Canada," writes Jack Tu, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), Toronto, Schulich Heart Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, and University of Toronto, with coauthors.
The authors suggest that the decline in heart failure rates may be due to preventive efforts to better control smoking, blood pressure and cholesterol, which can lower the rates of ischemic heart disease, a leading cause of heart failure. "Hypertension is the second most important cause of heart failure and other studies have shown that Ontario has one of the highest rates of blood pressure control in recent years, which may also contribute to fewer patients with incident heart failure," the authors write.
"Although the results of our study are encouraging, the population continues to age and risk factors for heart failure such as diabetes and obesity are increasing, particularly in young people, which may cause the downward trend in incidence of heart failure to plateau or reverse," conclude the authors.
Advertisement