A recent study analyzed the association between carotid artery intima media thickness, presence of plaque and the carotid target organ damage (cTOD) with the diet quality.
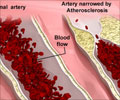
- Measurement of common carotid artery intima-media thickness or cIMT allows for detection of atherosclerotic plaques during initial phases of development
- Current study was undertaken to analyze the relationship between cIMT and diet quality
- Results reveal that diet quality index is not associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in intermediate cardiovascular risk patients.
TOP INSIGHT
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Identification of diet quality and its relation to cardiovascular disease is critical!
“Diet quality indices” is an indicator of the quality of your diet that is determined by a combination of various food items and/or nutrients that represent your dietary pattern. It is seen that the best value of the index is associated with positive changes in weight.
Past studies have shown a relationship between diet and the risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease (CVD). Diets such as Mediterranean diet have been shown to slow down the progression of cIMT in a few studies but there is not much evidence to conclusively prove the association between diet quality and cIMT.
Hence an analysis was undertaken to study the association between cIMT, the development of plaque and carotid target organ damage (cTOD) with the diet quality that was determined though a questionnaire called Diet Quality Index (DQI).
Study
- The cross sectional study analyzed was the MARK study, which had a total of 2384 participants from Spain between the ages of 35 and 74 years who had been diagnosed with intermediate cardiovascular risk.
- Out of the 2384 patients, carotid ultrasound was performed only in 500 patients. A total of 1884 patients were excluded from the study mainly based on terminal illness, institutionalization at the appointment time, amongst other criteria.,/li>
- The Diet Quality Index questionnaire used in this study included 18 food groups that were divided into 3 categories. Each category is given a score of 1, 2 or 3 points depending on the following:
- Frequency of consumption of food
- If the food consumed is considered beneficial (increased consumption, higher score)
- If the food is considered detrimental to health (increased consumption, lower score)
- The total possible score could range anywhere from 18, which denotes lowest quality to as high as 54, which denotes highest quality
- Carotid ultrasound was used to assess the cIMT, the presence of plaque (value of cIMT ≥1.5 mm or by a focal increase in thickness of 0.5 mm or 50% of the surrounding cIMT value).
- cTOD was assessed using cIMT values (cIMT > 0.9mm was considered as cTOD).
Results
- Among the 500 participants, 54.4% were male (mean age 60.3 ± 8.4 years).
- Mean DQI value was reported to be 40.08 ± 2.79, across both men and women population.
- The cIMT was reportedly lower in women (p < 0.01)
- Presence of plaque was reported in 83 (16.6%) of the patients.
- cTOD was reported in 85 (17%) of subjects.
- No significant association was found between DQI and cIMT in multiple linear regression after adjusting for age sex and other covariables.
- The logistic regression analysis showed no relation between DQI and carotid atherosclerosis (p = 0.890), the presence of plaques (p = 0.799) or cTOD (p = 0.942).
Conclusion
The results of this analysis did not reveal an association between DQI and cIMT, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques or the cTOD, which indicate that food quality indices may not be an important predictor of surrogate atherosclerosis markers as carotid damage.Limitations of the study
- Due to the cross-sectional design of this study, causal relationship between diet quality and carotid atherosclerosis could not be conclusively determined. Hence, more longitudinal studies and clinical trials should be conducted to evaluate the association between the two.
- DQI questionnaire used in this study took into consideration habitual consideration of only 18 specific food items while other food items that could possibly have either a positive or negative impact on cIMT were not part of this study.
- The Relationship Between Dietary Patterns and Carotid Intima Media Thickness, as an Early Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis - (http://www.fasebj.org/content/30/1_Supplement/1154.2)
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email