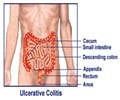
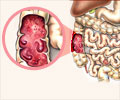
Ulcerative colitis is a long-term inflammatory disorder of the colon and rectum. Study found, tofacitinib to be more effective than placebo in reducing disease activity.
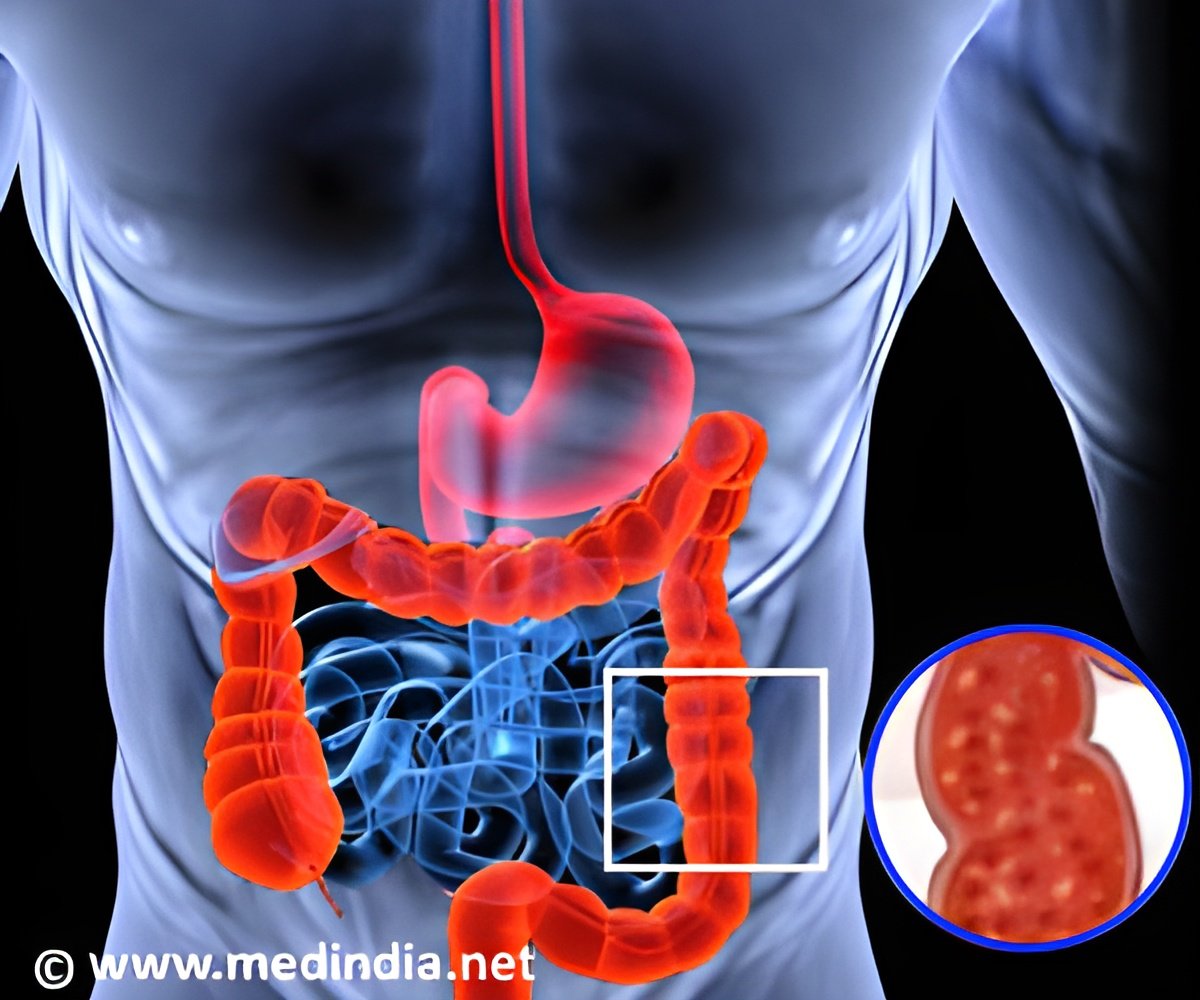
The study results showed that after 8 weeks, ulcerative colitis activity decreased by 32%, 48%, 61%, and 78% in patients treated with 0.5 mg, 3 mg, 10 mg and 15 mg tofacitinib, respectively. A 42% decrease in ulcerative colitis activity was also observed in placebo-treated patients. On the other hand, clinical remission was seen in 13%, 33%, 48%, and 41% of patients receiving 0.5 mg, 3 mg, 10 mg and 15 mg tofacitinib, respectively, while 10% placebo-treatment patients showed clinical remission.
Common serious side-effects of tofacinitib included influenza and nasopharyngitis. Other side effects were a decrease in neutrophil count (a type of white blood cell) and increase in LDL-cholesterol levels.
In conclusion, patients with active moderate or severe ulcerative colitis treated with high doses tofacitinib had a clinical response and clinical remission more frequently than those receiving placebo. The role of tofacitinib in maintenance therapy has not been established. Larger studies are required to establish the benefits and adverse effects of tofacitinib in active ulcerative colitis.
Reference: Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, in Active Ulcerative Colitis; William Sandborn et al; N Engl J Med 2012; 367:616-624
Source-Medindia