Emotional sensors in VR exergames adjust workout difficulty based on user emotions, creating personalized, engaging experiences that keep users motivated and reduce dropout rates.
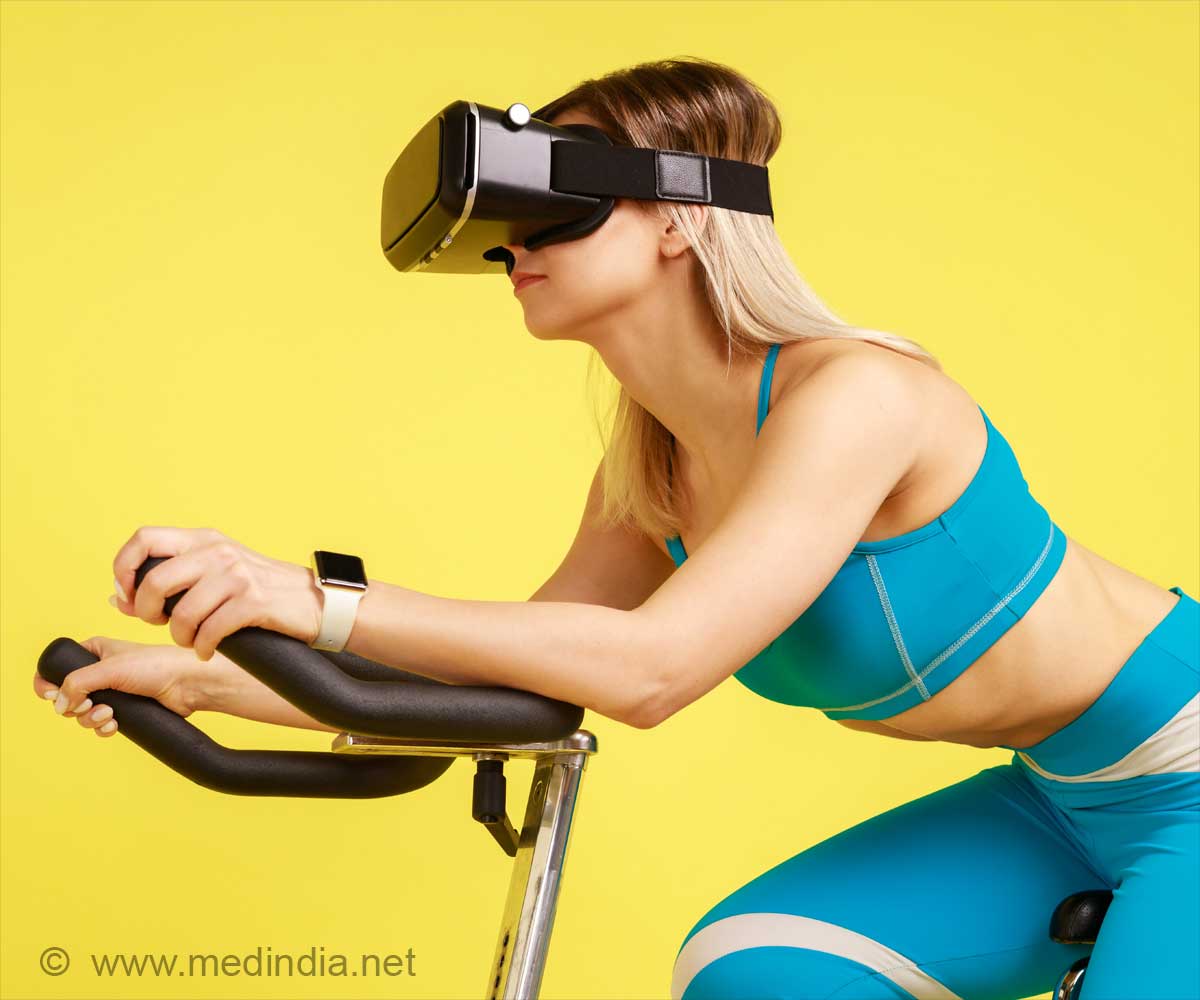

- Emotional sensors monitor heart rate, sweat, and pupil dilation to track user emotions during VR workouts
- Exergames adapt difficulty in real-time, offering challenges or rewards based on user stress or comfort
- Emotionally intelligent VR games could revolutionize fitness by making exercise more enjoyable and reducing dropout rates
Sweating the Details: Emotion Recognition and the Influence of Physical Exertion in Virtual Reality Exergaming
Go to source)..
Emotional sensors can detect stress or boredom during exercise, adapting the intensity to keep you engaged! #medindia #virtualfitness #VRexergaming’
Why Do Users Quit Exergaming?
Low Adherence: Many users quit exergaming once they experience discomfort or boredom.Challenges in Game Design: Designers struggle to maintain user engagement, especially when the exercise becomes monotonous.
Lack of Personalization: Current exergames often fail to adapt to the user’s emotional or physical state, leading to a loss of interest.
The Role of Emotional Sensors
Researchers at the University of Bath, led by Dr. Dominic Potts, are addressing this issue by introducing emotional sensors. These sensors monitor a user’s physiological responses during exercise, helping the system adjust the game to match the user’s emotional state.- Sensors embedded in VR headsets and wearable devices measure pupil dilation, heart rate, sweating, and facial expressions.
- These sensors detect emotional states such as stress, happiness, or boredom, and the game adapts in real time to keep the user engaged.
- If the sensors detect stress or fatigue, the game might offer more rewards or reduce the difficulty. Conversely, if the user is comfortable, the game could become more challenging.
Overcoming the Challenges of Emotional Tracking
Traditional sensors face difficulties tracking emotions during exercise due to the physical movement involved. The University of Bath team has made significant progress in overcoming these issues.Previous sensor technologies were unreliable during intense physical activity due to movement and environmental factors. By combining multiple sensors and cleaning data in real-time, researchers can now accurately track emotional changes even during vigorous exercise.
Key Guidelines for VR Exergame Designers
Based on their findings, the researchers developed eight essential guidelines for creating emotionally adaptive VR exergames:1. Adjust for Luminosity: Sensors that measure pupil size should account for lighting changes in the virtual environment.
2. Consider Baseline Sweat Levels: The game should factor in a user’s preexisting sweat levels to predict stress and nervous system arousal.
3. Clean Sensor Data in Real Time: Data collected should be filtered to remove irrelevant signals, ensuring accurate emotional tracking.
4. Use Multiple Sensors: Employing various types of physiological sensors helps improve emotional predictions, allowing for better user personalization.
Dr. Christof Lutteroth, co-investigator at CAMERA and director of the REVEAL research center, envisions a future where emotionally adaptive VR exergames become the norm. These systems would tailor workouts to individual users, keeping them motivated and engaged over the long term.
Emotionally intelligent exergames could be used by people of all ages and fitness levels, from schoolchildren to athletes in rehabilitation. As VR technology becomes more advanced, emotionally adaptive exergames could revolutionize how people approach fitness, turning exercise pain into pleasure.
The use of emotional sensors in VR exergaming could be a game-changer in the world of fitness. By adjusting the difficulty based on a user’s emotional state, this technology has the potential to make workouts more enjoyable, reduce dropout rates, and help people stay on track with their fitness goals.
Reference:
- Sweating the Details: Emotion Recognition and the Influence of Physical Exertion in Virtual Reality Exergaming - (https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3613904.3642611)
Source-Medindia