Early diagnosis could help curb Tuberculosis rates. But conventional methods and specialized personnel are not always available in remote or developing areas.
‘TB is contagious, but it’s not easy to catch. Experts came up with a more practical diagnostic test that can be read with a smartphone.’





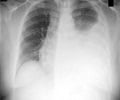
The World Health Organization estimates that in 2015, 1.4 million people died from TB, with most of these deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries. Early diagnosis could help curb these numbers. But conventional methods such as sputum smear microscopy, chest X-rays and molecular-based tests require equipment, electricity and specialized personnel that are not always available in remote or developing areas.So Chien-Fu Chen and colleagues set out to come up with a more practical diagnostic test that can be read with a smartphone, a technology that is increasingly available in emerging economies.
The researchers combined gold nanoparticles with single-stranded DNA sequences that bind to the genetic material of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that cause TB. These nanoparticles were then incorporated into a paper-based device.
Adding even a minute amount of lab-derived, double-stranded DNA from M. tuberculosis changed the color of the test spots within an hour. A smartphone camera was used to analyze the color change to determine the bacterial concentration. The researchers also tested a tissue sample from an infected patient to further demonstrate that the device could be used in the field.
Source-Eurekalert