Adequate nutrition is essential during pre-puberty to support proper growth and overall well-being, setting the foundation for a healthy transition into adolescence
- Puberty is a crucial stage in a girl's development, marked by significant physical and hormonal changes
- Encouraging healthy eating habits during pre-puberty is essential for long-term well-being and may reduce the risk of future health issues
- Consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, can ensure personalized nutrition guidance for a healthy puberty
Nutrition is the Backbone for Overall Growth
Adequate nutrition is essential for supporting proper growth, bone development, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. Providing a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients such as calcium, iron, protein, vitamins, and minerals is vital (1✔ ✔Trusted SourceHealthy Eating During Adolescence
Go to source). This ensures that girls have the energy and resources their bodies need to navigate these changes successfully. Additionally, promoting healthy eating habits at this stage sets the stage for a lifetime of good dietary choices and may help mitigate the risk of health issues later in life.
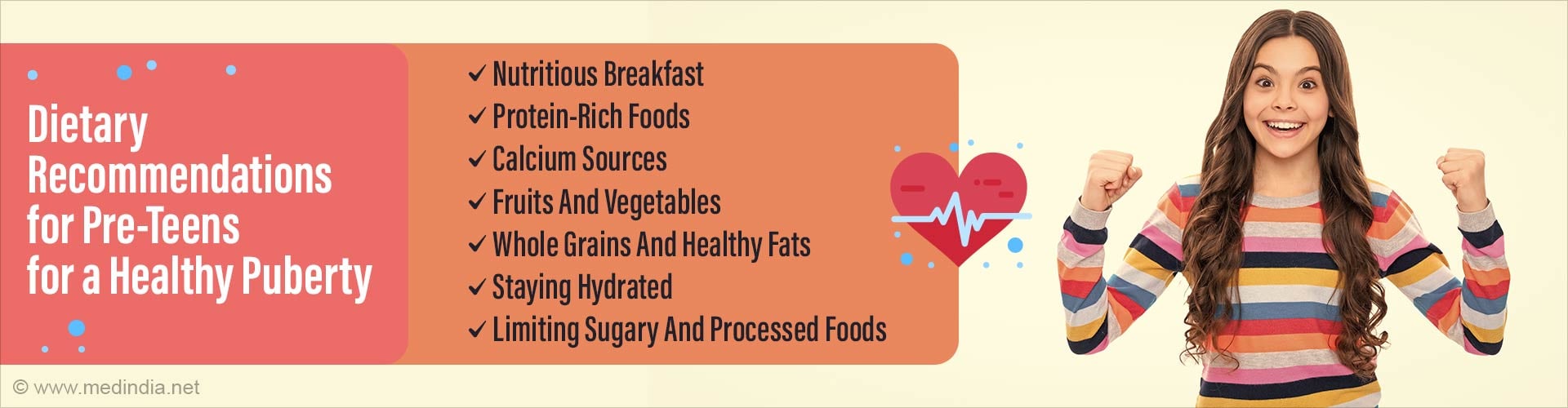
Dietary Recommendations for Pre-Teens for a Healthy Puberty
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for pre-teens (children aged 9-12) as they go through puberty, as it provides the necessary nutrients for growth and development.1. Encourage Breakfast:
Children in the modern world have adopted the trend of skipping breakfast. This norm should be avoided. A healthy breakfast helps kick-start the day and maintain energy levels. Whole-grain cereal, oatmeal, or whole-grain toast with protein (e.g., eggs) is a good option.2. Adequate Protein Intake:
Our Indian diet has less protein in general. Hence, it becomes crucial to incorporate enough proteins in every meal. Lean meats like chicken, turkey, and lean beef can be included. Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, for omega-3 fatty acids. Beans, lentils, and tofu for plant-based protein sources can also be included.3. Calcium-Rich Foods:
Include dairy products like low-fat or non-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese for calcium and protein. Fortified plant-based milk (such as almond or soy milk) for those who are lactose intolerant or prefer a vegan diet. Apart from dairy, consider other calcium sources like fortified cereals, calcium-fortified orange juice, and leafy greens.4. Fruits and Vegetables:
A variety of colorful fruits and vegetables for vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for at least five servings a day. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale for iron and calcium. Citrus fruits like oranges for vitamin C.5. Whole Grains:
Whole-grain bread, pasta, rice, and cereals for fiber and sustained energy. Quinoa and brown rice are excellent options too.6. Healthy Fats:
A handful of almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds for healthy fats, fiber, and essential nutrients. Avocado for monounsaturated fats. Olive oil for cooking. Fatty fish like salmon, trout, and sardines for omega-3 fatty acids.7. Water:
Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health. Encourage your pre-teen to drink plenty of water throughout the day.8. Limit Sugary and Processed Foods:
Minimize the consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, and fast food, as they can lead to weight gain and health issues.9. Iron-Rich Foods:
Iron deficiency anemia is a major cause of concern in females. It is necessary to examine whether the food includes enough iron in food from early stages of life . Include foods like lean meats, fortified cereals, beans, and lentils to prevent iron-deficiency anemia.10. Snacking:
Choose healthier snacks like yogurt, cut-up fruits and vegetables, whole-grain crackers with cheese, or a handful of nuts.It's essential to maintain an open and supportive environment for pre-teens and encourage them to make healthy food choices. Additionally, consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian if you have specific concerns or dietary restrictions for your child. They can provide personalized advice to ensure your child's nutritional needs are met during their puberty years.
Reference:
- Healthy Eating During Adolescence - (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/healthy-eating-during-adolescence)
Source-Medindia