Poor physical performance is linked to increased odds of dementia in older adults. Standing balance test may help doctors predict dementia risk in older adults.
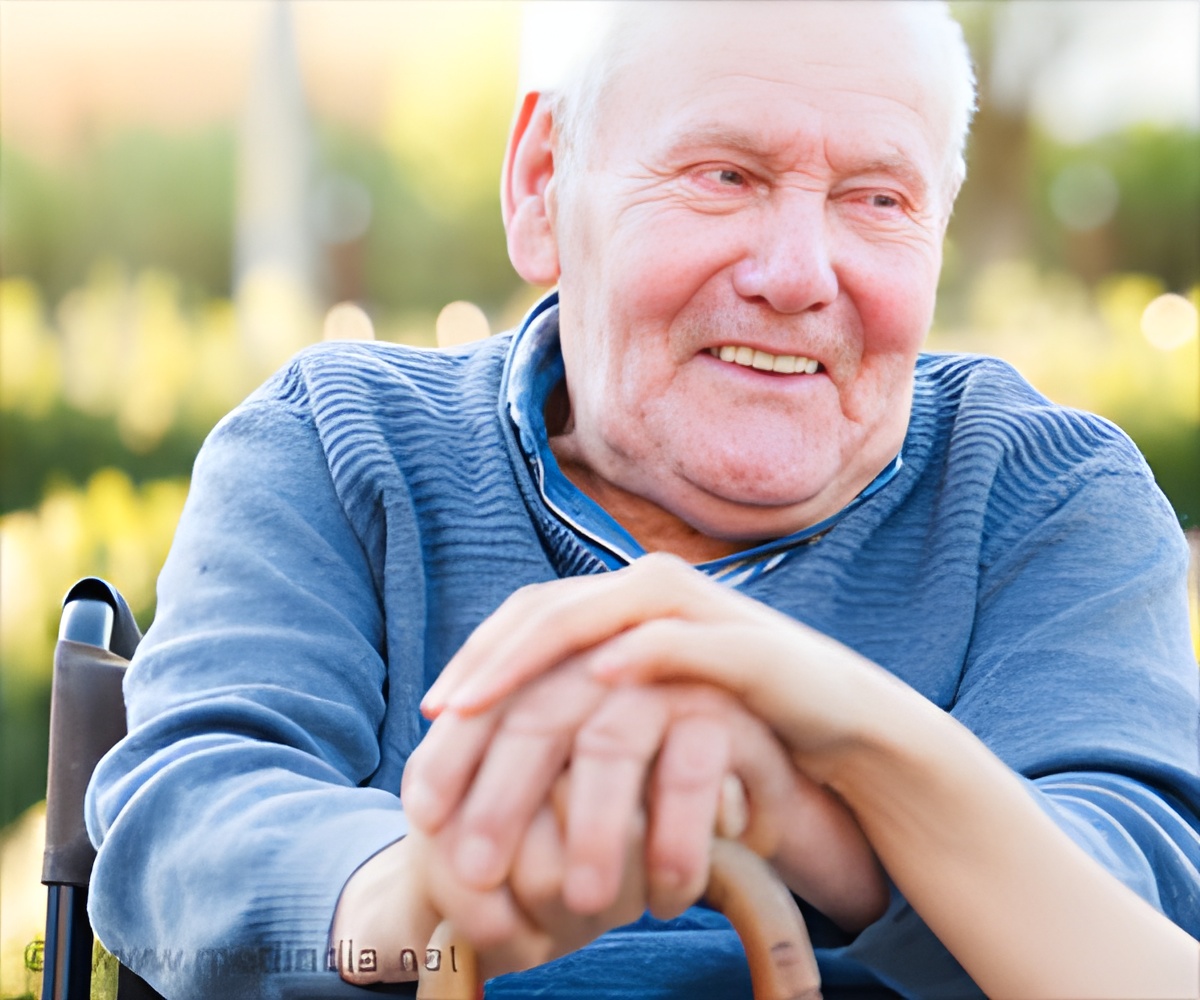

‘Walking and standing balance require complex brain activity. Testing these functions may help doctors predict older adults who might be most at risk of developing dementia.
’





The researchers examined 578 people aged 90 and older who were participants in The 90+ Study, a community-based longitudinal study--a research method that follows the same subjects repeatedly over a period--of the oldest-old in Southern California. Examiners see the participants every six months to conduct physical and neurological (the branch of medicine dealing with the study of nerves and the nervous system) examinations as well as cognitive tests, with the goal of looking critically at aging and dementia specifically. At the start of the study, about 50 percent of the participants were cognitively impaired (had trouble thinking or remembering), but did not have dementia. The rest were cognitively normal. Researchers followed the participants for 2.6 years and, during that time, almost 40 percent of participants developed dementia.
The researchers observed a unique link between dementia risk and poor performance on two different physical performance tests: the standing balance test and the four-meter (about 13 feet) walking test.
The researchers suggested that, since walking and standing balance require complex brain activity, testing these functions may help doctors predict who among the "oldest-old" might be most at risk of developing dementia. The researchers also note that future studies could lead to the development of prevention programs and treatment strategies.
The study is published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Advertisement