- Fat-Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E, and K - 9.315 - (http://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/nutrition-food-safety-health/fat-soluble-vitamins-a-d-e-and-k-9-315/)
- Vitamin A in Fruits and Vegetables - (https://www.fruitsandveggiesmorematters.org/vitamin-a-in-fruits-and-vegetables)
- Eat These Foods to Boost Your Immune System - (https://health.clevelandclinic.org/2015/01/eat-these-foods-to-boost-your-immune-system/)
- Study Shows Vitamin Slow RP - (http://www.blindness.org/treatments/study-shows-vitamin-slows-rp)
- Skin Health - Vitamin A - (http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/skin-health/vitamin-A)
- Vitamin A Deficiency and Clinical Disease: An Historical Overview - (http://jn.nutrition.org/content/138/10/1835.full.pdf+h)
- Facts About Age-Related Macular Degeneration - (https://nei.nih.gov/health/maculardegen/armd_facts)
- Vitamin A - (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-Consumer/)
What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is an essential fat-soluble vitamin present in many different kinds of foods. Vitamin A is present in nature in two different forms:
- Preformed Vitamin A: Preformed Vitamin A is found predominantly in meat and dairy products. It includes retinol, retinoic acid, and retinal.
- Provitamin A: Provitamin A includes carotenoids such as beta-carotene, which is found predominantly in plant based foods and dairy products.
Vitamin A plays a vital role in many bodily functions such as the immune system, eyesight and reproduction. Vitamin A helps develop and maintain bones and teeth, heart, lungs, kidneys and a host of other vital body organs.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin A / What are Important Sources of Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is found in both plant and animal sources of food. Fruits and vegetables such as apricots and mangoes, carrots, tomatoes, watermelon, pumpkins, cantaloupe, and greens such as broccoli, spinach, and lettuce have an abundance of vitamin A.
Liver is one of the richest animal sources of vitamin A. Kidney, cod, eggs, meat, and dairy products like cheese, cream and fortified milk are also rich sources of vitamin A. Regular consumption of vitamin A in our diet takes care of our eye health and ensures a healthy skin.

Recommended Intakes of Vitamin A
The best way to get the daily requirement of vitamin A is to eat a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, fortified dairy foods, and other sources of the vitamin. The average intake of infants less than 6 months is around 400 micrograms or mcg / day and those above 6 months but less than a year is around 500 mcg /day.
Recommended intakes for children, adolescents and adults:
For men and women (14 years and older), the intake should be around 900 mcg / day and 700 mcg / day respectively. Women who are pregnant are advised to have 770 mcg / day and those nursing, around 1300 mcg / day.
Children in the age groups of 1 to 3 years, 4 to 8 years and 9 to 13 years should consume 300 mcg /day, 400 mcg / day and 600 mcg / day respectively.
Benefits of Vitamin A
- Immune Function: Vitamin A is an antioxidant and plays a vital role in strengthening and maintaining our immune system. Vitamin A deficiency has been associated with an impaired immune system which causes repeated infections.
- Vision: Vitamin A plays a very important role in preventing and slowing down the progression of night blindness and retinitis pigmentosa. Adequate consumption of vitamin A helps to maintain our eyesight for a long period of time and protects against age related loss of vision. Low vision in darkness indicates a deficiency of vitamin A.
- Age related macular degradation: Vitamin A supplements in the form of beta-carotene along with other nutritional supplements have been shown to slow down age related macular degradation of eyes in older people. Studies have shown that a combination of multivitamins including beta-carotene along with zinc and copper can reduce the risk of age related macular degradation by up to 25%.
- Healthy Skin: Vitamin A is a miracle for our skin with topical vitamin A creams being used effectively to treat everything from acne marks to making our skin smooth, supple and wrinkle free. Regular consumption of vitamin A helps keep our skin young and supple.
- Fetal development: Vitamin A is very important for the embryonic development of babies in the womb and for the regulation of adult genes. In fact, populations having high maternal mortality rates and high infant mortality rates show dramatic reduction in mortality rates when the expectant mothers and newborns are given vitamin A supplements.

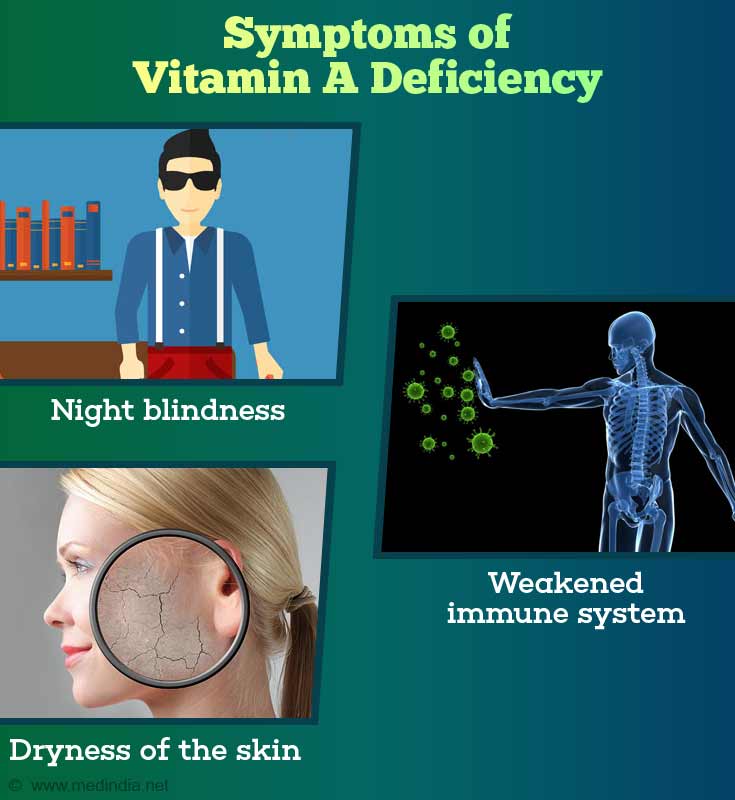
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
Vitamin A plays a major role in many basic life functions and its deficiency can manifest in many ways. The elderly and the chronically sick populations also tend to show a deficiency of vitamin A.
Some of the many symptoms of vitamin A deficiency are:
- Vitamin A deficiency causes the mucosa to dry up leading to the drying up of soft tissues. This can cause dryness of the skin. Extremely dry skin, brittle hair and nails that chip and break easily indicate a lack of vitamin A in the body along with deficiencies of zinc and vitamin C. Dryness of the skin may be the first sign of vitamin deficiency as the skin is a barometer of health. Dry skin due to vitamin A deficiency appears rough with raised bumps particularly on the back of arms.
- Weakened immune system: A weak immune system can cause repeated infections, and interfere with proper growth and development of children. Infections - especially repeated urinary, respiratory tract and middle ear infections indicate a vitamin A deficiency in the body.
- Loss of vision: If you notice that you are unable to see in the dark, a condition called night blindness or show signs of poor low-light vision and your eyes do not get accustomed to seeing in the dark quickly, then it is a sure sign of vitamin A deficiency. Consult your doctor immediately to avoid permanent damage to the eyes.
- Psoriasis, eczema and acne: Excessive dryness of the skin due to a vitamin A deficiency can contribute to aggravated skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema and acne which are not only very painful but quite difficult to cure.
Side Effects of Vitamin A
Being a fat soluble, excess vitamin A usually gets stored in the liver. Consuming large amounts of beta-carotene or other provitamin A carotenoids do not cause adverse effects although it can turn the skin orange or yellow, a condition that is reversible on reducing its intake.
Excess of preformed vitamin A can cause hypervitaminosis A; the condition mostly occurs when adults consume excess supplements or therapeutic retinoids rather than excess dietary intakes. Acute toxicity occurs if the vitamin has been consumed rapidly and in excess amounts, like around several thousand IUs in one shot.
Chronic intakes (consuming more than 25,000 IU regularly every day) can also cause toxicity; in such cases, the tissue levels of vitamin A stay high for a long time even after discontinuation of the supplement, and the resulting liver damage is not always reversible. Symptoms could include increased intracranial pressure, dizziness, nausea, headaches, skin irritation, pain in joints and bones, coma, and even death.











