- Fischer J, Lane I, Stokes J. Acute postrenal azotemia: etiology, clinicopathology, and pathophysiology. Cited in Compend Contin Educ Vet. 2009
- Postrenal Azotemia - Osmosis - (https://www.osmosis.org/learn/postrenal_azotemia)
- Prerenal Azotemia - Lima Memorial Health System - (http://www.limamemorial.org/health-library/hie%20multimedia-textonly/1/000508)
What is Azotemia?
Azotemia (azot = nitrogen; emia = blood) is a condition in which there is elevation of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine levels above normal values. The normal range of BUN is 8-20 mg/dL (2.5-7.1 mmol/L) and that of serum creatinine is 0.7-1.4 mg/dL (60-100 µmol/L).
In azotemia, the kidneys are not able to excrete adequate amounts of these compounds in the urine. This results in uremia (increased levels of urea in the blood) and kidney (renal) failure due to nephrotoxicity.
What are the Types of Azotemia?
There are 3 types of azotemia, which are briefly discussed below:
- Pre-renal Azotemia: This type of azotemia is so-called because it does not involve kidney dysfunction due to kidney disease/damage. It arises as a result of inadequate blood flow (hypoperfusion) to the kidneys. Thus, when the blood pressure is low, the kidneys are not able to adequately filter-out the waste products. As a result, the level of urea and creatinine increases in the blood. It can be caused by any factor(s) that lowers the blood pressure / volume, including shock, hemorrhage, and congestive heart failure. However, this type of azotemia can usually be reversed.
- Intra-renal Azotemia: This type of azotemia is an intrinsic kidney condition, which is why it is also termed as intrinsic azotemia. This type of azotemia arises from damage to the kidney causing severe nephrotoxicity, often resulting in uremia. It can arise as a result of various types of kidney diseases, including acute tubular necrosis, glomerulonephritis, and renal failure. Of these, acute tubular necrosis is the most common form of intra-renal or intrinsic azotemia.
- Post-renal Azotemia: Post-renal azotemia is caused by the blockage of urine flow below the level of the kidney. There may be several causes, the most common being blockage of the ureters or urethra by kidney stones.
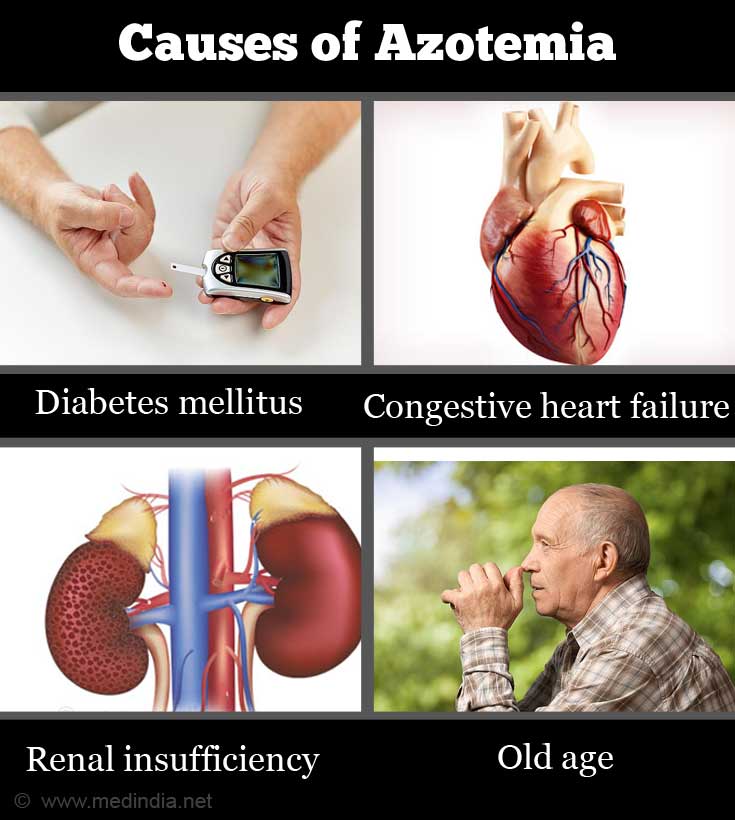
What are the Causes of Azotemia?
The causes can be categorized as general, which occurs in all types of azotemia; or specific to a particular type of azotemia. These are briefly highlighted below:
General Causes:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Congestive heart failure
- Renal insufficiency
- Old age
Specific Causes: These are listed according to the type of azotemia.
Pre-renal Azotemia: These include any factor(s) that lowers the blood pressure / volume and are listed below:
- Hemorrhage
- Congestive heart failure
- Severe burns
- Heat exposure / dehydration
- Shock
- Incessant vomiting / diarrhea
Intra-renal Azotemia:
- Medicines / Drugs: These include various nephrotoxic drugs like cyclosporine, certain antibiotics, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Besides these medicines, the hard drug, cocaine acts as a potent nephrotoxin and damages the kidney.
- Infection: Various types of infections, especially bacteremia (presence of bacteria in the bloodstream, sometimes causing sepsis) can damage the kidney tubules responsible for filtration of the blood.
- Vascular Disease: This can arise as a result of damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys or their blockage by blood clots.
Post-renal Azotemia: This occurs when there is blockage in the ureters or urethra that carry urine to the outside. Blockage can arise from the following causes:
- Kidney stones
- Catheter insertion
- Prostate enlargement
- Cancer
What are the Symptoms & Signs of Azotemia?
Some of the common symptoms and signs of azotemia include the following:
- Decreased urine output (Oliguria)
- Discoloration of urine (red tinge)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Rapid heart rate (Tachycardia)
- Pale skin
- Dry mouth
- Thirst
- Edema

What are the Consequences of Azotemia?
Pre-renal and post-renal azotemia can be reversed by suitable treatments and do not have any serious consequences. However, intra-renal azotemia has a very serious consequence, as it can cause acute kidney failure, loss of baby during pregnancy and can be potentially fatal if it is not treated promptly.
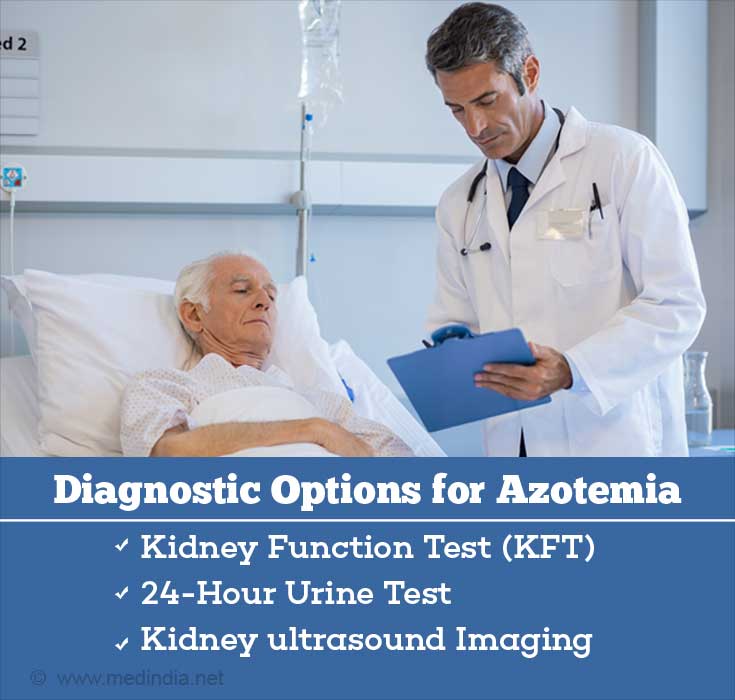
How do you Diagnose Azotemia?
The diagnostic work-up involves the following:
- Medical History: A detailed medical history, where information is gathered about any current / past diseases, infections, current medications, and any family history of kidney disease.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will perform a thorough physical exam, where he / she will feel (palpate) to see the condition of the kidneys before ordering other investigations.
- Catheterization: This procedure is generally used when urine output is low. A thin plastic tube (catheter) is inserted into the urethra to ease the urine flow as well as to see if there is any blockage.
- Kidney Function Test (KFT): These are blood tests that measure the levels of BUN, blood urea, serum creatinine, serum uric acid, sodium, potassium, and chloride in kidney failure patients.
- 24-Hour Urine Test: In this test, a 24-hour sample of urine is obtained to measure the specific gravity, osmolality, protein, sodium and creatinine concentrations to assess the condition of the kidneys.
- Kidney Imaging: If the KFT results are positive, indicating that there is indeed kidney failure, the doctor may order X-rays or ultrasonography (USG) of the kidneys to visualize any gross abnormalities within the kidneys.
How do you Treat Azotemia?
Azotemia can be treated by the following modalities that aim to treat the underlying cause and to purify the blood of impurities. Treatment depends on the type, underlying cause and severity. In case of pregnancy, the mother’s renal function and baby should be closely monitored.
- Medications: These include medicines that make the heart pump harder and increase the cardiac output (positive inotropic drugs) e.g. digoxin, amiodarone, calcium, levosimendan, dopamine, epinephrine, and theophylline. Antibiotics are prescribed for treating any blood infections or urinary tract infections (UTI). Insulin may be used to control blood glucose levels that may have caused azotemia. Loop diuretics may be used to excrete excess accumulated body fluid. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate can be used for lowering potassium levels in the blood.
- Hemodialysis: Hemodialysis is used to purify the blood by removing urea, creatinine and other toxic substances. The blood comes out of the patient’s body via a tube from a vein in the arm and is passed through the dialysis machine. This machine contains a cylinder having an artificial membrane that filters the blood. The purified blood is then returned back into the patient’s body. This cycle goes on for approximately 4 hours, after which the entire blood in the body becomes purified.
- Peritoneal Dialysis: This procedure is similar to hemodialysis except that artificial membrane is not used. The membrane around the intestine (peritoneal membrane) within the abdomen is used as a natural filter. The blood passing through the minute capillaries of this membrane filter-out the toxic substances into the abdominal cavity containing dialysis fluid, which is sucked (aspirated) outside through a tube from time to time and replaced with fresh dialysis fluid.