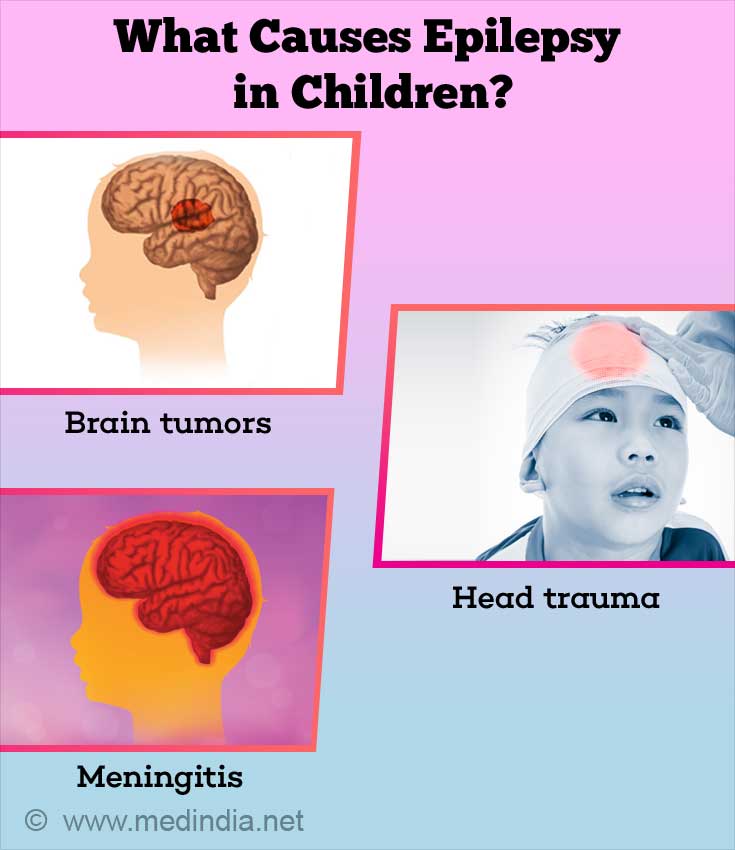
Causes of Epilepsy
- ‘No known cause’ (Idiopathic) in most instances
- Abnormal brain structure or malformation - eg, tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomas
- Brain tumors
- Genetic conditions – eg phenylketonuria, galactosemia
- Infections - meningitis and encephalitis, parasitic infections (especially cysticercosis) are a frequent cause of epilepsy in under developed countries
- Head trauma.
Common Triggers
These triggers may stimulate abnormal brain activity and should be avoided or controlled- Lack of sleep
- Prolonged watching of television/computer screen
- Stress
- Drugs, alcohol abuse
- Skipping meals
- Flickering lights
- Electrolyte disturbances - eg, hypernatremia (high sodium), hyponatremia (low sodium), hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), hypocalcaemia (low serum calcium), hypomagnesaemia
Complications of Epilepsy
- Focal seizure complications
- Emotional disturbances – anger, lack of humor, aggressive and violent behavior
- Obsessions
- Hyper/hyposexuality
- Memory disturbances
- Prolonged aimless wandering followed by amnesia and inability to recall the incident
- Generalized seizures
- Injury to body eg tongue biting, lip and cheek injuries, injuries due to falling down
- Aspiration of secretions or vomitus
- Drowning
- Shoulder dislocation
- Skull or spinal fractures
- Status epilepticus
What are the Types of Epilepsy in Children?
Absence or petit mal' seizures – Petit mal epilepsy typically present as frequent (100 times per day or more) episodes of short spells of staring into space spells (lasting a few seconds). It starts in childhood and rarely persists into adult lifeInfantile spasms – Seen in infants between 4 to 8 months of age. Occurs as a series of jerks of muscles of the limbs and body especially on waking
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy – Begins during adolescence, starting as early morning with arm and shoulder muscle contraction and jerky movements that may progress over time to seizures that affect the whole body (generalized tonic clonic seizures). It is an inherited condition
Some rarer forms of epilepsy in children include -
Dravet’s syndrome – Sudden appearance of severe seizures with muscle jerks, recurrent seizures involving the whole body with or without fever and occasionally status epilepticus (rapid seizures in succession without intervening period of consciousness)
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome – Seizure disorder in children (can be absence type, myoclonic, generalized tonic clonic or atypical) associated with mental retardation due to brain bleed, inherited metabolic conditions, brain infections or hypoxia (lack of oxygen)
Benign Rolandic epilepsy (benign focal epilepsy) – Recurrent seizures in children 4-10 years seen as focal oral or facial movements, sensory disturbances especially at night. Some children may have generalized seizures. It is more common in boys. The condition usually resolves before the end of adolescence
Benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes – Presents as generalized seizures in older children. There is no structural brain lesion and the condition has an excellent prognosis
Panayiotopoulos syndrome – Starts between 3 to 10 years of age. Child becomes pale and feels sick and typically vomits during the seizure. The seizures are prolonged lasting nearly 60 minutes sometimes. Many episodes occur during sleep