- Mousley M. Selecting appropriate footwear for patients with diabetes. Nursing Times. 2004 Nov 16-22; 100 (46):48-50.
- Ketosis - (http://www.diabetes.co.uk/blood-glucose/ketosis.html)
- Diabetes logbooks - (https://dtc.ucsf.edu/types-of-diabetes/type2/treatment-of-type-2-diabetes/monitoring-diabetes/diabetes-log-books/)
- Diabetes alert - (http://main.diabetes.org/dforg/pdfs/2015/2015-cg-medical-id-cards-2015.pdf)
- Glucagon injection kit - (http://www.diabetes.co.uk/diabetes-medication/glucagon-injection-kit.html)
- Diabetes Complications - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/basics/complications/con-20033091)
- Diabetes treatment: Using insulin to manage blood sugar - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-treatment/art-20044084)
Overview of Diabetes
Diabetes or diabetes mellitus (DM), is an endocrine cum metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time and includes symptoms such as frequent urination, increased thirst and hunger.
What are the Types of Diabetes Mellitus?
There are three main types of diabetes mellitus:
- Type 1 DM also called "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or " juvenile diabetes ", which occurs due to the failure of pancreas to produce enough insulin.
- Type 2 DM also called "non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes", caused mainly due to insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly i.e. become resistant.
- Gestational diabetes - High blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
Blood Sugar Levels and Blood Glucose Chart
For a normal healthy individual, fasting blood sugar should be around 70–99 mg/dL and “post prandial” blood sugar that is measured two hours after meals should be less than 140 mg/dL. However, fasting blood sugar of around 101-126 mg/dL and post prandial sugar of around 140 – 200 mg/dL suggests early diabetes. In individuals with established diabetes, fasting blood sugar is more than 126 and post prandial blood glucose is more than 200 mg/dL.
What are the Complications of Diabetes?
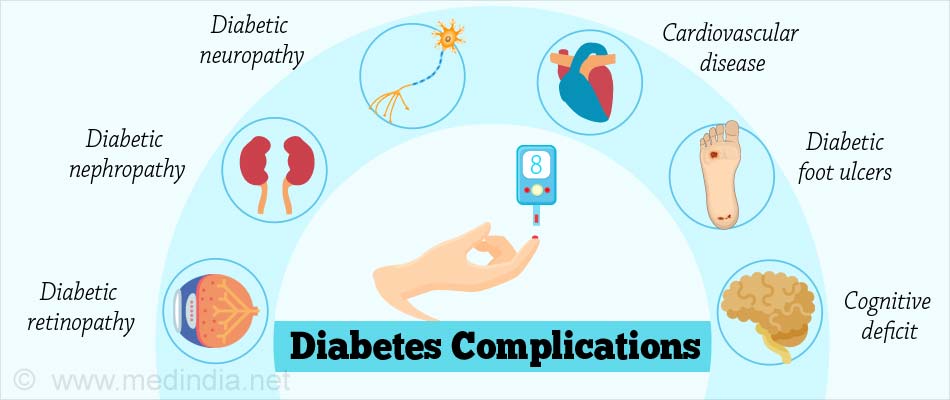
The main complications of long-standing and uncontrolled diabetes include the following
Diabetic retinopathy: Damage of blood vessels in the retina of the eye resulting in loss of vision.
Diabetic nephropathy: Damage to the kidneys leading to tissue scarring, protein loss, chronic kidney disease, sometimes requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Diabetic neuropathy: Damage to the nerves of the body is the most common complication of diabetes and includes symptoms such as tingling, numbness, pain, and changed pain sensation, which can damage the skin. Diabetic foot ulcers may occur which are difficult to treat and sometimes requires amputation.
Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes doubles the risk of cardiovascular diseases and about 75% of deaths in diabetics are due to coronary artery disease. It also causes stroke and peripheral artery disease.
Cognitive deficit: Diabetic individuals have a 1.2-1.5 fold higher rate of decline in cognitive function.
How to Manage and Treat Diabetes?
Early diabetes may be treated with modifications in diet, lifestyle and regular exercise. If these measures fail, then medications may become necessary. A diabetic individual should follow certain guidelines, which will help in managing the disorder and preventing complications. These are called Diabetes Essentials or 'Must Know Facts' for a Person with Diabetes. Diabetes is a disease, which if diagnosed on time, can be managed easily by regular check-ups, taking medications as prescribed, and making lifestyle changes.
1. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels:
People suffering from DM should go for regular blood glucose level measurements or check their sugar levels at home by means of a glucometer. American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines encourage self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) or home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) by glucometer due to the following reasons:
- Regular blood glucose testing allows the diabetics to take care of themselves without visiting doctors and labs regularly.
- Helps the patient and the doctors to see if the treatment program is working and also helps to plan their meals, activities, medications, and exercise regimes.
- Regular testing allows for a quick response to high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) or low blood glucose (hypoglycemia).
Currently, a lot of companies and research groups are working on non-invasive devices such as Glucotrack, Glucosense and GlucoWise that can determine blood glucose levels in a fast and painless manner.
Getting an HbA1c blood test done which measures how effective blood glucose control has been over previous three months, helps the healthcare team to decide the treatment.
2. Have your blood pressure measured regularly:
About 25% of people with Type 1 diabetes and 80% of people with Type 2 diabetes have high blood pressure. If you are diabetic, try to keep your blood pressure well controlled as high blood pressure increases the risk of developing heart diseases, stroke and some other complications.
- Measure your blood pressure regularly.
- Take two or three readings every time you measure to make sure your results are accurate.
- Observe the effect of change in lifestyle on blood pressure.
- Sometimes, medication is necessary to lower the blood pressure.

3. Have your blood fats (lipid profile) measured:
Most diabetics have high serum cholesterol levels, which contributes to coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis. Diabetes tends to lower high-density-lipoprotein (HDL) or good cholesterol levels but raises triglycerides and low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) or bad cholesterol levels leading to diabetic dyslipidemia.
- Get blood lipoprotein profile regularly done to check and manage your LDL, HDL and triglycerides levels.
- Lifestyle modifications and statins are commonly used to reduce high cholesterol levels.
4. Take insulin and medications regularly:
Insulin therapy is an important part of diabetes treatment. It maintains the blood sugar levels by regulating sugar in the bloodstream and storing excess glucose for energy. Insulin is generally given either by using injections or insulin pen injector or sometimes by insulin pumps.
Oral anti-diabetic medications for type 2 diabetes should also be taken as prescribed to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.

5. Get your weight checked regularly:
In people with type 2 diabetes, losing just 5% of your weight can be a big achievement.
Weight loss can:
- Lower blood sugar
- Reduce blood pressure
- Improve cholesterol levels
- Lighten the stress on your hips, knees, ankles and feet
- Give more energy and let you breathe easier
- Consult a nutritionist or diabetes educator to find out the healthy ways of reducing the weight that you can stick with for a lifetime.
6. Have a healthy diet:
Diabetes is a disorder that requires life-long diet management and control.
- Eat small and frequent meals with some healthy snacks in between the meals.
- Have snacks rich in protein, fiber, and whole grains, but low in fat and not exceeding 100-150 calories.
- According to ADA guidelines, diabetics should eat foods low on the glycemic index such as a vegetable sandwich, biscuits, nuts and seeds like flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, almonds and walnuts, buttermilk, skimmed milk, low calorie popcorn, sprouts or fruit (but should avoid banana, sapodilla (chikoo) or mango).
- Always carry some snacks especially when going out as, if a meal is missed, it can lead to a hypoglycemic attack. Since short-acting insulin peaks after 2-2.5 hours of injection, it is important to eat a healthy snack at that time.

7. Have your kidney function monitored regularly:
Diabetics can develop kidney dysfunction or nephropathy. It is essential that renal function tests such as blood urea, serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate (EGFR) as well as urinary proteins are measured and monitored at least once a year. In the initial stages of kidney dysfunction, there are no symptoms and urinary protein may be the first sign of kidney disease. Since early kidney disease can be successfully treated, it is important to undergo renal function tests to identify the problem early.
8. Keep yourself active:
Physical activity, along with healthy eating and proper medication helps to manage diabetes. Yoga and meditation play an important role in the control and management of DM.
Various benefits have been observed following yoga such as:
- Significant reduction in both fasting and postprandial blood glucose
- Good glycemic status for long periods of time
- Lowering of drug requirement
- Reduced complications like infection and ketosis
- Decrease in free fatty acids
- Increase in lean body mass and decrease in body fat percentage

9. Always carry a glucose source when going outside:
This is a fast-acting carbohydrate that helps in raising the blood glucose level during hypoglycemia. This can be in the form of –
- 3 tsp (15 g) of glucose
- 3 tsp (15 g) sugar
- 4 glucose tablets
- 1 tube of glucose gel
- Regular soft drink (not low-calorie or reduced sugar)
- Milk with sugar
- ½ cup of fruit juice
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 1 tablespoon of corn syrup
- 2 tablespoons of raisins
All diabetic individuals are advised to always carry a quick glucose source to prevent hypoglycemia, which if not treated, can be dangerous to the brain tissue.
10. Keep a stock of Glucagon Injections:
In conditions of severe hypoglycemia,where treatment by mouth has not been successful in raising the blood glucose levels, glucagon should be injected.
- Glucagon is a hormone that signals the liver to release glucose into the blood.
- Glucagon comes as a kit, which has to be diluted according to the manufacturer’s instructions before injecting and when injected, it takes about 10-15 minutes to raise blood glucose levels.
11. Get your eyes screened for signs of retinopathy every year:
People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can lead to sight loss if it's not treated. Consult your optician every two years for a regular eye test.
12. Regular examination of feet:
Diabetic people with neuropathy are susceptible to injury caused by their footwear like foot ulcerations and toe deformities. Tips for keeping healthy feet are:
- Get the skin, circulation and nerve supply of your feet checked regularly.
- Consult diabetic foot specialists and certified pedorthists to get custom made footwear.
- Avoid shoes that are too loose or too tight and those with pointed toes.
- Do not wear shoes with very flat soles or high heels as they do not allow even distribution of foot pressure.
- Wear leather or canvas shoes to allow proper circulation of air.
- Footwear should have good ankle support and soft insoles.
- Wear shoes with laces, Velcro or buckles, as these make it easier to adjust the shoe.
13. Get support if you are a smoker:
Quit smoking if you have diabetes as smoking increases the risks of developing complications of diabetes and it may affect blood glucose levels and increase insulin resistance.

14. Keep a diabetes identification card with you all the times:
All the diabetic individuals should always carry a diabetes identification card that has information regarding the person’s name and address, a contact number in case of emergency, the doctor's name and phone number, and the insulin dosage. This can help in saving a diabetic person's life in an emergency with timely measures and also help the medical professionals in providing the right treatment.
15. Maintain a log book:
It is difficult to remember details about multiple blood sugar values, the type of diet, medication, exercise pattern and the dose of insulin; however, entering all this information in a log-book makes it easy for the healthcare team to check the degree of control and decide the treatment accordingly.
It contains blood sugar levels at various times on different days and takes into consideration different variables such as:
- The level of stress
- Type and duration of exercise
- Amount of carbohydrate or sugar consumed
- Type and dose of medications
16. If you are diabetic and planning to have a baby:
If you are diabetic and are planning to have a baby, then try to get your blood glucose levels close to the normal range before you get pregnant. High blood glucose levels can increase the chances of birth defects, such as heart, brain and spine defects and also increase the chances of miscarriage or a still baby.
Tips for a healthy pregnancy with diabetes:
- Change your meal plan to control the sugar levels
- Do routine physical activity
- Take medications regularly
- See specialist diabetes healthcare professionals to help you manage your diabetes
- Keep checking your blood pressure, kidney function and vision regularly

17. Emotional and psychological support:
As diabetes is a lifelong condition, it is important to discuss your issues and concerns with specialist healthcare professionals, so that they can support and advise you in the right way.