- Drug Hypersensitivity Syndrome - (http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/puarticles/dhs.htm)
- Drug Allergies - (http://www.worldallergy.org/professional/allergic_diseases_center/drugallergy/)
- Guideline for the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4479479/)
- Drug Allergy Overview - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/drug-allergy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371835)
- Immunology - Chapter Seventeen - (http://www.microbiologybook.org/ghaffar/hyper00.htm)
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Types and Treatment Options - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2003/1101/p1781.html)
What is Drug Hypersensitivity?
Drug hypersensitivity reactions are drug reactions which are unpredictable. They result from an interaction between a drug substance and the immune system of a hypersensitive person. Hypersensitivity reactions refer to symptoms which would normally be tolerated by non-hypersensitive persons.
These could be immediate reactions, which occur within one to six hours of consuming the medicament or could be delayed reactions, which occur after several days. At times, they can affect several organs of the body.
The exact mechanism is unknown, but reports indicate the effects could be due to the direct toxic effect of the drug, within a few hours of administration of the drug or due to allergic reactions involving the immune system. The latter occurs when the immune system incorrectly identifies the drug substance as a harmful substance and in response, develops an antibody to that specific drug.
What are some of the Drugs that Cause Hypersensitivity?
Some of the most common drugs which cause hypersensitivity reactions are:
- Allopurinol
- Penicillins and Cephalosporins
- Olanzapine
- Isoniazid
- Trimethoprim
- Dapsone
- Atenolol
- Sulphonamides
- Anticonvulsants like carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin
- Antipsychotic tranquilizers
- Anti-thyroid drugs

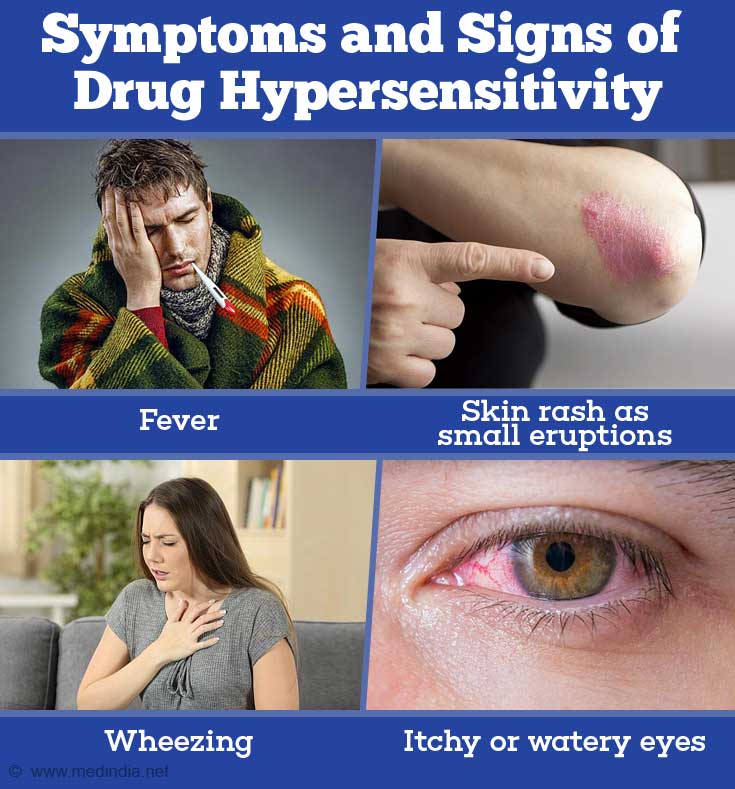
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Drug Hypersensitivity?
The symptoms could include:
- Fever
- Skin rash as small eruptions
- Wheezing
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes
- Inflammation of internal organs
- Mild to life-threatening anaphylactic reactions
Anaphylaxis is a rare and life-threatening drug reaction, symptoms of which could include:
- Trouble in breathing due to constriction of airways
- Drop in blood pressure
- Abdominal cramps
- Loss of consciousness
Other less common symptoms could include:
- Serum sickness - which would lead to fever, rash, joint pain, and nausea
- Drug-induced anemia - causing shortness of breath, fatigue and irregular heartbeats
- Inflammation of the kidneys (nephritis) - with symptoms like blood in urine, fever, and confusion
What are the Different Types of Drug Hypersensitivity?
Drug sensitivities are broadly classified as:
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR):
1. Type-A reactions - ADRs of the type-A are predictable pharmacological reactions to a drug.
2. Type-B reactions - The other ADRs, which are unpredictable and that vary from patient to patient are known as type-B reactions or hypersensitivity reactions.Type B reactions can be further classified into two types:
- Immunological reactions - The hypersensitivity in these cases is due to an immunological reaction. These could be either immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated, which are immediate reactions or non-IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, which are usually delayed in response
- Non-immunological drug hypersensitivity reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions can also be divided into four types of reactions, depending upon the mechanism involved and the time taken for the reaction.
- Type I: This is also known as an immediate or anaphylactic reaction, which is usually observed within 15-30 minutes of exposure to the drug. This type is IgE mediated, and the reactions could include skin, nasopharynx, eyes, gastrointestinal tract or bronchopulmonary tissues.
- Type II: This is also known as cytotoxic hypersensitivity; the antigens are endogenous chemicals, known as haptens. These are IgM or IgG mediated. Examples include thrombocytopenia and drug-induced hemolytic anemia.
- Type III: These are also known as immune complex hypersensitivity reactions, which are usually IgG mediated. The reaction could be general, e.g., serum sickness or could involve individual organs like skin, lungs, joints, and kidney.
- Type IV: This is also known as cell-mediated or delayed type hypersensitivity reactions. An example is tuberculin reaction (Mantoux reaction), which peaks after 48 hours after injection of the antigen, tuberculin.
What is the Mechanism of Hypersensitivity Reactions?
Hypersensitivity reactions could be IgE (immunoglobulin) mediated or non-IgE mediated.
IgE- Mediated reactions-occur immediately
The drug allergens bind to IgE antibodies in mast cells and basophils, leading to the formation of new mediators.
Examples of these reactions include urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylaxis.
Non-IgE Mediated reactions- delayed reactions
The drug allergen can cause
- Cell-based cytotoxic or cytolytic reactions - examples of these reactions include immune hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia
- Drug immune complex reactions - example serum sickness and drug-induced lupus
- T-cell- mediated reactions
How do you Diagnose Drug Hypersensitivity?
It is essential to identify the trigger causing the reaction and the pathological mechanism to understand the severity of symptoms to be expected in the patient and to suggest the risks to the patient along with treatment options.
The diagnostic tests would depend on the patient history, type of symptom, and the time lapsed after the reaction. The tests must be performed within four weeks to six months of the occurrence of the reaction. The diagnostic test would also depend on whether the initial reaction was IgE or non-IgE mediated.
The various methods for diagnosing drug hypersensitivities are:
Diagnostic allergy tests
The diagnostic allergy tests are useful in screening allergenic or non-allergic hypersensitivity reactions and not the toxic or pharmacological ADRs.
The diagnostic investigations must be performed by a professional allergist at a special allergy center.
The in vitro tests could include:
- Measurement of mediators like histamine, tryptase or leukotrienes in peripheral blood, urine, nasal or bronchial secretions
- Allergen-specific IgE levels measured usually using radioimmune assay methods
- ELISA test (CAST-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay): this is an in-vitro allergy provocation test
The in vivo tests could include:
- Skin tests to diagnose IgE-mediated allergy by evaluating the sensitization. However, they are not suitable for all types of patients. Some test substances themselves can cause reactions in healthy individuals. In rare cases, the skin testing can cause systemic life-threatening reactions.
- Patch tests to diagnose delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
- Drug provocation (challenge) tests (DPTs) that involve reproducing the symptoms of hypersensitivity in the patient using the suspected drug. This test should be done under strict supervision of allergy experts.
At times, the skin or diagnostic tests are negative and give false indications. It is important to understand that the diagnostic tests are evaluated for their indications and contraindications and performed only under medical supervision.
After the assessment, the data is documented as a ready reckoner for the patient, to identify the drug which must be avoided and suggest the use of alternative drugs, where possible.

How do you Treat Drug Hypersensitivity?
Treatment involves eliminating or withdrawing the use of the trigger drug and careful monitoring of the patient.
For treating the IgE-mediated reactions, the following actions can be taken on case basis:
- Antihistamines can be administered for non-serious or mild cutaneous reactions
- Steroids like prednisone are usually prescribed in severe cases of hypersensitivity involving dermatitis, hepatitis or pneumonitis
- For serious reactions like anaphylaxis emergency action is required to maintain the circulation and breathing; drugs like epinephrine or promethazine are prescribed if needed
- Other treatment options could include administering intravenous immunoglobulins and/or immunomodulatory drugs such as cyclosporin, rituximab, and cyclophosphamide
The non-IgE-mediated reactions can be managed by:
- Use of antihistamines for mild reactions
- Tapered dose therapy of corticosteroids
- Eye care, skin care, respiratory care, proper nutrition along with an intravenous dose of immunoglobulin

What are the Risk Factors for Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions?
Drug hypersensitivity reactions are unpredictable. However, some factors must be assessed to predict the likelihood of such reactions.
Some of the risk factors include:
Drug factors:
- Nature of drug
- Degree of exposure
- Route of administration
- Cross-sensitization
Host factors:
- Age and sex
- Genetic factors
- Concurrent medical illness (e.g., human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), asthma)
- Previous drug reaction
How Does One Prevent Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions?
- The patient must avoid consuming the causative agent. One must be careful when consuming anticonvulsants as almost all types of anticonvulsants cause drug hypersensitivity reactions
- Genetic factors could play an important role. Hence, one must be aware of any drug hypersensitivity reactions in a family
- The patient must wear a medical alert bracelet to indicate the sensitizing drugs







