- University Of Nebraska–Lincoln - UNL Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources - (https://food.unl.edu/escherichinia-coli-o157h7-e-coli)
- US National Library of Medicines- E Coli Infections - (https://medlineplus.gov/ecoliinfections.html)
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention- Infectious Diseases Related to Travel - (https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2018/infectious-diseases-related-to-travel/escherichia-coli-diarrheagenic)
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention-E coli - (https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/general/index.html)
What is E. coli Infection?
E. coli (Escherichia coli) is a type of gram negative bacteria that normally lives in the gastrointestinal tract of people and animals and most strains of this bacteria are harmless. However, some types can cause illness in humans, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever and vomiting if you eat or drink foods containing infected strains of the bacteria.
Though E. coli is mostly associated with diarrhea, you can also get urinary tract infections, cholecystitis, bacteremia, meningitis, pneumonia, breathing problems and other illnesses. Around 80 percent of urinary tract infections are caused by E coli. Infected E coli bacteria can be found in water, food, soil or on surfaces that have been contaminated with animal or human feces.
Some kinds of E. coli cause disease by making a toxin called Shiga toxin. These are called “Shiga toxin-producing” E. coli or STEC and cause bloody diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever and can sometimes cause serious diseases such as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP).
What are the Causes of E. coli Infection?
E Coli bacteria are passed in the feces of humans and other animals. You become infected through fecal oral route when you swallow E. coli bacteria via:
- Water: This can be due to contaminated municipal water supplies or public water spaces such as wells lakes, hot tubs, Jacuzzis, water park fountains, hot tubs and swimming pools. People should be careful when drinking water, using ice or eating vegetables washed with water which could be contaminated.
- Unhygienic practices: The bacteria can be passed to you if you do not wash hands after using the bathroom or changing diapers and then eating food or preparing food for others with the infected hands.
- Processed meat: An undercooked hamburger or ground meat that carries E. coli is a frequent source of infection. When meat is processed, sometimes bacteria from the animal gut can make their way into the meat. This happens more with ground meat because it comes from more than one animal.
- Unpasteurized milk: E. coli can get into the milk from the cow’s udder or from the milking equipment.
- Vegetables and fruit: This happens when manure from animals mixes with the supply of water and contaminates the vegetables, especially spinach, alfalfa sprouts and lettuce. You can also contaminate food if you allow a knife or cutting board that has touched infected, uncooked meat to come into contact with raw food such as salad.
- Other foods and beverages: You might also get E. coli from unpasteurized fruit juices, cheese and yogurt made from raw milk.
- Contact with farm animals or pets.

How do you Diagnose E. coli Infection?
To diagnose E. coli infection, a sample of your stool is send to a laboratory to test for the presence of E. coli bacteria. The bacteria may be cultured to confirm the diagnosis and identify specific toxins, such as those produced by E. coli O157:H7. A blood test may also be performed to detect antibodies that your body has made against the bacteria.
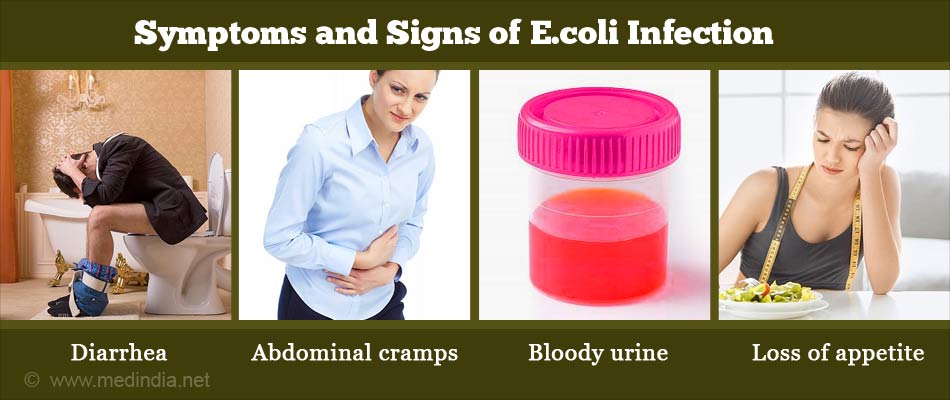
What are the Symptoms and Signs of E. coli Infection?
Symptoms and signs of E. coli infection typically begin two to four days after exposure to the bacteria and include:
- Diarrhea, which may range from mild to severe and bloody
- Fever around 100 F to 101 F
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloody urine
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Dehydration
How to Treat E. coli Infection?
Most E. coli infections are self-limiting meaning, the condition would run its course and subside without medical treatment. Sometimes antibiotics such as Ciprofloxacin and Bactrim may be used in severe cases to shorten the duration and intensity of infection. However, if Shiga toxin producing E. coli is suspected, antibiotics should be avoided as they may worsen your symptoms by increasing the production of Shiga toxin.
For patients with profuse diarrhea or vomiting, it is important to rest and get plenty of fluids to replace what the body is losing and preventing dehydration. You should consume low fiber foods such as rice, toast, crackers. Avoid dairy foods and food high in fat as they can make your symptoms worse.
What are the Risk Factors of E. coli Infection?
Young children and elderly have a higher risk of developing serious illness and complications. People with a weakened immune system such as those with HIV, undergoing chemotherapy or taking immunosuppressive medications are more prone to complications. Patients who have a lower amount of stomach acid, either due to medicines or due to stomach resection and other gastric surgeries also have a greater risk of infection.
How to Prevent E. coli Infection?
At present there is no vaccine or medication which can protect you from E. coli infection.
Some tips to prevent infection with E. coli include:
- Washing hands thoroughly with warm water and soap regularly, especially after using the toilet, changing diapers, before and after preparing foods, before eating and after touching animals. Also wash your hands more frequently if someone in your household is sick. Children should be supervised when washing their hands.
- Don’t drink untreated water from lakes, rivers, streams, ponds, or shallow wells.
- Cooking meat properly. Ground beef and meat should be cooked to a temperature of at least 160°F.
- Drinking pasteurized milk and fruit juices.
- Washing vegetables thoroughly, especially green leafy vegetables and peeling fruits and vegetables before eating them.
- Storing meat and non-meat foods separately. Also use separate cutting boards for non-vegetarian and vegetarian foods.
- Do not swallow water when swimming or playing in lakes, ponds, streams, swimming pools and kid’s pools.
- Thoroughly wash hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils with warm, soapy water after they touch raw meat to prevent cross contamination.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces immediately after a vomiting or diarrheal incident.