- Endocrinology- (https://www.ucsfhealth.org/conditions/endocrinology/)
What is a Hormonal Imbalance?
You probably don’t realize your fatigue, disturbed sleep cycle, migraine or your sudden chills can be symptoms of hormonal imbalance. To understand the connection, you need to get a clear idea of what hormones are, the different types of hormones and how they help to keep the body systems functioning efficiently.
Hormones are chemicals secreted by the endocrine glands and regulate almost all the important functions of the body.
Endocrine glands are glands (organs that secrete chemicals) of the endocrine system that release their products (hormones), directly into the blood rather than through a duct. They are therefore also referred to as ductless glands in contrast to exocrine glands like the salivary glands, sweat glands and the prostate gland for instance, which release their secretions into ducts that carry them to the site of action.
Hormones are critical to life function. Without hormones, we really cannot survive since they control most aspects of all our bodily functions. For example, without hormones a woman cannot get pregnant, a man cannot impregnate a woman, a child cannot grow and attain adolescence (puberty) or reach adulthood. Without hormones, we cannot sleep, we cannot metabolize the food we eat, we cannot appropriately fight infection or react to stress. The list is endless.
Any alteration in the level of any of these hormones resulting in either too much or too little of these chemical substances can cause serious disruption in the various metabolic functions essential for optimal health. This imbalance can manifest in several ways depending on the gland involved and the type of metabolic disturbances.
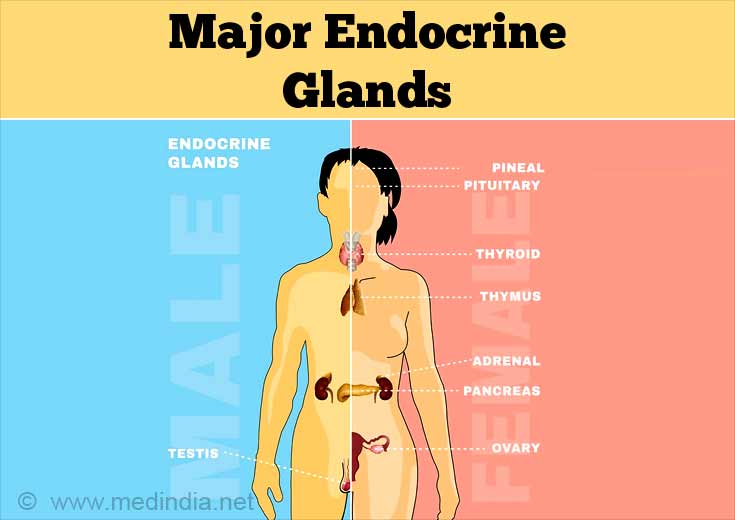
The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary, pancreas, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland ovaries, testes and adrenal glands.
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions
| Endocrine gland | Hormone secreted/Functions |
| Pituitary gland(master gland that controls the other glands) | Oxytocin, Antidiuretic hormone, Growth hormone, Prolactin, Thyroid stimulating hormone, Adrenocorticotropic hormone, Luteinizing hormone, Follicle stimulating hormone |
| Pineal gland (brain) | Melatonin (concerned with diurnal rhythm) – sleep and wake cycle |
| Thyroid gland (neck) | Thyroid hormone (basal metabolism and activity) |
| Parathyroid gland (neck) | Parathormone (calcium metabolism) |
| Pancreas | Insulin (glucose utilization, conversion of excess glucose to fat) |
| Adrenal cortex (superior to the kidneys) | Aldosterone, cortisol (response to stress, anti-inflammatory effect, metabolism of carbohydrate, protein and fat), maintenance of salt and water balance |
| Ovary (female gonad) | Estrogen and progesterone (female sexual characteristics and reproduction) |
| Testes (male gonad) | Testosterone (androgen) (male sexual characteristics and reproduction) |
What are the Causes/Risk Factors of Hormonal Imbalance?
Several factors can result in hormonal imbalance. Majority of the causes include the following:
- Genetics – occurrence of specific gene alterations that increase the risk
Obesity – one of the main causes of hormonal imbalance - Tumors of endocrine glands or other organs that secrete hormones – due to the tumor your endocrine glands begin to malfunction
- Lack of exercise and sedentary lifestyle
- Stress – affects adrenal hormone secretion often with serious consequences
- Refined food products - Sugars, food colors and preservatives directly impact hormonal balance, including the major hormone insulin
- High levels of inflammation in body caused by poor diet and sedentary lifestyle
- Food allergies, lack of good probiotic bacteria
- Use of oral contraceptives – containing estrogen and progesterone combination
- Radiation and chemotherapy for cancers
- Autoimmunity – body produces antibodies that damage and destroy the endocrine gland, for example. autoimmune thyroiditis
- Inorganic animal products such as dairy products
- Toxins in daily use - cosmetics, skin creams, plastics, Teflon-type coatings, clothing dyes, cleaning products

What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance?
The symptoms of hormonal imbalance vary depending on the gland affected and may often be non-specific and develop gradually. Given below are some cardinal signs and symptoms that can occur in both men and women, only men, only women and children. The list is by no means exhaustive.
| Group | Clinical features |
| Both sexes |
|
| Women(ovarian insufficiency) |
|
| Men(hypogonadism) |
|
| Boys(at pubertal age) |
|
| Girls(pubertal age) |
|

How do you Diagnose Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormonal imbalance may not be easy to diagnose because the clinical features may be vague and non-specific, yet troublesome and disrupt one’s daily routine and function. If you have any of the clinical features described above, consult your family doctor or GP who may refer you to an endocrine specialist (endocrinologist) for further evaluation.
Situations where hormonal testing may be warranted
- Girl who fails to develop sexual characteristics (e.g. breast development, menses in girls)
- Boys who do not develop hair growth in body and face, absence of deepening of voice, lack of muscle mass, impaired growth of penis at adolescence
- Men and women with fertility issues
- Any of the aforementioned clinical features
The endocrinologist will take a detailed history and do a thorough physical examination and based on clinical suspicion may recommend certain tests
Blood tests
- Levels of most hormones can be detected in the blood. A blood test may be requested to check thyroid, estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol levels.
- Additional blood tests as appropriate such as blood sugar levels, serum electrolytes, serum calcium levels and autoantibodies (to rule out autoimmune disease) may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Ultrasound imaging
An ultrasound uses sound waves to image the various organs of the body. Diseases of the uterus, ovaries, testicles, thyroid, or pituitary gland can be diagnosed by ultrasound testing.
Pelvic examination
In women with infertility issues, an internal pelvic examination may be necessary to feel for any abnormal lumps or cystic lesions.
Additional imaging
CT (computerized tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be done as appropriate to give more detailed information about disease conditions of the endocrine gland.
Miscellaneous tests
Miscellaneous tests such as thyroid scan, sperm count in men with infertility, biopsy of any suspicious looking mass or area in the endocrine gland to rule out cancer or other pathology.
How do you Treat Hormonal Imbalance?
Treatment of hormonal imbalance depends on the cause.
| Condition | Possible Treatments |
| Thyroid overactivity (hyper) | Antithyroid medication, radioactive iodine, surgery if appropriate |
| Thyroid underactivity (hypo) | Thyroid hormone replacement |
| Diabetes mellitus | Diet and exercise, insulin, oral anti-diabetic agents |
| Adrenal cortexinsufficiency - aldosterone | Fludrocortisone acetate to maintain salt and water balance |
| Cortisol excess (Cushing syndrome) | Ketoconazole, aminoglutethimide and metyrapone, surgery, radiotherapy |
| Adrenal medulla growth and excess hormone production - pheochromocytoma | Surgery, radiotherapy |
| Parathormone excess | Surgery, medications such as Calcimimetics, hormone replacement, bisphosphonates |
| Menopausal symptoms | Estrogen therapy, vaginal estrogen, |
| Female infertility/PCOS | Oral contraceptive pills to regulate periods, anti-androgen therapy to reduce acne, excess facial hair |
| Male hypogonadism | Testosterone replacement as appropriate |
| Pituitary tumor with excess hormone | Surgery |
How do you Prevent Hormonal Imbalance?
As the adage goes, “prevention is better than cure”. Medical treatment of hormonal imbalances is associated with many side effects. The following measures may prevent or at least partly reduce the development of hormonal imbalance
- Eat a healthy anti-inflammatory diet. Include fresh, organic, unrefined food
- Replace carbohydrates in diet with healthy fats e.g. nuts, coconut oil, avocado, fresh salmon
- Avoid oils high in omega-6 fats e.g. sunflower oil, corn oil, peanut oil
- Exercise and walk regularly and maintain a healthy weight
- Reduce stress levels by practising breathing exercises, meditation and maintain healthy emotional balance
- Use cosmetics containing natural oils such as coconut oil, shea butter, castor oil; avoid body care products containing harmful chemicals such as DEA, parabens, propylene glycol and sodium lauryl sulfate
- Consider supplements that balance hormones such as evening primrose oil, vitamin D, probiotics, bone broth
- Avoid synthetic hormone supplements as they have several undesirable effects
- Get a good night’s sleep
- Spend time outdoors and with friends and family
- Adaptogen herbs are a special class of healing herbs that promote hormone balance, enhance immunity and protect the body from a wide variety of diseases and harmful effects of excess stress. These include holy basil (tulsi), aswagandha, rhodiola and medicinal mushrooms