- What is an inflammation? - (http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/arthritis-diet/foods-to-avoid-limit/food-ingredients-and-inflammation.php)
- 8 Food Ingredients That Can Cause Inflammation - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/pmh0072482/)
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body's attempt at self-protection from harmful stimuli, irritants, injury and pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and fungi. Inflammation is the process in which chemicals from the body's white blood cells are released into the blood or affected tissues to eliminate the offending agent. This natural defense process brings increased blood flow to the area, resulting in swelling, pain, redness, increased warmth and some immobility in the area. Inflammation is part of the body’s healing process.
The word inflammation is derived from the Latin word "inflammo", meaning "I set alight” or “I ignite".
Role of Inflammation in Autoimmune Diseases
Though inflammation is primarily the body’s self-defense mechanism to heal, it can also play a role in some chronic diseases when it becomes disordered. There are some diseases known as autoimmune diseases where the body’s immune system which normally protects the body, triggers an inflammatory response to its own healthy tissues mistaking them for harmful pathogens or irritants. This results in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, allergies, psoriatic arthritis, myasthenia gravis (disease in which the immune system attacks the nerves and muscles throughout the body), and multiple sclerosis (disease in which the immune system attacks the protective coating around the nerves).
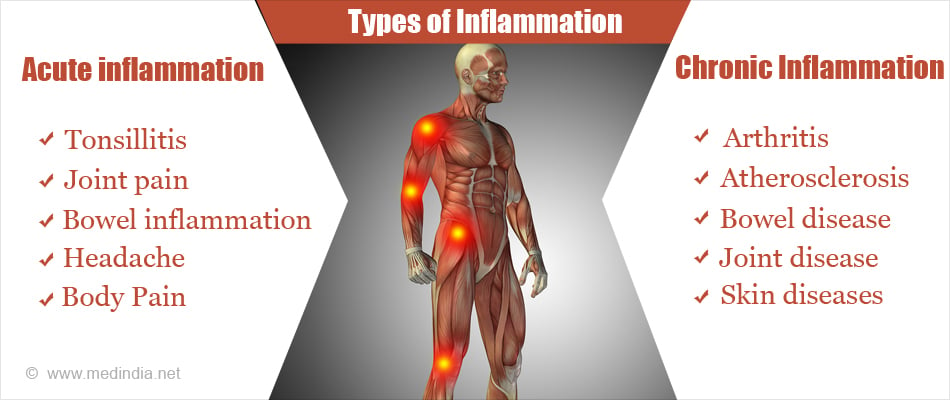
What are the Types of Inflammation?
There are two types of inflammation:
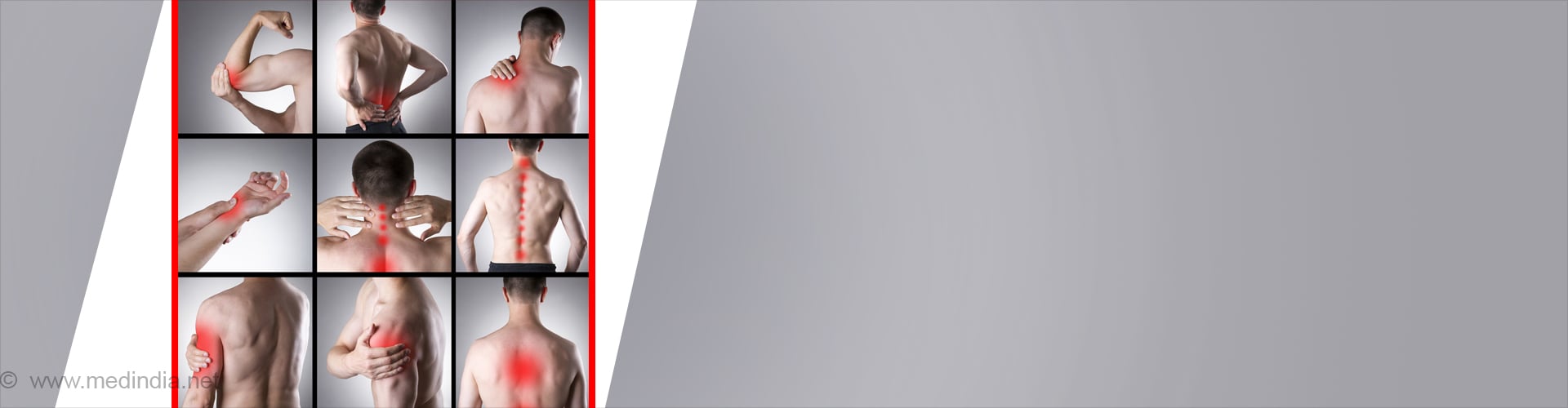
- Acute inflammation- This response is immediate, is short term and the effects subside after a few days; examples are sore throat, tonsillitis, flu, injury, joint pain, bowel inflammation and sprain. The onset is sudden and usually accompanied with all classic signs of inflammation (heat, pain, redness, swelling, reduced mobility). It is usually accompanied with fever, chills, headache, body pain, loss of energy and appetite.
- Chronic inflammation- The response takes longer to occur and is long term with prolonged low grade features of inflammation. This results in wear and tear conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma. It may persist for months, or even years. Persistent inflammation has been linked to a variety of ailments, including heart disease, joint disease, bowel disease, skin diseases, atherosclerosis and periodontitis. A large number of chronic inflammatory diseases are autoimmune diseases.
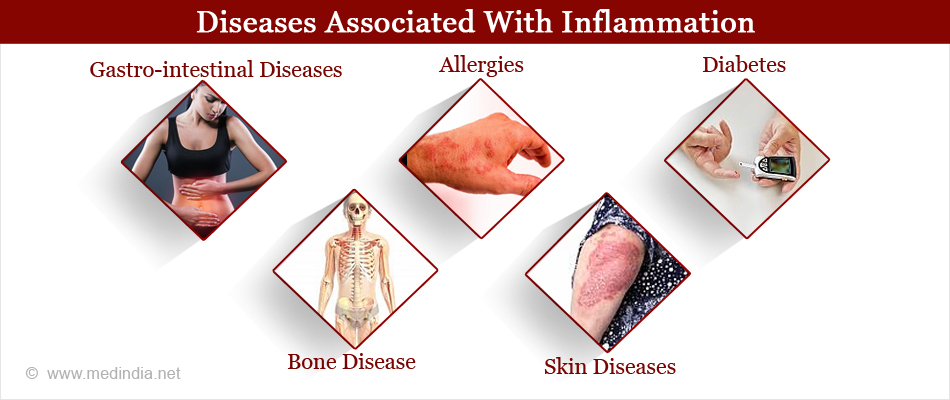
What Diseases are Associated with Inflammation?
Joint diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis (inflammation of the joint synovial membranes), gouty arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, bursitis, and ankylosing spondylitis (inflammation of the vertebrae, ligaments, and the sacroiliac joints).
Gastro-intestinal diseases: Celiac disease (allergy to gluten protein), and Crohn's disease (inflammation of the small intestine).
Allergies: Asthma and hay fever. Asthma involves inflammation of the airways. In hay fever the nose, ear and throat mucous membranes become inflamed. Life threatening inflammation or anaphylaxis that affects the whole body may occur due to an allergic reaction to drugs, or insect bites.
Heart disease: Chronic inflammation has been linked to diseases of heart and blood vessels. The buildup of fatty, cholesterol-rich plaque in blood vessels causes chemicals to be released from the white blood cells. These chemicals respond to the fatty plaque as foreign invaders. Inflamed blood vessels and fatty plaques can cause blockages and blood clots, which may lead to heart attacks.
Diabetes: This endocrine/metabolic disease may result when there is destruction of the endocrine cells of the pancreas (islets) due to autoimmune inflammation with a reduction or lack of insulin secretion from the islets resulting in high blood sugar levels (diabetes).
Lung and bronchial issues: Chronic inflammation in the lungs is found in asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Bone disease: Chronic inflammation is associated with increased bone loss and lack of new bone formation. Also, inflammation in the gut can decrease the absorption of nutrients that are important to bone health, like calcium and vitamin D.
Depression: Studies indicatethat people with depression had 30 percent more brain inflammation than those who were not depressed.
Cancer: The immune cells attack small cancer tumors in an inflammatory response. These immune cells infiltrate the tumor, but instead of killing it, the tumor uses the nutrients and oxygen that are part of the inflammatory response to grow.
Skin diseases: Acne, boils, lupus, psoriasis, and dermatitis.
What are the Causes of Inflammation?
- Pathogens - bacteria, viruses, fungi.
- Physical agents - External injuries, radiation
- Chemical agents – Allergies (eg nickel), exposure to harmful chemicals eg ammonia
- Obesity - can cause an inflammatory response within fat cells.
- Chronic stress - increases risk of inflammation. The stress hormone cortisol plays an important role in regulating the inflammatory response. It is found to increase the production of certain inflammatory white blood cells.
- Smoking increases white blood cell count and causes high levels of C-reactive protein. Air pollution also has a similar effect.
- Bacteria in the gut - About 70% of body’s immune cells reside in the intestines. The bacteria that are inside the gastrointestinal tract can either suppress or activate inflammation. Studies have identified specific microbes that seem to be related to developing or worsening rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and AIDS.
- Alcohol - in excess causes a fatty liver. The accumulation of fat can result in chronic liver inflammation, in turn leading to hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Oral contraceptives - Studies have found that 30% of pre-menopausal women taking the pill had high levels of C reactive protein.

What are the Symptoms of Inflammation?
The five cardinal signs of inflammation are:
- Dolor - Latin term for "pain"
- Calor - Latin term for "heat"
- Rubor - Latin term for "redness"
- Tumor - a Latin term for "swelling"
- Functio laesa - which in Latin means "injured or loss of function”
These acute inflammation signs are visible only when the affected area is on or very close to the skin. When inflammation occurs deep inside the body, only some of the signs may be detectable.
How do you Diagnose Inflammation?
A clinical diagnosis is made in the presence of physical cardinal signs such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. However for internal diseases where no external signs are visible, certain tests are advised. Blood tests show elevated white cells and increased level of inflammatory markers described below.
Complete Blood Count (CBC) - an increase in white blood cells is very common in acutely ill patients. It occurs in response to a wide variety of conditions, including viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection, cancer, hemorrhage, exposure to certain toxins, and medications.
- C-Reactive Protein (High Sensitivity) - This is also called an acute phase protein. The level of CRP increases when a person is suffering from diseases that cause inflammation.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - measures the rate at which the red blood cells separate from the plasma and fall to the bottom of a test tube. The rate is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). A high ESR is an indicator of inflammation in the body. This is a prognostic marker and is useful to assess response to treatment or monitor the patient over a period of time.
How do you Treat Inflammation?
Anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) are most commonly used to treat short term problems such as pain, swelling and fever. They include Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, and Acetaminophen.
- Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and swelling by reducing the activity of the immune system. These are synthetic drugs that are similar to a hormone cortisol produced in the body. They are used to treat a variety of inflammatory diseases and conditions.

How do you Manage Inflammation with Diet?
Anti-inflammatory diet - Follow an anti-inflammatory diet that recommends eating fresh fruits and vegetables, cold water fish (such as salmon, tuna, herring), healthy fats such as olive oil, and eating moderate portions of nuts and seeds.
Omega 3 fatty acids - Consumption of omega-3 fatty acids protects the body against damages caused by inflammation. Avocados, walnuts, and oils such as olive and canola along with other nuts are rich sources.
Berries and tart cherries have high anti-inflammatory properties. They are useful for those suffering from joint pain and arthritis.
Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa and bulgur wheat have been associated with decreased CRP levels. The fiber in whole grains helps with weight loss and feeding beneficial gut bacteria associated with lower levels of inflammation.
Spices such as ginger, turmeric, oregano, cayenne, and cloves possess anti-inflammatory compounds that inhibit the process of inflammation.
How do you Prevent Inflammation?
Several triggers are known to promote inflammation of the tissues in the body. Avoiding these would help to keep inflammatory responses in check. At the same time it is recommended that an anti-inflammatory diet such as the one described above is beneficial to one’s health.
- Reduce sugar intake.
- Eat less saturated fats such as those found in pizza, cheese, red meat, full fat dairy products, pasta, and deep fried foods. High levels are an indicator for heart disease and are known to trigger fat tissue inflammation.
- Avoid trans fats that are known triggers of systemic inflammation. These are found in most packaged items and fast foods as fried food, snacks, cookies, margarine, and donuts.
- Avoid excess consumption of omega 6 fatty acids found in soy, sunflower, vegetable, corn and peanut oils, mayonnaise and many salad dressings. Excess consumption of omega-6s can trigger the body to produce pro inflammatory chemicals.
- Limit refined carbohydrates or white flour products such as white bread, white rice, potatoes, french fries, and breakfast cereals made from refined carbohydrates. These foods raise blood sugar rapidly and fuel the production of advanced glycation end (AGE) products that stimulate inflammation.
- Avoid mono sodium glutamate (MSG) which is a flavor-enhancing food additive mostly found in Chinese food. This chemical can trigger chronic inflammation, and affect liver health.
- Follow a gluten free diet that excludes the protein gluten found in grains such as wheat, barley and rye. Gluten is known to aggravate arthritis and promote inflammation.
- Avoid aspartame, which is a non-nutritive, intense artificial sweetener that may trigger an inflammatory response.
- Avoid excess alcohol intake that weakens liver function and can cause inflammation. It is best eliminated or used in moderation.
- Consume good spices. Regular usage of ginger, black pepper, cinnamon, turmeric has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Breastfeeding babies for at least three months is known to protect against inflammation in children and young adults.