- What is Ovarian Cancer? - (http://ovarian.org/about-ovarian-cancer/what-is-ovarian-cancer)
- What Is Cancer? - (https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer)
- European Society for Medical Oncology - (http://www.esmo.org/guidelines/gynaecological-cancers/newly-diagnosed-and-relapsed-epithelial-ovarian-carcinoma)
- Diagnosis and Management of Ovarian Cancer - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2016/0601/p937.html)
- Ovarian Cancer - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567760/)
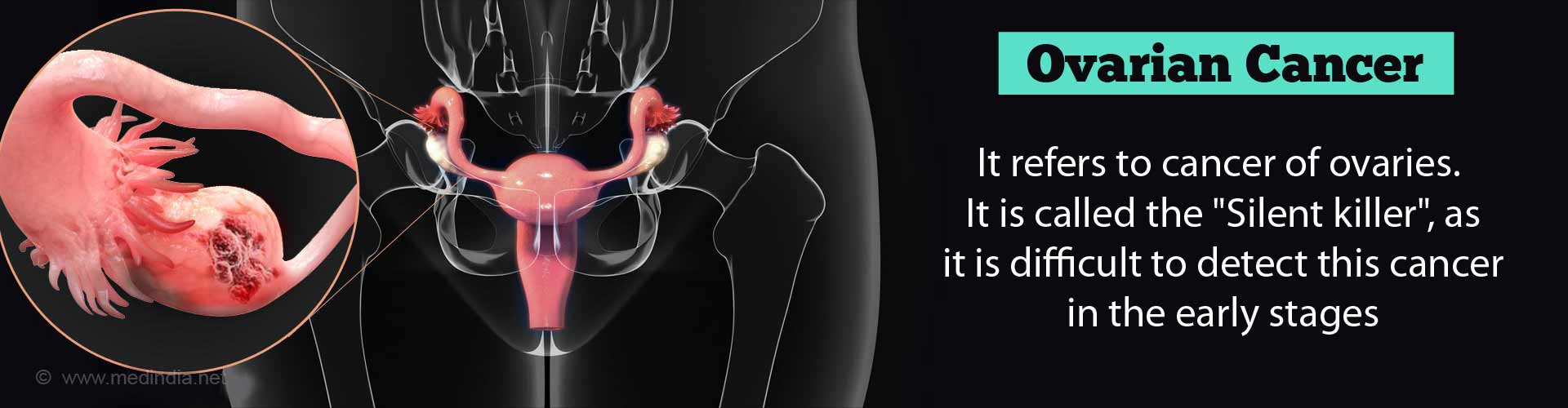
What is Ovarian Cancer?
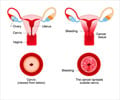
Ovarian cancer starts when cells inside, near or on the outer layer of the ovaries grow abnormally out of control.
Ovarian cancer is the 5th most common cancer in women and the most common cause of gynecologic cancer deaths. The lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer in women is less than 2%; this risk is higher in women with a strong family history of ovarian and breast cancer.
Cells are the basic units of all living organisms and form organs when they are grouped together. The term cancer indicates an uncontrollable division and growth of cells of a particular organ. The cancer cells thus produced are immature and non-functioning; they crowd out the normal functioning cells and cause disease of the body organ.
What are Ovaries and What is their Function?
The female reproductive system consists of internal organs such as the uterus, cervix, vagina, ovaries and fallopian tubes. The external structures include the breasts and labia.
The ovaries are two small almond shaped organs that lie on either side of the uterus in a depression called the ovarian fossa. They are connected to the uterus by fallopian tubes which are hollow muscular tubes.
The ovaries’ primary function is to store the ova (eggs) which a female child is born with; these ova reach maturity at puberty and every month one ovum is released during menstruation. The ova pass through the fallopian tubes into the uterus. The ovaries also produce estrogen and progesterone which are the female hormones. They regulate menstruation and development of sex organs.
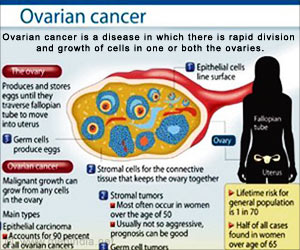
What are the Different Types of Ovarian Tumors?
Ovaries contain 3 different types of cells: the epithelial cells, the germ cells and the stromal cells. Tumors can develop in any of these cells.
- Epithelial tumors: Epithelial tumors originate from the epithelial cells; this forms the outermost layer of the ovary. Epithelial cancers account for 90% of all ovarian cancers.
- Germ cell tumors: These tumors develop from the cells that produce the eggs.
- Stromal cell tumors: Ovarian stromal cells are structural tissue cells that hold the ovary together and produce the female hormones. Tumors arising from these stromal cells are called stromal tumors.
Germ cell tumors and stromal tumors are quite rare.
Other related cancers are -
Primary peritoneal cancer is cancer that develops in cells from the peritoneum or abdominal lining. It is very similar in appearance, symptoms, and spread like the ovarian epithelial cancer as well as in treatment methods.
Fallopian tube cancer is cancer that starts in the fallopian tubes and is also similar to the ovarian epithelial cancer in terms of symptoms and treatment methods.
What are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer?
The exact cause of development of ovarian cancer is still unknown. Risk factors have been found for epithelial ovarian cancers which are mentioned below; these do not apply for the other types of ovarian cancer.
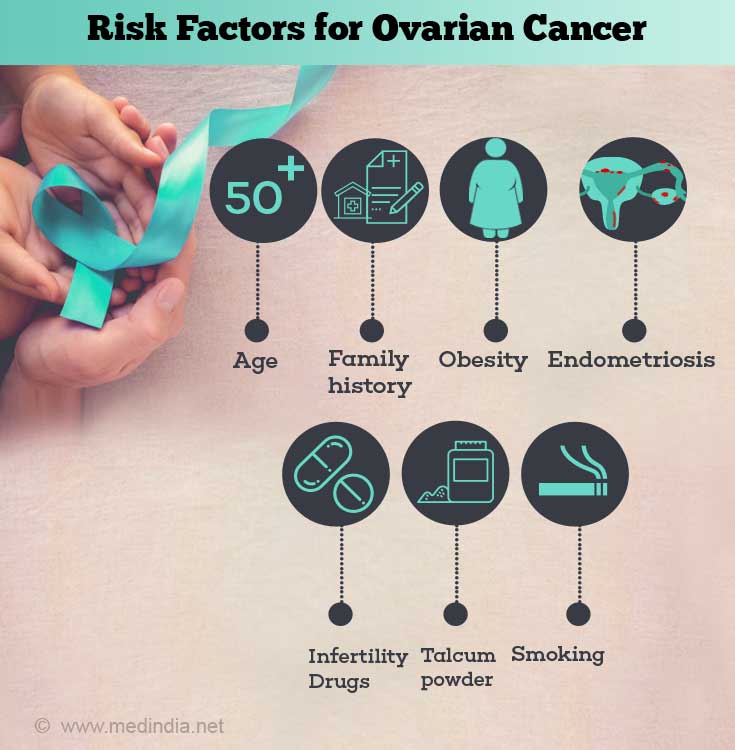
- Age: Ovarian cancer is mainly seen in post-menopausal women, usually over 50 years of age.
- Reproductive history: Women who have never been pregnant or who have had their first full term pregnancy after 35 years of age are at a higher risk.
- Obesity: Women who are obese, with a BMI of > 30 are at an increased risk.
- Endometriosis is a condition when tissue that usually lines the inside of the uterus grows outside it, like in the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- Drugs: Some studies have found that taking clomiphene citrate (a drug used in infertility treatment) for more than a year; taking male hormonal drugs (e.g. danazol) or post-menopausal women taking estrogen only hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) for more than 5 years increased risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Assisted reproductive technologies like in-vitro fertilization
- Family history of ovarian cancer: The risk of developing ovarian cancer increases if the woman’s first degree relative has had ovarian cancer. The risk increases with the number of relatives affected (both on the maternal and paternal side of family).
- Family cancer syndromes: There is a link between developing ovarian cancer and family history of other cancers such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer and other cancers. This is due to change (mutation) in the gene causing cancers; this gene is inherited among family members. Hereditary ovarian and breast cancer syndrome is caused by inherited mutations mainly in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes; these mutated genes are also responsible for fallopian tube, pancreatic and peritoneal cancers. The lifetime ovarian cancer risk with BRCA1 mutation is between 35-70% and with BRCA2 mutation is 10-30%.
- Talcum powder: Using talcum powder over the genital area or on sanitary napkins (maybe due to the asbestos that used to be added to talcum powder prior to 1970s) has been shown to cause a slightly increased risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Smoking has been related to increased risk of developing mucinous ovarian cancer.
Did You Know?
Aging in cells may boost ovarian cancer spread.Some of the ways to lower your risk factors are as follows:
- Women who have had their first full term pregnancy before 26 years of age or who had multiple full term pregnancies are at a lower risk to develop ovarian cancer.
- Breastfeeding helps to lower ovarian cancer risk as it prevents ovulation.
- Using birth control pills or depot injection also lowers ovarian cancer risk as it inhibits ovulation.
- Research has shown that women who had tubal ligation or a hysterectomy with conservation of ovaries are at a lower risk to develop ovarian cancer. Further studies are still needed to corroborate this fact.

What are the Different Stages of Ovarian Cancer?
Staging is the process of finding the extent of spread of cancer and is important as it will guide the diagnosis, treatment and the prognosis of the disease. Staging is done with the help of imaging and during surgery.
- Stage 1: The cancer is within the ovary/ovaries and/or the fallopian tube/tubes.
- Stage 2: The cancer is in one or both ovaries and/or fallopian tubes and has spread to other organs in the pelvis (uterus, urinary bladder, sigmoid colon or rectum).
- Stage 3: The cancer has spread beyond the pelvis to the lining of the abdomen or has spread to the lymph nodes in the back of the abdomen.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to distant organs like liver, spleen, lungs, brain or skin.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer usually causes symptoms when the cancer has spread beyond the ovaries, although in some patients even early stage cancer can cause symptoms. They include:
- Abdominal bloating
- Upper or lower abdominal pain
- Feeling full despite eating smaller amounts of food
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of weight
- Acid reflux
- Nausea, vomiting
- Urinary frequency or urgency
- Fatigue
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Menstrual changes
- Low back pain
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal swelling due to fluid
- Abdominal or pelvic mass (not fibroids)

How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
If any of the symptoms are severe and occur frequently (more than 12 times/month), and is a change from a woman’s normal self, ovarian cancer needs to be ruled out.
- Medical history: A detailed history of symptoms, risk factors and family history should be taken.
- Physical examination: A detailed physical examination of the abdomen and pelvis helps to identify any tumorous growths or fluid in the abdomen.
- Imaging studies: A transvaginal ultrasound and an ultrasound of the abdomen are performed to identify pelvic or abdominal masses. MRI or CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis is performed to identify the extent and spread of the disease. A CT scan of the chest and/or positron emission tomography (PET) scan is performed to check if the cancer has spread to chest and other parts of the body.
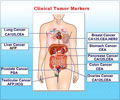
- Tumor markers: Tumor markers or biomarkers are proteins found in abundance in cancer cells when compared to healthy cells. CA 125 (Cancer Antigen 125) is a protein found in ovarian cancer cells and is measured by a blood test. Some germ cell tumors cause increased levels of tumor markers such as Alpha fetoprotein (AFP), Beta HCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin) and /or LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase). Some stromal cell cancers can increase the levels of estrogen, progesterone and a substance called inhibin.
- Blood tests include complete blood picture, liver function tests, kidney function tests and ESR.
- Laparoscopy: This is a procedure in which a doctor can look at the insides of the abdominal cavity. This is useful to confirm the diagnosis and the spread of the cancer.
- Colonoscopy: If the cancer has been found to spread to the large bowel, a colonoscopy is done to confirm the diagnosis and remove it.
- Tissue biopsy: A definitive diagnosis of cancer can be made by taking a small tissue sample from the tumor during surgery and studying it under the microscope. In rare cases (when the woman cannot have surgery due to ill health or in advanced cancer) the biopsy can be obtained during laparoscopy (or colonoscopy) and also from an ultrasound or CT scan guided percutaneous biopsy procedure. There are some concerns that cancer cells can spread through this type of tissue biopsy.
- Paracentesis: In patients with ascites, a small sample of fluid is aspirated through a needle attached to a syringe and studied for cancer cells.
- Genetic tests to identify inherited mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA 2 can be offered to women with a strong family history of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Color Doppler Ultrasound (USG): Doppler studies can help identify the blood flow in the ovarian masses coming from the numerous new tumor blood vessels.The sound waves from ultrasound are changed into different colors that indicate the speed and direction of blood flow in the vessel.
- Transvaginal Sonography (TVS): Type of ultrasound where ultrasound probe is inserted gently into the vagina to view for mass (tumor) in the internal organs like ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes. It is the most efficient screening procedure for ovarian cancer.
- Human epididymis protein 4 (HE4): This is a tumour marker protein that is expressed in almost one-third of ovarian cancers patients who lack another marker called CA 125 in their blood. It is helpful in estimating the disease progression and its recurrence.
Other serum tumour markers that can be used for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer are serum α-fetoprotein and quantitative beta-human chorionic gonadotropin for germ cell tumors.
How is Ovarian Cancer Treated?
Most of the ovarian tumors are benign tumors, which are non-cancerous and do not spread beyond the ovaries. These are usually treated by removing a part or the full ovary. Tumors that are cancerous are called malignant tumors and can spread beyond the ovaries to distant parts of the body. These are usually fatal if not treated appropriately.
There are various types of treatments; the choice of treatment depends on the type and staging of cancer.
Surgery: Surgery is the main treatment for majority of ovarian cancers. The affected ovary/ovaries along with the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and omentum are removed.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is treatment of cancer by using two or more drugs. These are given intravenously or orally. Chemotherapy is often given after surgery to destroy any remnant cancer cells, to shrink the tumor or to relieve the patient of their symptoms. Gemcitabine, capecitabine, melphalan and other similar drugs are usually used.
Targeted therapy: The metabolism of cancer cells is different from surrounding healthy cells. In targeted therapy, injected drugs attack only the cancer cells without destroying the healthy cells. Bevacizumab, olaparib, and rucaparib are commonly used.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy refers to destroying cancer cells by using high energy X-rays / particles. Radiotherapy is now not so commonly used and is usually given to women who are in advanced stages of cancer, who cannot undergo surgery, who have cancer recurrence after surgery or to relieve symptoms.
Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy is use of hormones or hormone blocking drugs to destroy cancer cells. Commonly used drugs are anastrozole, exemestane, tamoxifen and goserelin.
Newer therapies involving use of cytokines, chromatin remodeling proteins and immunomodulators are being tested as treatment options.
Once the treatment is completed, patients should see their doctor every 3 months; this is done to identify recurrence of ovarian cancer or development of a new cancer (breast cancer, colorectal cancer, or leukemia) early on. The patient is examined and investigations such as tumor markers and imaging studies are performed as necessary.
Prognosis and Recurrence
The prognosis of ovarian cancer directly depends on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis. The failure of early diagnostic strategies significantly results in poor outcomes.
The incidence of ovarian cancer is rising in women globally.

Top Ten Known Facts about Ovarian Cancer Incidence & Prognosis
- Almost 295,000 cases of ovarian cancer were diagnosed in 2018 and almost 185,000 deaths.
- This incidence is expected to reach 371,000 by 2035 (55%), with an increase in the death rate of 67% (254,000).
- The exact scientific mechanism behind this increasing prevalence of ovarian cancer among women remains unknown. However, the risk factors and lack of early diagnostic screening escalate the burden of this ovarian cancer.
- It is estimated that 75-80% of women with advanced-stage ovarian cancer have tumor progression or recurrence with a median survival rate of 40% - 50% at 10 years and 5-year survival rates up to 80% and 25% (in metastasis). Hence almost 750,000 women are residing with five years of an ovarian cancer diagnosis.
- Depending upon the stage of cancer, the survival rate for stage I is between 70% to 92%, and stage IV is less than 6%.
- The prognosis also depends upon the response to specific platinum-based Chemotherapy.
- Patients having recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer account for 3 years of median survival period and those with platinum resistance have just 1 year of survival period.
- Any incomplete treatment or surgical removal may increase the chances of cancer recurrence.
- Hence an effective treatment can be rendered to the patients if these cancers are diagnosed at an early stage – when confined only to the ovary.
- It is therefore advised that every woman should have a regular gynecologist visit in concern to the persistence of these symptoms.
Palliative Care in Ovarian Cancer
Palliative care is about providing quality of life to the women with advanced stage ovarian cancer.
- Patients with ovarian cancer develop various end-stage complications at the advanced stage of the disease (stage III to IV).
- Distressing symptoms like pain, nausea, vomiting, respiratory symptoms, urinary tract infection, kidney failure, swelling, cancer-related fatigue and neuropathy, hypercalcemia, and anxiety or depression are the mainstay for the management of palliative care.
- Spiritual and existential issues become central with no realistic hope of a cure. Hence psychological and social care is required both for the patient and their caretakers.
- Palliative care focuses on maximizing quality of life through aggressive management
Health Tips
- Eating a well-balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grain products and limiting red meat intake has been shown to prevent various types of cancers.
- Stopping smoking is beneficial for a healthy life.
- Exercise helps to improve physical and mental health.
- Practicing relaxation therapies or meditation helps to control stress and anxiety.