- What are the Late Effects of Polio / Post-Polio Syndrome? - (https://britishpolio.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/pdf/complementary%20therapies2.pdf)
- A guide for people with polio or Post Polio Syndrome (PPS) - (https://www.poliohealth.org.au/late-effects-of-polio/)
- What is post-polio syndrome? - (https://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/patient-caregiver-education/fact-sheets/post-polio-syndrome-fact-sheet)
What is Post-Polio Syndrome?
Post Polio Syndrome (PPS) is an illness of the nervous system that affects polio survivors 15 to 40 years after an early attack of the poliomyelitis virus. Around 25 to 40 percent of people who survive paralytic polio may experience gradual progressive weakening in muscles, fatigue, joint pain and a gradual decrease in the size of muscles.
Some people with PPS have only minor symptoms, while others develop more visible muscle weakness and atrophy (decrease in muscle size). PPS is rarely life-threatening, it usually progresses very slowly but the symptoms can significantly interfere with your ability to function independently. Respiratory muscle weakness, for instance, can result in trouble with normal breathing and also affect sleep. Weakness in swallowing muscles can result in aspiration of food and liquids into the lungs and lead to pneumonia.
Unlike polio, PPS is not contagious. This syndrome does not imply a progressive deterioration of health and the quality of life of the patient can be kept stable with help of treatment, good nutrition and weight control.
What are the Causes of Post-Polio Syndrome?
The exact causes of PPS are unknown. The main theory is that PPS is the result of the gradual deterioration of nerve cells or motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord that were damaged by the polio virus.
During acute polio infection the nerve cell is invaded by poliovirus and many of the motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord are destroyed. These motor neurons carry messages between your brain and muscles. Destruction of the infected nerve cells results in a lack of nerve supply to the muscles and can result in loss of muscular function, weakness or even paralysis.
To compensate for the loss of these motor neurons, the remaining neurons sprout new fibers, and connect with other muscle fibers. These new sprouts degenerate over time due to over exertion, resulting once again in muscle fibers that no longer contract and manifest as new weakness and loss of function.
These new connections may result in recovery of movement and more power in the affected limbs but it also pushes the nerve cell body to nourish the additional fibers. Over the years this results in the slow deterioration of the neurons which again leads to loss of muscle strength.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Post-Polio Syndrome?
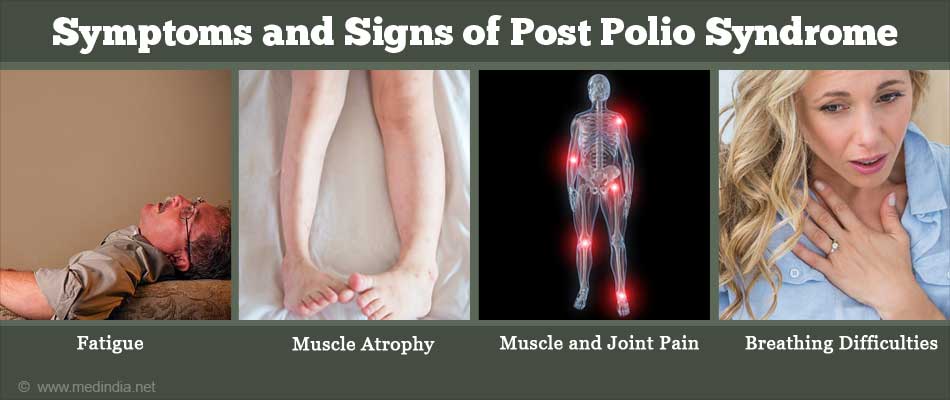
Common signs and symptoms of post-polio syndrome show up very slowly and include:
- Unaccustomed Fatigue. It may include muscle fatigue, general fatigue, and mental fatigue. Fatigue is the most common symptom of post polio syndrome.
- New Weakness in Muscles. Weakness can occur in muscles that were previously affected by a polio infection as well as in muscles that were not previously affected. There may also be associated shrinking of affected muscles, known as atrophy.
- Muscle and Joint Pain. Muscle pain is usually felt as a deep ache in the muscles or muscle cramps and spasms. The pain is often worse in the evening after the day#$#s activities. There may be soreness of joints, stiffness with a reduced range of movement.
- Difficulty in Movement. Many people with post polio syndrome will require a walking aid such as crutches, a stick or a wheelchair.
- Breathing Difficulties. In some people with post-polio syndrome, the breathing muscles become weak and may cause problems such as breathlessness, interrupted breathing while sleeping and increased risk of lung infections.
- Swallowing Problems. Weakness in the muscles used for chewing and swallowing may lead to choking, gagging, changes in your voice and speech such as low volume, hoarseness or a nasal sounding voice.
- Increased Sensitivity to Cold. Patients with PPS have a decreased ability to tolerate cold temperatures and may require additional layer of clothing to keep their body warm.
How do you Diagnose Post-Polio Syndrome?
Doctors diagnose PPS after taking a comprehensive medical history, physical examination and by excluding other disorders that could cause the symptoms. There are no special tests to diagnose PPS. Some tests may be done to rule out other conditions which mimic PPS.
The following criteria help to diagnose PPS:
- A history of paralytic polio in the past, followed by a long period of at least 15 years with no symptoms.
- Slow progressive and persistent new muscle weakness, decreased endurance with or without generalized fatigue, muscle atrophy, or muscle and joint pain.
- Symptoms that have persisted for at least a year.
- X Rays of chest, spine or joints to rule out other possible causes such as arthritis, osteoporosis and alignment disorders.
- Electromyography (EMG) to measure the electrical activity in the muscles and nerves. This determines whether polio has damaged your nerves and muscles.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) of the spinal cord.
- Muscle Biopsy or a Spinal Fluid Analysis can be used to exclude other muscular and neurological conditions having symptoms similar to PPS.
- Lung Function Tests to measure your lung capacity.
- Endoscopy and Esophageal Muscle Test to investigate swallowing problems.
How do you Treat Post-Polio Syndrome?
PPS is an irreversible condition and currently there are no effective drugs that can stop the deterioration or reverse the effects of the syndrome. Hence the emphasis is on effectively controlling the symptoms and learning how to stay active in spite of muscle weakness. However, a number of controlled studies have demonstrated that support therapies can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Non-Fatiguing exercises - interspersed with brief rest periods may improve muscle strength and reduce tiredness. Exercises that involve gentle stretching and slow movement are often recommended.
Try to Maintain a Healthy Weight. This will help lessen the strain on your joints and muscles.
Use of Assisting Devices - such as a cane, walking sticks, crutches, different types of braces or splints and customized shoes. These help to relieve weight on weak limbs and prevent falls.
Treat Depression - which is common in people who have post polio syndrome.
Preliminary studies indicate that intravenous immunoglobulin may reduce pain and increase quality of life in post polio survivors.
Acupuncture - has also been documented as an effective treatment for pain. Improvements in pain and fatigue have been frequently reported.
Chiropractic - Chiropractors use their hands to make gentle, specific adjustments to stiff joints and tight muscles, improve the efficiency of the nervous system, reduce pain, improve mobility and release the body#$#s natural healing ability.
Hydrotherapy - can have a soothing effect on the body, helping to reduce stress and tension, promote relaxation and manage pain.
Osteopaths - use gentle stretching and mobilizing techniques as well as manipulating joints, to help bring about the healing process.
Yoga, Pranayama, Tai chi, and Qi gong practice, promote flexibility, improve oxygenation and decrease general fatigue.
Pain Killers - may be used in moderate doses.
Drugs such as Amantadine (used to treat Parkinson#$#s disease), Pyridostigmine (used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis) or giving high doses of steroids to treat PPS are still in the trial stages and studies have not shown any positive results so far.

How do you Prevent Post-Polio Syndrome?
Currently there is no way to prevent the development of PPS or stop the further damage of surviving neurons. However, it is recommended that polio survivors maintain a well-balanced diet, exercise regularly, keep weight under control, get adequate sleep and avoid smoking and lead a better quality of life.
Polio can be prevented through immunization. Polio vaccine, given multiple times protects a child for life.







