- Sebaceous Cysts - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/sebaceous-cysts)
- Trichilemmal cyst - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/trichilemmal_cyst)
- Epidermoid cyst - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/epidermoid_cyst)
- Sebaceous cyst - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sebaceous_cyst)
- Eyelid lumps - (http://www.goodhopeeyeclinic.org.uk/lidlumps.htm)
What is Skin Cyst?
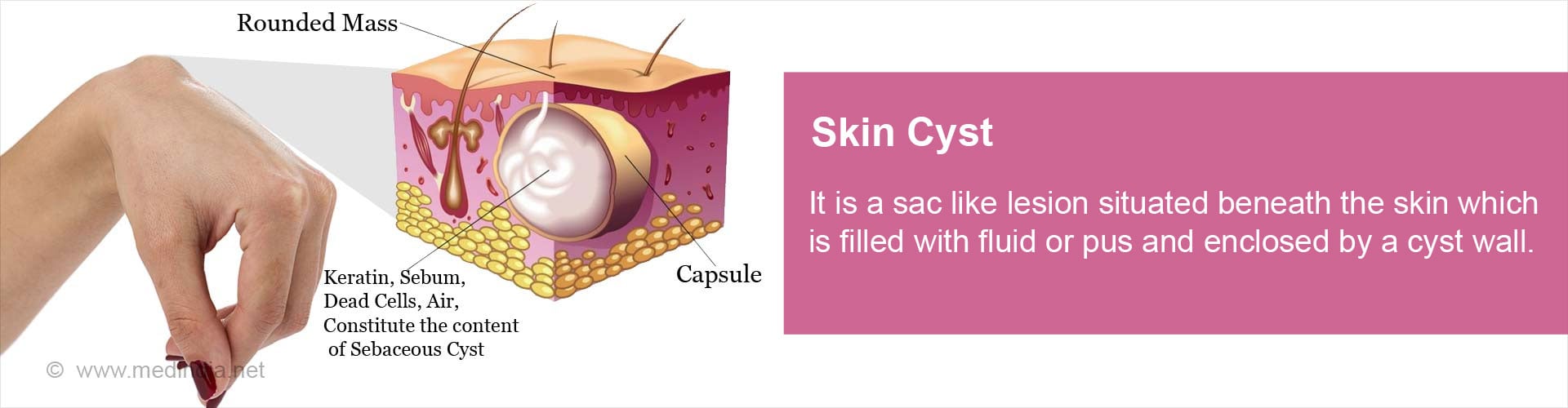
Skin cyst is a sac like lesion situated beneath the skin which is filled with fluid or pus and other secretions, and enclosed by a cyst wall.
Structure of Skin - In Brief
The skin is made up of 2 layers, an outer layer called the epidermis, and an inner dermis that makes up 95 percent of the skin. The epidermis is lined by flat cells (squamous epithelium) or keratinocytes arranged in five layers. The epidermal keratinocytes secrete a protein called keratin that gives the skin its distinctive resilience and texture. The epidermis and the dermis meet at the dermo-epidermal junction. The dermis consists of two layers, an outer papillary layer that contains blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics and a deeper reticular layer composed of coarse collagen fibers.
Both the epidermis and the dermis contain accessory skin structures namely the hair follicles, sweat glands and the sebaceous (oil producing) glands. These accessory structures are lined by keratinocytes in their ducts.
What are the Types of Skin Cysts?
The following are a few types of epidermoid cysts or skin cysts.
a. Sebaceous cyst: The sebaceous glands within the skin is the site of origin.
b. Pilar cyst: The sebaceous glands with hair follicle is the site of origin. They are common on the scalp. The cyst on the scalp and head are mostly pilar cysts. These may be multiple.
c. Meibomian Cyst: It is known as a chalazion. It is a cyst due to the involvement of the meibomian glands of the eyelid.
d. Acne Cyst: Acne can present with black heads, white heads, oily skin, pimples, cysts and scars. Acne can cause facial cysts although any part of the body can be involved.
What are the Risk Factors for Development of Skin Cysts?
Although any one can develop skin cysts, the following factors increase the chances of developing cysts
- Post-pubertal age
- Skin injury or irritation
- Certain rare genetic disorders
What are the Causes of Skin Cyst?
Skin cysts are also referred to as epidermoid cysts. They occur when there is an excess growth of epidermal cells (keratinocytes). The various reasons for this include:
- Occlusion of ducts of hair follicles and sebaceous glands in the skin (the most common cause)
- Penetrating injury that causes epidermal cells to move deeper into the dermis
- Trapping of epidermal cells (keratinocytes) along embryonal fusion lines
The cause and content of the skin cyst depends on the type of the cyst:
The epidermal cells multiply and form a sac like structure lined by flattened skin epithelium. These lining epidermal cells secrete keratin, into the center of the cyst. Other contents of the cyst depending on the cause include dead skin and hair, sebum, and infected cyst that may contain pus and bacteria.
- Pilo-sebaceous cysts form due to the blockage of the skin glands or the hair follicle swelling. Skin trauma and genetics also play a role in the sebaceous cyst formation. They affect the hairy areas of the body.
- Meibomian Cyst: Chronic inflammation and blockage of the meibomian gland of the eye lid cause the meibomian cyst.
- Acne cysts are common during puberty among both males and females when there is increased secretion of oily sebum from the sebaceous glands. Genetics, stress, infections, hygiene, food, hormones and environmental factors play a role in the occurrence of acne. Acne cyst is a large, painful and pus filled lesion which can happen due to clogging of the skin pores with dead skin, bacteria or oil deeper in the skin.
What are the Symptoms of Skin Cyst?
- The skin cyst is a lump beneath the skin. The skin cysts are usually benign, slow-growing and painless.
- The sebaceous cysts are usually beneath the skin and they can involve the skin of any body part except the palms and soles. They are usually keratin cysts. They have a central black punctum.
- The chalazion is an eyelid lump which is due to the result of an infection which blocks the meibomian gland of the eye that secretes an oily substance. It usually subsides in 2-4 months, if it does not subside then surgical removal is the option.
- In patients with severe acne, the nodulocystic lesions are present. These lesions can be red and painful. It will be usually associated with pimples and scars on the skin.
What are the Complications of Skin Cysts?
If untreated, epidermoid cysts can undergo certain complications including the following:
- Inflammation – the cyst becomes red, swollen and painful in the absence of infection
- Infection – Bacterial infection of the cyst results in pus formation, which may then have to be drained
- Rupture of the cyst
- Skin cancer – Rarely skin cysts are associated with skin cancer
How do you Diagnose Skin Cyst?
- Taking the history of the illness from the patient is important.
- General patient examination and examination of the lesion helps in making the diagnosis.
- Sometimes a biopsy may be required to rule out other major skin growths. Biopsy is a procedure where a small portion of the cyst is removed and examined under the microscope.
How do you Treat Skin Cyst?
- Small skin cysts which are small and painless can be left untreated.
- Sebaceous cyst treatment:
- Small sebaceous cysts can be treated with intralesional steroids.

- Large, infected or ruptured sebaceous cysts require a surgical excision.
- Meibomian cyst/ Chalazion: During the initial stage topical antibiotics and warm compress can help to resolve the chalazion. Intralesional steroid can be an option if it is resistant to initial treatment. If the cyst is firm and if it does not resolve, it requires a surgical removal.
- Cystic acne treatment: Oral contraceptive pills may be used to maintain hormonal balance. Topical and oral antibiotics and retinoids, intralesional steroids and photodynamic therapy are useful.
How do you Prevent Skin Cysts?
- To prevent the recurrence of the meibomian cyst, prevent the meibomian glands from blocking. Clean the eye lids with cotton and warm water. It is important to clean the scales (if present) from the edge of the lower eye lid with the moist cotton bud. Once the eye lid seems clean without any scales you may stop the procedure. A healthy and balanced diet including green leafy vegetables and omega 3 fatty acids is important.
- To prevent the cystic acne it is essential to eat a healthy diet rich in niacin, vitamin E, low glycemic index and fiber rich foods.
- Management of stress is essential; a good sleep and adequate exercise are equally important.
- Do not squeeze or irritate any skin cyst to prevent further complications because it can lead to the rupture and infection of the cyst.