- Testicle - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/testicle)
- Dohle GR, Elzanaty S, Casteren NJ. Testicular biopsy: clinical practice and interpretation. Asian J Androl. 2012 Jan; 14(1): 88–93. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.57
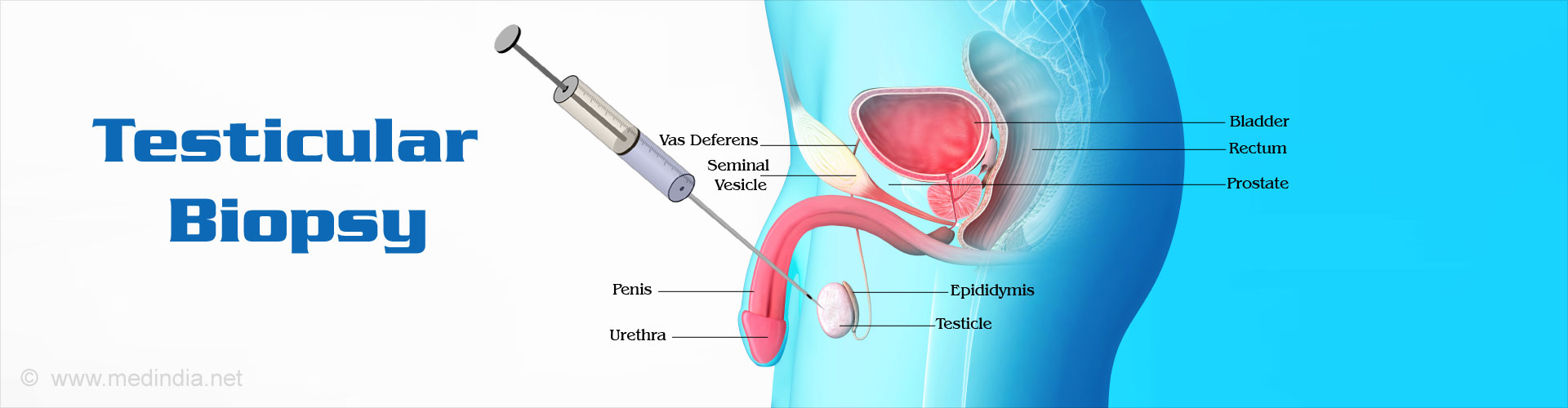
What is a Testicular Biopsy?
A testicular biopsy involves obtaining a bit of testicular tissue sample, which is then sent for microscopic examination to look for any evidence of disease or pathology in the testes.
Structure and Function of Testes
The testes (singular: testis) are a paired ovoid glandular organs situated within the scrotum between the upper thighs in males.
The major function of the testes is the production of the male hormone testosterone and sperms (spermatogenesis), making them key organs of the male reproductive system.
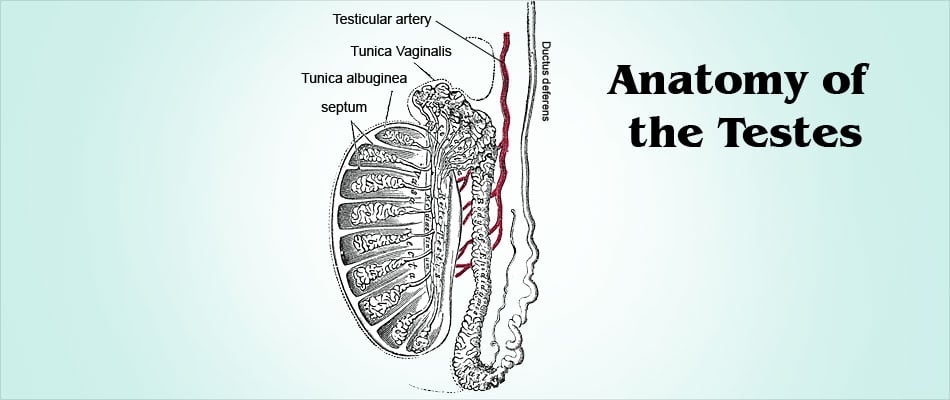
Each testis is approximately 2 inches long and 1 inch in diameter. The left testis is slightly lower than the right and both testes are covered by a tough fibrous capsule called the tunica albuginea. Both testes are also covered by a layer of peritoneum, the tunica vaginalis, which is an extension of the peritoneum of the abdominal cavity. The testes are richly supplied by blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics.
Since the testes are suspended within the scrotum by a tubular structure called the spermatic cord, they are liable to undergo twisting or torsion, with occlusion of blood supply, leading to severe pain and unless immediately diagnosed and treated, permanent testicular damage may ensue.
Each testis is subdivided into several smaller segments called lobules by invaginations of the tunica albuginea connective tissue. Each lobule in turn is made up of several tightly coiled tubular structures called seminiferous tubules. Both sperm production and testosterone secretion take place within the seminiferous tubules.
The sperms are formed by a process of maturation beginning with the immature germ cell undergoing a series of changes to form the mature gamete or sperm. This process of spermatogenesis takes approximately 70 days to complete and is regulated by a complex interplay of hormones. It is also essential that the temperature of the testes is maintained about 4 to 5o F lower than the body temperature for normal spermatogenesis to occur. The scrotum has an inbuilt mechanism to maintain the testes and the sperms at the right temperature. For instance, if the outside temperature becomes too cold, the cremaster muscle of the scrotum will reflexly contract and keep the testes warm by bringing them closer to the body.
The testes also secrete the male hormone testosterone, which regulates sperm production, sex drive (libido), secondary sexual characteristics of the male such as distribution of body hair, deepening of voice, and development of muscle mass and bodily strength.
What are the Types of Testicular Biopsy?
A testicular biopsy may be performed in the following 2 ways
- Percutaneous testicular biopsy (performed via skin; no incision)
- Open surgical biopsy
Percutaneous biopsy does not need an incision or stitches. A needle is inserted through the scrotal skin into the testis and a sample of tissue is drawn into a syringe that is attached to the needle. It is also referred to as fine needle biopsy.
A variation of percutaneous biopsy is a core needle biopsy, where a spring loaded needle is used to draw out a ‘cylinder of cells’. In this method, a larger sample of tissue is obtained compared to fine needle biopsy.
Open surgical biopsy involves making a surgical incision in the scrotal skin and obtaining a sample of testicular tissue, followed by closure of the incision using stitches or sutures.
Why is a Testicular Biopsy Done?
A testicular biopsy is generally done for the following purposes, namely
- Investigation of the cause of male infertility after doing other tests such as semen analysis and hormonal assays
- Confirmation of the occurrence of normal spermatogenesis in men with obstructive azoospermia before planning surgical correction to relieve obstruction in the vas deferens. In obstructive azoospermia, the testes produce sperms, but they are unable to reach the semen due to an obstruction in the conducting tubule called the vas deferens.
- Extraction of sperm (testicular sperm extraction; TSE) from men with non-obstructive azoospermia. In non-obstructive azoospermia, some sperms may be produced by the testes but do not appear in the semen in the absence of any obstruction. The extracted sperms are then used for
in vitro fertilization . A part of the biopsy sample obtained for this procedure is also sent for microscopic examination. - To evaluate infertile men with risk factors for cancer of the testes, such as those with undescended or hidden testes (cryptorchidism) where testes are absent from the normal location in the scrotum, previous testicular malignancy or testicular atrophy. However, the test is not usually used for the diagnosis of testicular cancer since it can result in the spread of the cancer.
What is the Procedure for a Testicular Biopsy?
Preparation for a Testicular Biopsy
The testicular biopsy procedure requires minimal preparation.
The patient needs to discuss with the doctor regarding regular or over-the-counter medications that he may be using. Some of these have to be stopped prior to and during the procedure as advised by the doctor. These include those that can cause bleeding like blood thinners like heparin and warfarin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and aspirin.
In case the procedure is being performed under general anesthesia, the patient needs to remain fasting for at least for 8 hours prior to the test. Additionally, if a sedative has been prescribed to be taken at home the night before, it is advisable not to drive oneself alone to the surgery.
Testicular Biopsy Procedure
The biopsy may be performed either in an outpatient setting or following admission. Typically, the procedure takes between 15 to 20 minutes.
The patient is asked to lie on his back and the scrotal skin and surrounding areas cleaned with antiseptic solution to remove bacteria.
The procedure may be undertaken using local anesthesia where the scrotal skin is infiltrated with an injection of local anesthetic. In this procedure, the patient remains aware of the procedure, though he may be mildly sedated. However, many doctors prefer to use general anesthesia since the procedure requires the patient to remain perfectly still.
Open biopsy
Typically, a small 2 to 3 cm incision is made on the scrotal skin and a tiny pea sized amount of testicular tissue is then removed. The incisions made on the testis as well as the scrotal skin are then stitched using absorbable suture material so that the removal of stitches is not necessary. The same procedure may be repeated on the opposite side. The testes are then bandaged.
Percutaneous biopsy
In a fine needle biopsy, a small testicular sample is drawn out using a needle inserted through the scrotal skin. In a core biopsy, a larger bore needle is inserted through the scrotal skin and one might hear a loud snapping noise as the testicular tissue sample is being obtained. Whatever procedure is being followed is then repeated on the opposite testis.
What are the Precautions to be taken following a Testicular Biopsy?
Following a testicular biopsy, the patient may be advised to follow certain precaution such as:
- Keeping the biopsy area dry and refraining from washing for several days following the procedure
- Using acetaminophen for pain and discomfort
- Avoiding aspirin for at least a week after
- Avoiding sexual activity for one or two weeks
- Using an athletic supporter for a few days after the procedure
Though a mild swelling, pain and discoloration is normal, it is important to immediately call the doctor in the following instances
- Severe pain and swelling
- Severe bleeding staining large portions of the dressing
- Fever > 100oF
What are the Risks of a Testicular Biopsy?
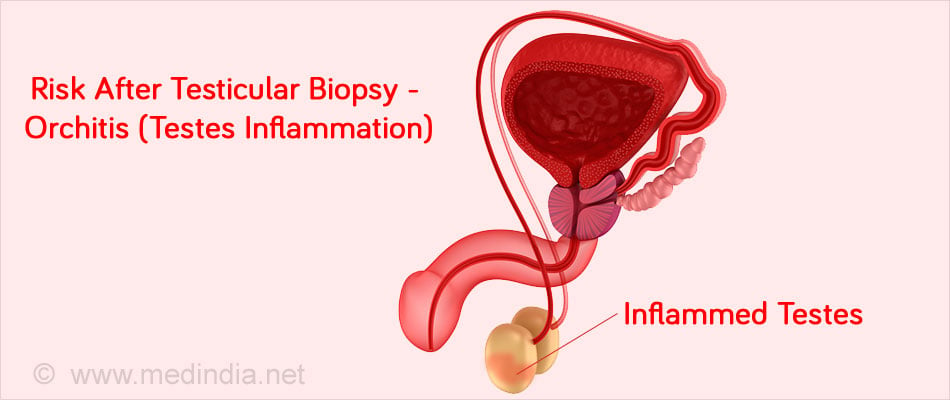
The procedure is generally safe and carries minimal risks. However, occasionally bleeding may be severe and there is a small risk of infection (orchitis).
Very rarely, if the testicular biopsy is done in the presence of testicular cancer, it increases the risk of spread. For this reason, a testicular biopsy is rarely performed in suspected testicular cancer. In such cases, radiological investigations are done to confirm the diagnosis, and the affected testis is removed surgically by a procedure called radical orchidectomy.
How are the Results of a Testicular Biopsy Interpreted?
A sample of the testicular tissue obtained by biopsy is sent for pathological examination. The pathologist examines the tissue under the microscope, and the results are generally available within 48 to 72 hours.
- The pathologist will be able to evaluate the degree of spermatogenesis present in the testes. In some cases, sperms may be absent due to which the person is infertile. In other cases, sperms may be absent from the semen but present in the testes due to an obstruction in the vas deferens. In cases of non-obstructive azoospermia, the sperms can be harvested and can be used for in vitro fertilization
- Occurrence of testicular inflammation or infection such as tuberculous orchitis may also be diagnosed by a biopsy.
- Presence of a spermatocele (cyst on the ducts of the testes) may also be diagnosed by microscopy.
- Occurrence of testicular cancer or carcinoma in situ (CIS) can also be diagnosed.