- What Is Adenoiditis? - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536931/)
- Enlarged Adenoids - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001649.htm )
- Enlarged Tonsils and Adenoids: Overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536881/)
- About Adenoiditis - (https://www.stlouischildrens.org/conditions-treatments/adenoiditis )
- All You Need To Know About Adenoids - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/ConditionsAndTreatments/adenoids )
- Adenoids and Adenoidectomy - (https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/adenoids.html )
- Adenoidectomy - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/adenoids-and-adenoidectomy/ )
What is Adenoids / Adenoiditis?
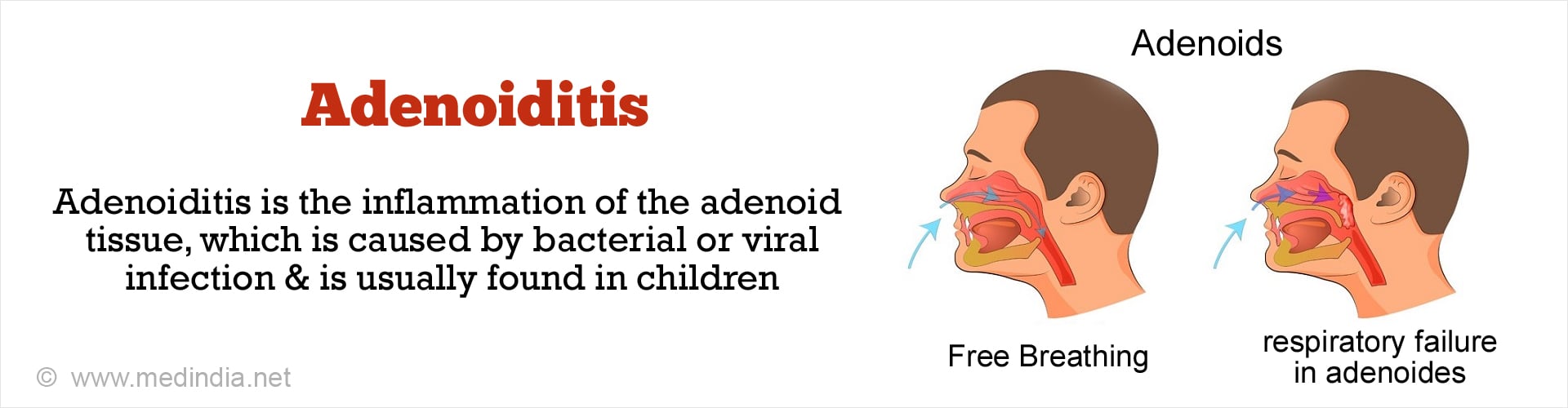
Adenoids / Adenoiditis are lymph tissue which lies in the upper respiratory tract between the nose and the back of the throat. They are part of the glandular tissue encircling the back of the throat. Unlike tonsils, they are not visible through the mouth and special instruments are needed to see them. Adenoiditis is the inflammation of the adenoid tissue that is caused by bacterial or viral infection.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What Is Adenoiditis?
Go to source)
Adenoids, along with the tonsils are first line of defense in the throat of children. Both adenoids and tonsils are located near the entrance of the respiratory tract, which allow them to catch incoming infections. It is stipulated that they play a major role in helping to form antibodies to the “germs” which help the child to resist and fight future infection.
Adenoids are usually found only in children. They grow from birth and are the biggest by the time the child is 3 to 5 years old. In the teenage years, adenoids progressively shrink and disappear completely by adulthood. Many children have their tonsils and adenoids removed when they are young, however they do not suffer any loss in their future immunity to respiratory tract infections.
Causes of Adenoids / Adenoiditis
In adenoiditis, the adenoid tissue gets infected which can typically last for weeks or even months. The infection is caused usually by viruses, such as the Epstein-Barr virus or bacteria such as Streptococcus. Adenoiditis could lead to repeated nasal infections with continuous thick green or yellow drainage. Middle ear infection namely otitis media is commonly seen in children with adenoiditis because the adenoid tissue is situated close to the eustachian tubes in the back of the nose. Your child is more susceptible to infections of the adenoidal tissues if you have recurring infections in the throat or neck or suffer from infections of the tonsils frequently.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Enlarged Adenoids
Go to source)
Symptoms of Adenoids / Adenoiditis
The swelling or enlargement of the adenoid tissue generally restricts passage of air through the upper respiratory tract, leading to difficulty in breathing through the nose. This problem leads to:
- Predominant breathing through the mouth, which eventually causes sore/dry throat
- Stuffy nose/nasal congestion
- Snoring and trouble sleeping due to difficulty in breathing
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Earache
- Sounding nasal when talking or conversing
- Nasal discharge with greenish yellow mucus, which may be a sign of infection
Viral infection usually recedes after 48 hours, however bacterial adenoiditis typically persists for about 7 days.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Enlarged Tonsils and Adenoids: Overview
Go to source), (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Adenoiditis
Go to source)

Complications of Adenoids / Adenoiditis
Middle ear infection: Since the adenoids are situated next to the Eustachian tubes of the middle ear, inflammation of adenoids may block the opening of the tubes leading to middle ear infection.
Glue ear: In adenoiditis, blockage of the Eustachian tubes causes build-up of mucus in the middle ear, which interferes with the movements of the tiny bones and consequently affects hearing.
Sinus infection: The sinuses are hollow regions located within the facial bones which contain pockets of air and communicate with the nasal passage. Enlarged adenoids may both the opening of the sinuses into the nose, thereby resulting in accumulation of secretion in the sinuses, which can get infected.
Vomiting: This happens when the child inadvertently swallows a great deal of pus, mainly while sleeping at night.
Chest infections: If the adenoids become severely infected with a virus or bacteria, your child may experience chest infections like pneumonia or bronchitis due to spread of the infection to the lungs, bronchi and so on.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
All You Need To Know About Adenoids
Go to source)

Diagnosis of Adenoids / Adenoiditis
- When you visit the doctor’s office with adenoiditis, he would ask a few questions to diagnose the condition and check if the condition is hereditary. He would also ask the history of your child’s ear, nose and throat problems.
- Physical examination of the head and neck is conducted, which reveals enlarged adenoids and nasal discharge.
- The adenoids, unlike the tonsils, cannot be seen by looking directly in the mouth. Your doctor would use a special mirror in your mouth or use an endoscope (flexible tube placed through the nose). Swabs are used to obtain samples of micro-organisms for bacteriological cultures during examination of the throat region.
- If needed, blood tests are done to verify the presence of microorganisms that may show in blood.
- X-rays of the throat or neck may be necessary to gauge the size of the enlarged adenoids and also the extent of infection.
- Sleep study is sometimes conducted to check for any obstructive sleep apnea.
- Optic fiber endoscopy could also be done to visualize the inflamed adenoid.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Adenoids and Adenoidectomy
Go to source)

Treatment for Adenoids / Adenoiditis
In most cases, the child recovers with symptomatic treatment. If required, the pediatrician will decide the best treatment for your child, which depends on the nature, type and severity of the infection, as well as the number of times the child has developed infections. If the child has middle ear infection or sinusitis, treatment is initiated to reduce pain in the ears. Antibiotics would be started for your child if deemed necessary by the doctor.
Sometimes, the pediatrician refers the child to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) surgeon to have the adenoids removed by a procedure known as adenoidectomy. Along with the adenoids, sometimes the tonsils are also removed at the same time.
Adenoidectomy:
- It is the surgical procedure for removal of adenoids. Adenoidectomy is recommended if the child has recurrent ear infections and has large adenoids that cause significant blockage of the nasal passage, which can interfere with breathing especially while sleeping at night.
- The surgery is generally performed by an ENT surgeon in a hospital or outpatient surgical center under general anesthesia. The child can have the surgery and could go home on the same day if the doctor approves it. The adenoids and the tonsils are usually removed through the mouth, so no additional cuts or incisions are made. Most kids bounce back to their normal activities in less than a week. (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Adenoidectomy
Go to source)

Complication and Risks: As with any surgery, there are risks involved with adenoidectomy too. They include bleeding from the site of adenoid removal, infection, as well as anesthetic reactions. The child may also sound nasal while talking because after the adenoids are removed, the gap between the back end of the nasal cavity and the top of the mouth may not close properly. However, this may be a temporary occurrence and some kids may require speech therapy to correct this.