- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) - (http://www.heart.org/heartorg/conditions/heartattack/symptomsdiagnosisofheartattack/transesophageal-echocardiography-tee_ucm_441655_article.jsp)
- Aortic dissection - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/aortic-dissection/basics/definition/con-20032930)
- About Aortic dissection - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000181.htm)
What is the Aorta?
The aorta is a major blood vessel carrying blood from the heart to the rest of the body. As the heart pumps blood, it first enters the aorta and is then delivered via connecting vessels to the rest of the body.
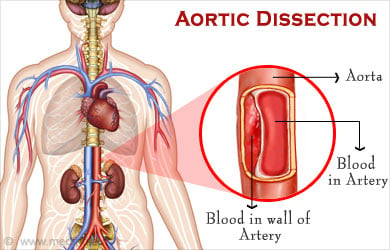
What is an Aortic Dissection?
Aortic dissection refers to a serious condition where there is a tear in the wall of a major artery leading to blood flow within the layers of the aorta. A tear in the inner lining causes blood to leak into the middle layers of the aorta thereby creating two passages for blood: the true lumen (the normal passage) and a false lumen (new passage).
Blood flow into the new lumen leads to several complications like multiple tears and reduction in the amount of oxygen and nutrients reaching organs in the body. Reduced blood flow to the organs can lead to ischemia. The brain, heart, intestines, kidneys, arms and legs may be affected by an aortic dissection. In extreme cases, the aorta can also rupture.
Aortic dissection is not very common and males in the age group 60-80 are more prone to this condition. Aortic dissection symptoms are often confused with other heart conditions leading to delayed diagnosis. It can be detected early and, if treated on time, it improves survival rates.
Types of Aortic Dissection
Aortic dissections are divided based on which part of the aorta is affected:
- Type A is the most common and risky aortic dissection. It occurs in the part of the aorta that leaves the heart. It can also be a tear in the upper aorta (ascending), which can extend to the abdomen.
- Type B is a tear in the lower aorta (descending). This type can also extend to the abdomen.
Causes of Aortic Dissection
While the exact cause of aortic dissections are not known, some of the risk factors include:
- Atherosclerosis – hardening of the arteries
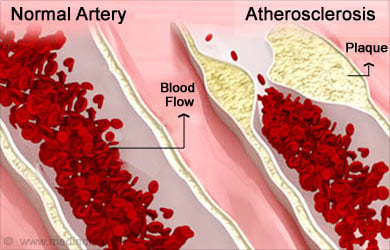
- Aging – occurring frequently among men in the age group 60-80
- High blood pressure – which leads to weakening of the artery walls
- Pregnancy
- Heart surgeries (coronary bypass) and procedures (cardiac catheterization)
- Connective tissue disorders like Marfan’s Syndrome
- Rare genetic disorders like Turner Syndrome
- Other inflammatory diseases that lead to vasculitis (damage to blood vessels)
- Blunt injuries to the chest
Symptoms of Aortic Dissection
The symptoms of aortic dissection are often deceptive and can be mistaken for other heart disorders. It is critical to identify an aortic dissection to increase chances of survival. Some of the symptoms of aortic dissection are:
- Sudden and severe chest pain: This often gets mistaken as a heart attack because of the sudden onset and severity. Pain due to an aortic dissection is usually a sharp, searing pain. It is usually experienced below the chest bone and can extend to the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, abdomen and hips.
- Fainting and giddiness
- Anxiety and confusion spells
- Rapid and heavy sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weak, rapid pulse
- Breathing difficulties

Rarely symptoms may include swallowing trouble due to pressure in the esophagus.
Diagnosis and Tests
An aortic dissection is sometimes difficult to detect as the symptoms often get confused with heart attack or other heart conditions. Some of the diagnostic tests used to detect an aortic aneurysm are:
- Chest X-Ray
- Chest MRI
- CT scan of the chest
- Doppler test
- Echocardiogram (ECG)
- Aortic angiography
- Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
Treatment and Drugs
An aortic dissection is a serious condition requiring immediate treatment interventions. Surgery and medications are used to treat an aortic dissection. Surgery is required when the dissection occurs in the part of the aorta that leaves the heart. Dissection occurring in other parts of the aorta can be treated with medications.
The two surgical techniques include:
- Standard, open surgery where an incision is made in the chest or abdomen.
- Endovascular aortic repair where no major incisions are required.
Drugs like intravenous beta-blockers which reduce high blood pressure and reduce heart rate are usually prescribed. Sometimes vasodilators are used in combination with beta- blockers. Analgesics like morphine may be required to relieve the severe pain.
If the aortic valve is damaged, a valve replacement surgery is usually recommended.
Complications
An aortic dissection may lead to other complications due to stopped or decreased blood flow to other major organs and parts of the body. Some of the complications include:
- Organ damage to the brain, heart, kidneys and intestines
- Damage to the legs
- Stroke
- Aortic valve damage
- Death due to internal bleeding
Prognosis
Though an aortic dissection is a life-threatening condition, early diagnosis and treatment can improve chances of survival. Most patients survive if immediate surgery is performed before the aorta ruptures. Chances of surviving a ruptured aorta are low. Most patients who survive need to be on lifelong medications for controlling high blood pressure. They need to be constantly monitored and need to follow a healthy lifestyle.
Prevention
Tips to avoid and prevent aortic dissections:
- Controlling blood pressure
- Avoiding smoking of cigarettes
- Maintaining ideal body weight
- Low-sodium diet with a good mix of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Regular physical activity and exercise
- Pre-emption by checking out genetic risk factors and seeking medical help and counseling