- Cervical Cancer - (https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical)
What is Cervical Cancer?
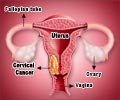
Cancer is a disease caused by the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells. Cancer that affects the lining of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus, is known as cervical cancer.
The cells lining the cervix comprises of two types, the squamous or flat cells and the columnar cells.
The region in the cervix where there is a transition from one cell type to another is called the squamo-columnar junction. This is the area that is most prone to develop cancer. Cancer of the cervix develops gradually and becomes full-blown over a period of time.
Cervical cancer is mostly caused by Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). The risk factors for cervical cancer includes
- Smoking
- Unprotected sex
- Having many children
- Prolonged use of birth control pills
- Having HIV infection.
A Pap-smear test is done to find out any changes occurring in the cervical cells before they turn into cancer; the sample for the test is obtained from the squamo-columnar junction.
Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. Cervical cancer treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiation.
What is Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia?
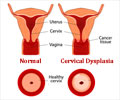
The abnormal changes that the cervical cells develop transform them to a pre-cancerous state, which is referred to as 'Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia' (CIN).
Based on its degree or intensity, and the thickness of the epithelium involved, these changes are classified as
- Low grade CIN
- High grade CIN
This may eventually progress to form a localized cancer. The cancer later spreads beyond the epithelium to involve adjacent tissues and even distant organs.
Normally it affects middle age women who are sexually active.
How is Cervical Cancer Transmitted?
Cervical cancer is not in itself a sexually transmitted disease, but is usually the consequence of infection and epithelial damage from a sexually-transmitted virus. Over 99 percent of all cervical cancers are the consequence of damage by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Two HPV types (16 and 18) cause 70% of cervical cancers and precancerous cervical lesions.
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease, affecting literally millions of women each year with new cases. But only a small subgroup of these women goes on to get cancer. HPV is mainly transmitted through sexual contact and most people are infected with HPV shortly after the onset of sexual activity. Cervical cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection with certain types of HPV.
What are the Histological Types of Cervical Cancer?
Over 90 percent of cervical carcinomas start in the surface cells lining the cervix and are called squamous cell carcinoma. And about 5 to 9 % start in glandular tissue (adenocarcinoma) of the cervix. Adenocarcinomas are more difficult to diagnose, but they are generally treated the same way as squamous cell carcinomas and the survival rate, stage for stage, is similar.