- American Academy of Family Physicians. A Primary Care Approach to the Patient with Claudication.
- Peripheral artery disease. The Merck Manuals: The Merck Manual for Healthcare Professionals.
About
Claudication refers to pain and/or cramping in legs that is caused by inadequate blood flow. The term comes from the Latin word ‘claudicure’ that means to limp. Claudication is typically felt while walking and usually subsides with rest. But a severely compromised blood supply can even cause claudication at rest.
The term ‘intermittent claudication’ is used when pain comes and goes with exertion and rest, respectively. Claudication is technically a symptom of a disease. It is important to know that claudication can also occur in your arms.
Causes of Claudication
The most common cause of claudication is peripheral artery disease (PAD). In PAD, the arteries that supply blood to the limbs are compromised. This is usually due to atherosclerosis, a condition leading to hardening of arteries by deposition cholesterol plaques. While walking or exercising, our muscles are at an increased need of oxygen which has to come through blood. Plaque deposition compromises blood supply and there is lack of oxygen, which results in cramping.
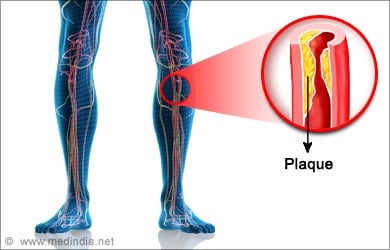
Jaw claudication occurs when the arteries supplying the jaw muscles are inefficient; this is usually due to a condition called giant cell arteritis.
Neurogenic claudication is due to a neural problem like lumbar canal stenosis and has to be distinguished from vascular claudication.
Risk Factors of Claudication
The risk factors of claudication include:

- Elevated cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Diabetes

- Obesity
- Older age: Age older than 70 years (smokers and diabetics are at risk at an earlier age, usually in their fifties)
- A family history of atherosclerosis, peripheral artery disease or claudication
Symptoms of Claudication
The common symptoms of claudication include:
- Pain while exercising or even at rest
Pain or discomfort can occur in your feet, calves, thighs, hips or buttocks. Claudication can also occur in your arms. During the early course of the disease, pain is intermittent, i.e. it may come and go. It may be relieved with rest. However, severe disease can cause pain even at rest.
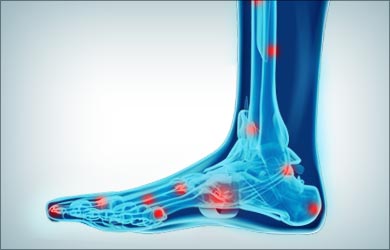
- Skin changes
Reduced blood supply can lead skin discoloration or ulcerations. Extremities of the body may look bluish or feel cold to touch. Ulcers may develop in lower legs, feet, toes, arms or fingers.
Severely compromised circulation can lead to gangrene and require limb amputation.
Diagnosis of Claudication
- Your doctor may employ various clinical methods and tests to diagnose claudication. Examination for peripheral pulsations is an important diagnostic tool.
- Segmental blood pressure measures in different parts of the leg (calf, low thigh, high thigh) can detect blockage.
- Ankle-brachial index compares the blood pressure in your ankles to the blood pressure in your arms.
- Doppler ultrasound is perhaps the most common investigation used to assess blood flow to your limbs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) angiography are noninvasive tests used in the diagnosis.
Treatment of Claudication
Treatment modalities include:
Medications: Medical therapy aims at preventing blood clots from forming. Aspirin is a common drug prescribed for this purpose. Other similar drugs include clopidogrel (Plavix), dipyridamole (Persantine) and ticlopidine. Cilostazol (Pletal) improves blood flow by widening arteries and reduces the symptoms. Pentoxifylline decreases the viscosity of blood.
Angioplasty: This is a procedure that widens damaged arteries using an inflatable balloon; sometimes, a stent is placed so as to keep a particular area of the artery open.
Vascular surgery: Surgical grafting or bypassing an artery may be done in severe cases. Here, the damaged part of a vessel is either replaced with a graft or is bypassed.
Prevention of Claudication
A healthy lifestyle can prevent claudication.

- Adhere to a healthy diet so as to maintain adequate cholesterol levels.
- Keep
diabetes and high blood pressure under control as per your doctor’s advice







