- Dentures - (https://medlineplus.gov/dentures.html )
- Types of dentures - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/dentures#types-of-dentures)
- Complete Denture - (https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/complete-denture)
- A systematic review of studies comparing conventional complete denture and implant retained overdenture - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28666845/)
- Tooth Supported Overdenture Retained with Custom Attachments: A Case Report - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4502008/)
- Mandibular Implant-supported Overdentures: Prosthetic Overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6196685/)
- Permanent Dentures - (https://www.omicsonline.org/scholarly/permanent--dentures-journals-articles-ppts-list.php)
- Dentures vs Implants: A Look At Prosthetic Teeth Costs, Pros, and Cons - (ive-dentistry/dentures-vs-implants/)
- Polyamide as a Denture Base Material: A Literature Review - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4476124/)
- Flexible denture base material: A viable alternative to conventional acrylic denture base material - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3276859/)
- Oral mucosal lesions in denture wearers - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20461847/)
- Creating complete dentures that are stable in function - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18557503/)
- Significance of saliva for the denture-wearing population - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11808055/)
- Allergic effects of the residual monomer used in denture base acrylic resins - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4745248/)
- Oral mucosal lesions associated with the wearing of removable dentures - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6792333/ )
- Eating Advice for People Who Wear Dentures: A Scoping Review - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9319444/)
- Taking Care of Your Teeth and Mouth - (https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/taking-care-your-teeth-and-mouth)
- Denture cleanliness and hygiene: an overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9270218/)
- Denture Adhesives - (https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/dental-devices/denture-adhesives )
- Denture Adhesives: A Guide for Patients - (https://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/Dentistry/DenturesAdhesives.pdf )
About
Dentures, also known as false teeth, are dental prosthesis that replace the natural teeth with artificial substitutes.
A denture may be defined as a dental prosthesis that replaces the natural teeth with artificial substitutes. Dentures are essentially prosthesis that are custom made for each patient, take support from the oral tissues, and can be removed by the patient. These prosthesis can be variably classified based on the material with which they are made, the number of teeth they replace, or the tissue from which they get their support. The goal of dentures is to restore a patient's appearance and function (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dentures
Go to source).
Types of Dentures
Based on number of teeth they replace, dentures may be classified as:
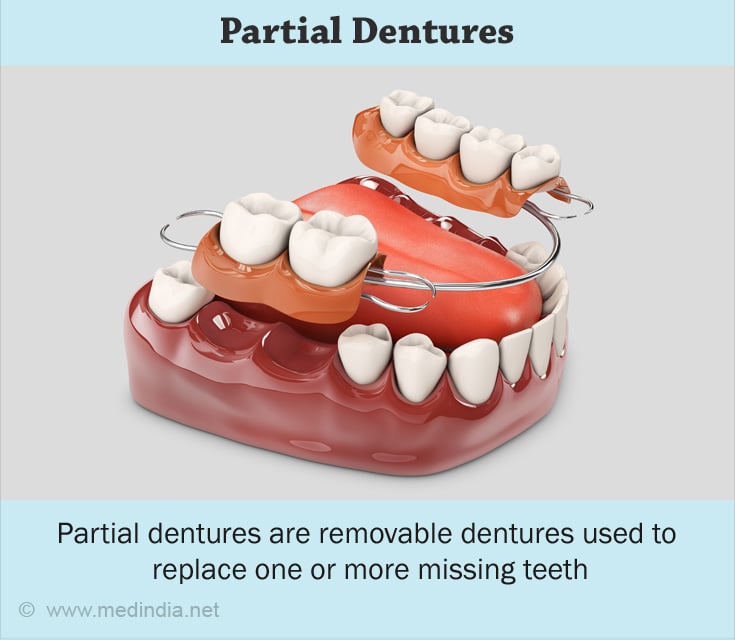
Partial dentures:
When dentures replace some of your teeth, they may be referred to as ‘partial dentures’. These dentures require support from both soft tissue and teeth. They may be bound to your teeth using metal wires known as clasps.
These dentures may be made of acrylic or metal. In the latter situation, they are called ‘cast partial dentures’ as the denture framework is made by casting the metal (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Types of dentures
Go to source).
Complete dentures
When dentures replace all your teeth, they are known as complete dentures. These dentures are most often made of acrylic, as they can be colored to replicate the color of your gums. These dentures can draw support from the oral soft and hard tissues. In some cases, these prosthesis may be fabricated by taking support from dental implants and tooth roots that have been root canal treated. In the former case, they are referred to as tooth supported over dentures, and in the latter as implant supported over dentures (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Complete Denture
Go to source).
Based on the tissue from which they take support, complete dentures may be classified as:
Conventional complete dentures
Conventional complete dentures take support from the soft tissue and bone of the jaws. These are the most commonly fabricated dentures. The chief advantage of these prosthesis is their relative cost-effectiveness compared to the other treatment options (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
A systematic review of studies comparing conventional complete denture and implant retained overdenture
Go to source).
Tooth supported overdentures:
If the dentist believes that some of the tooth can be saved in the oral cavity, he or she may decide to treat it with root canal therapy and reduce it to the level of your gums. Overdentures provide better retention and aid in the preservation of jaw bone
However, the disadvantage of this prosthesis is that the treatment time is longer as compared to a conventional prosthesis and that the costs are higher (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tooth Supported Overdenture Retained with Custom Attachments: A Case Report
Go to source).
However, the disadvantage with this prosthesis is that the treatment time is longer as compared to a conventional prosthesis and also the costs are greater.
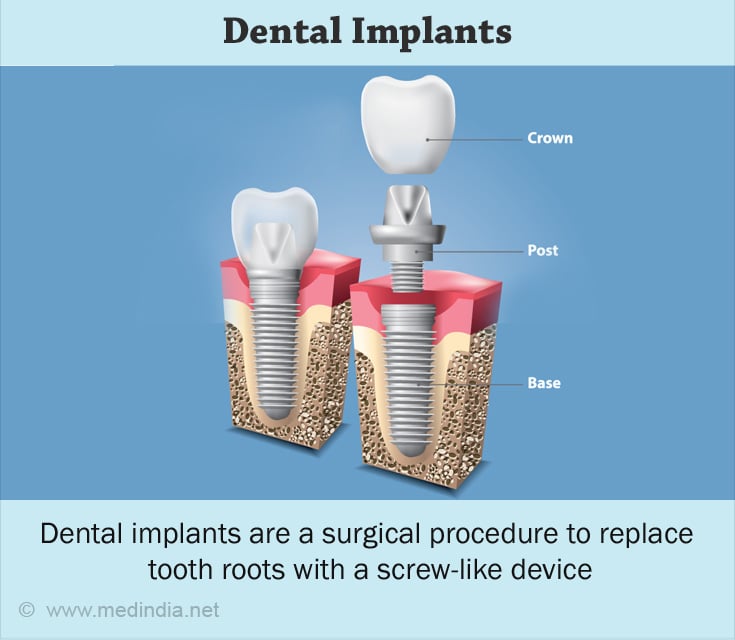
Implant supported over dentures:
In some cases, dental implants may be placed in the jaw bone to increase the retention and support of the denture. The number of implants that need to be placed may range from 2 to 6; however, a greater number of implants may be necessary based on the amount of bone that is available. These prosthesis offer the advantage of excellent retention. The only disadvantage of this treatment option is the relatively greater cost and longer treatment time.
The treatment time is longer as there must be a time gap of 3-6 months between the surgery for implant placement and when the final prosthesis is given. However, in the interim period, the patient can do with a conventional denture (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Mandibular Implant-supported Overdentures: Prosthetic Overview
Go to source).
Permanent Dentures
The method of permanent dentures is used to replace one or more missing natural teeth. They are attached to existing teeth as well as replacement teeth to cover the gap left by a lost tooth or teeth. The bridge is secured by cementing it to natural teeth that have been drilled into a conical form on each side of the false tooth (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Permanent Dentures
Go to source).
Dentures vs Implants
Dentures and implants can both be successful methods of restoring lost teeth. Dentures are a less expensive choice, but they don't last as long and can create additional issues, like as looseness, discomfort, and difficulty speaking and eating. While implants are the greatest option for replacing natural teeth, they may not be affordable for everyone due to their high cost (8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dentures vs Implants: A Look At Prosthetic Teeth Costs, Pros, and Cons
Go to source).
Pros of dentures
- Aesthetically pleasing
- Cost-effective
- No surgery required
- Help stop mouth from sagging inwards
Cons of dentures
- Wear down and need to be replaced periodically
- Potentially require a lot of preparation - tooth removal, making molds, fitting
- Can become loose and make clacking noises
- Don't stop the bone from deteriorating
Pros of implants
- Look just like natural teeth
- Implants replace tooth roots and support bone health
- They fuse to your jaw bone and can last a lifetime
- Total stability for eating and speaking
Cons of implants
- Getting implants can take as much as a year
- Surgery is required for placement
- You may have pain after getting implants during recovery
- Bone graft or sinus lift may be necessary
- They are the most expensive option
Materials for Dentures
Materials used to fabricate dentures include acrylic resins, nylon based plastics (flexible dentures), and metal denture base materials.
Acrylic resins are the most commonly used materials. These materials have excellent aesthetics and are easy for the dentist to adjust (9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Polyamide as a Denture Base Material: A Literature Review
Go to source).
Flexible denture base materials are made up of nylon based polymers (10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Flexible denture base material: A viable alternative to conventional acrylic denture base material
Go to source). These dentures have greater flexibility and better translucency than acrylic. These properties make wearing these dentures more comfortable. Their translucency picks up the color of the underlying tissue, making them more aesthetic. However, they have a tendency to pick up stains from foods and beverages.
Metal denture bases are not used very often and are used only in cases when the dentist deems it necessary.
Fabrication
A patient will have to visit the dentist a minimum of 5-6 times for a conventional denture.
During the initial visit, the dentist will record a primary impression of the patient’s upper and lower ridges. This will be used to construct a model on which a custom tray is made. This tray will help record a more accurate impression of the patient. The final, or secondary impression is used to construct the master cast. The dentist will then record the jaw relation that is the relation of the upper and lower jaws. The teeth are then arranged on a temporary denture base, and the dentist will try this temporary denture in the patient’s mouth. This allows the patient to suggest changes to the shade and position of teeth. This will be followed by the final appointment, when the processed denture can be given to the patient.
Problems with Dentures
As with all prosthesis, dentures have an inherent adjustment period.
As with any prosthesis, dentures are artificial replacements to your natural teeth that are often resting on a movable foundation. There is an adjustment period after a new prosthesis is given. Over time if the patient does not take adequate care of the prosthesis, it can also lead to problems. Some of the common problems associated with dentures are:
Problems with new dentures
- Ulcers and soreness: One of the most common problems in patients with new dentures is ulcers and soreness. It is most often due to sharp edges or nodules. The dentist will simply trim off the offending part to ensure relief(11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Oral mucosal lesions in denture wearers
Go to source).
- Difficulty in speech and mastication: A new denture acts as a foreign object in the mouth, and the patient should not expect it to function like your natural teeth. Like all prosthesis, you must learn to use them efficiently. The dentist will give you instructions on how to eat and learn to speak with your new dentures. The problem should not last very long with a properly constructed denture. However, if the problem persists, be sure to visit your dentist (12✔ ✔Trusted Source
Creating complete dentures that are stable in function
Go to source). - Loose dentures: In certain cases, the denture may be loose and get displaced while eating and speaking. The cause of this problem could range from a poorly constructed prosthesis to minor over extensions that can be corrected. In the former case, a new prosthesis may need to be made. In some cases, a loose denture could be due to the patient's poor bone structure; in such cases, it is better to opt for more sophisticated treatment options such as implant supported over dentures.
- Excessive salivation: The denture acts as a foreign object in the mouth that could cause excessive salivation. This is a self-limiting problem and subsides with time (13✔ ✔Trusted Source
Significance of saliva for the denture-wearing population
Go to source). - Allergic reaction: Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to a new denture. The symptoms may range from inflammation and burning sensation to more severe symptoms such as respiratory distress. In case a patient suspects an allergic reaction, he should stop wearing the denture at once and consult his dentist or physician (14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Allergic effects of the residual monomer used in denture base acrylic resins
Go to source).
- Clicking sounds: You will probably experience clicking sounds with your new denture. This is due to the contact of your upper and lower teeth. The issue will be resolved in due course. However, if it persists, contact your dentist.
Problems with old dentures:
- Stomatitis: Stomatitis refers to the inflammation of the oral tissues. It is most often caused by candidiasis. The cause of this problem is often poor oral and denture hygiene (15✔ ✔Trusted Source
Oral mucosal lesions associated with the wearing of removable dentures
Go to source). - Loss of masticatory efficiency: This may be due to prolong use of dentures and the only solution is to get new dentures made.
- Sagging and ulcers at the corners of your mouth are caused by tooth material loss. The solution to the problem is to get a new denture made.
- Lip and cheek biting: With time, the denture material wears off. The solution to this problem is getting a new denture made.
Getting used to New Dentures
A new denture requires practice to get used to and use efficiently.
How to Eat with New Dentures?
It takes time to start eating with new dentures. Start with soft and semi-solid foods that are easy to chew. Once you are comfortable with these foods, start on more solid foods (16✔ ✔Trusted Source
Eating Advice for People Who Wear Dentures: A Scoping Review
Go to source).
- Cut food into small pieces and chew foods on both sides. This will keep your dentures stable.
- Don’t try to take bites of hard foods such as an apple with your front teeth; this will dislodge your denture.
- Chew on food with your back teeth.
- Take small sips of water or beverages; do not use a straw as this can cause your dentures to dislodge.
How to speak with new dentures?
Learning to speak with new dentures is difficult as the new denture may feel awkward and the problem is further compounded by increased salivary flow. Reading a newspaper aloud, whether alone or in front of a mirror, will help you identify mispronunciations and boost your confidence.
Pain and soreness
New dentures may cause pain and soreness. Your dentist will tell you to visit him on the 2nd or 3 rd day.
Your denture may get dislodged when you cough or sneeze; this is a normal occurrence. Keep your hand or handkerchief in front of your mouth to prevent this.
Guidelines for the Care and Maintenance of Dentures
It is important that the patient regularly clean his mouth and denture to prevent infections and foul odor.
Daily removal of the bacteria present in the oral cavity and on complete dentures is of paramount importance to minimize denture stomatitis and help contribute to good oral and general health. Based on the best available evidence, an American College of Prosthodontists task force has suggested the following guidelines for the care and maintenance of dentures:
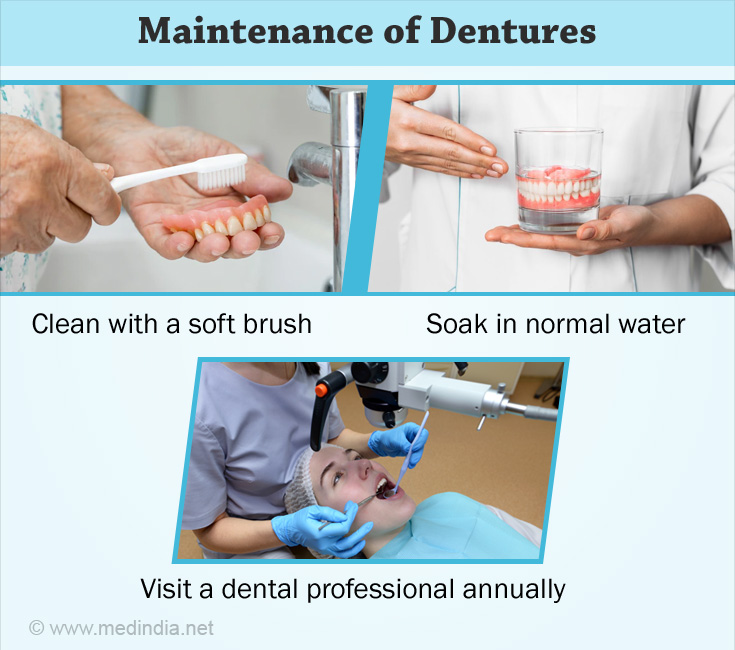
Oral hygiene maintenance
Brush your remaining teeth, gums, and tongue every morning and evening with fluoride-containing toothpaste to prevent tooth decay and gum disease. In a completely edentulous patient, massage your denture bearing tissue with your finger; this ensures adequate blood supply to these tissues and keeps them healthy (17✔ ✔Trusted Source
Taking Care of Your Teeth and Mouth
Go to source).
Give proper rest to your denture-bearing tissues by removing your denture overnight.
Denture care instructions
It is important that the denture be kept clean; this will prevent infection of your tissues and foul odor. The following measures can be taken to keep your dentures clean (18✔ ✔Trusted Source
Denture cleanliness and hygiene: an overview
Go to source):
- Dentures should be cleaned daily. A non-abrasive cleaner such as a soft brush and paste or cleansing tablets and solutions should be used.
- Do not use any of these products inside your mouth as they may contain harmful chemicals.
- Rinse the denture properly before reinserting in the mouth.
- Manufacturer instructions regarding denture cleansers should be followed carefully.
- Dentures should be cleaned annually by a dentist or dental professional by using ultrasonic cleansers.
- Dentures should never be placed in boiling water this can distort your denture.
- Dentures should not be soaked in sodium hypochlorite bleach, or in products containing sodium hypochlorite, for periods not exceeding 10 minutes.
- Dentures should be stored immersed in water after cleaning or when not replaced in the mouth, to avoid distortion.
- A yearly check up of your denture is a must.
Denture adhesives
Denture adhesives are available as powders or pastes and can improve the retention or fit of your denture. A well-made denture will not require a denture adhesive to have a good fit. Your dentist will only recommend an adhesive if he or she believes that your bone quality is poor and that a good fit is impossible even with a well-made denture (19✔ ✔Trusted Source
Denture Adhesives
Go to source).
To use a paste adhesive:
Wet your denture and place pea-sized amounts of the cream on the inner surface of your denture. Place the same in your mouth (20✔ ✔Trusted Source
Denture Adhesives: A Guide for
Patients
Go to source).
To use a powdered adhesive
Clean and rinse your denture: sprinkle a layer of the powder on the denture; you can then place the denture in your mouth.
On average, a denture adhesive will last for 4-5 hours. In case you consume food or hot beverages, you may need to re-apply the same. It is important that the adhesive be removed properly before you decide to place a second layer. Thoroughly clean the denture with a soft tooth brush and then place it in water. Apply the adhesive only after you make sure the denture is clean.