- Xerostomia: Understanding the Diagnosis and the Treatment of Dry Mouth - (https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/jfmdp/journal-of-family-medicine-and-disease- prevention-jfmdp-1-008.php)
- Salivary Glands - (https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/63843)
- Dry mouth - An overview - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26684490/)
- Xerostomia: an update for clinicians - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20887509/)
- Diagnosis and treatment of xerostomia (dry mouth) - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19639449/)
- Diagnosis of salivary gland disease using ultrasound and sialography: a comparison - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2545387/)
What is Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth or xerostomia is a condition where the mouth becomes excessively dry due to decrease in salivary secretions(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Xerostomia: Understanding the Diagnosis and the Treatment of Dry Mouth
Go to source).
Saliva is secreted in the mouth by glands called the salivary glands. There are three sets of main salivary glands, the parotid glands on either side of the face behind the cheeks, the submandibular glands in the lower jaw and the sublingual glands that open below the tongue. In addition, several small glands also secrete saliva. Saliva helps us to chew and swallow food. It also brings about initial digestion of food. It has antiseptic properties and prevents germs from thriving in the mouth, thereby helping to maintain oral health(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Salivary Glands
Go to source).
What are the Causes of Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth could be a temporary issue in conditions like anxiety disorders or nervousness. It may occur at night while sleeping due to breathing with the mouth open. In addition, it could be a symptom of a variety of conditions which include:
- Dehydration: Dehydration can result in dry mouth. Dehydration may occur due to several causes like diarrhea, fever, lack of drinking water, etc. The dry mouth in this condition usually returns to normal once the body is rehydrated.
- Sjogren's Syndrome: Sjogren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder, where the body produces antibodies against the salivary glands as well as the lacrimal glands of the eyes, which secrete tears. Thus, along with dry mouth, the patient has dry eyes as well. Sjogren's syndrome may be associated with other autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Medications: Several medications can cause dry mouth. Salivary secretion is usually controlled by nerves called parasympathetic or cholinergic nerves. Drugs that block the nerves can cause dry mouth. Drugs that have an anticholinergic effect include antihistamines, antidepressants, and antispasmodics. In addition, several drugs used for high blood pressure and diabetes also cause dry mouth.
- Cancer Therapy: Radiation treatment for cancer in the head and neck region, or Hodgkin's cancer can damage the salivary glands and thereby result in dry mouth. In addition, chemotherapy used in cancer treatment can also affect the salivary glands and cause decreased secretion.
- Salivary Duct Obstruction: The salivary gland secretes saliva into the mouth through a small tube called the salivary duct. Obstruction of the salivary duct may occur due to formation of a small stone in the duct, thereby resulting in dry mouth.
- Disease Conditions: Several diseases and illnesses can also cause dry mouth. These include:
- HIV/ AIDS: Dry mouth is sometimes noted in HIV patients. It may occur due to damage to the salivary glands due to inflammation.
- Diabetes: One of the symptoms of diabetes is increased thirst, which may be accompanied by dry mouth. The high blood sugar level associated with diabetes commonly causes dry mouth.
- Parkinson's disease: Though drooling of saliva is a common complaint in patients with Parkinson's disease, decrease in salivary secretion resulting in dry mouth is frequently seen in these patients.
Dry mouth in the above disease conditions may also be due to the medications used in their treatment. Other diseases like Alzheimer's disease, amyloidosis and viral infections may also be associated with dry mouth(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dry mouth - An overview
Go to source).

What are the Symptoms of Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth is a symptom in itself. In addition, the patient may also experience the following due to reduced salivary secretion:
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulty in talking
- Difficulty in wearing dentures
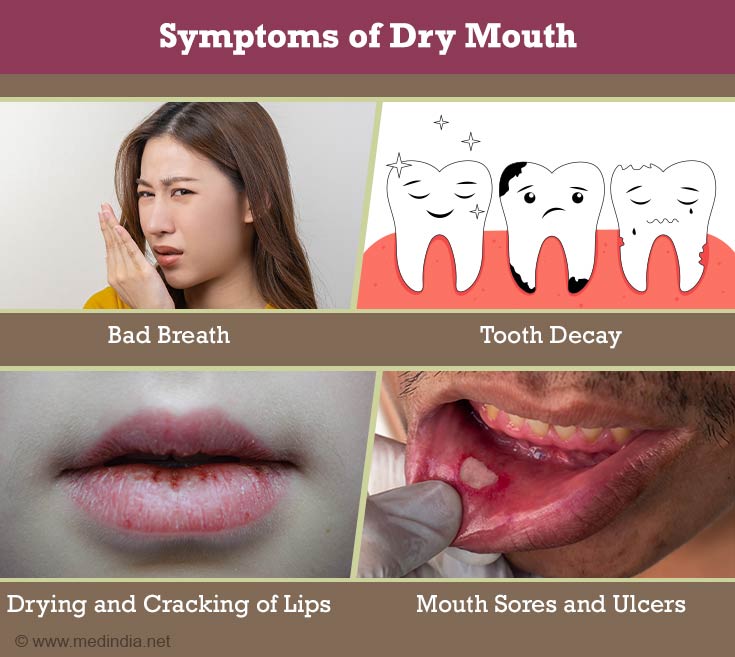
- Bad breath
- Tooth decay
- Changes in taste
- Drying and cracking of lips
- Mouth sores and ulcers
- Sore throat(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Xerostomia: an update for clinicians
Go to source)
How is Dry Mouth Diagnosed?
Dry mouth is usually diagnosed based on the history and physical examination of the patient. There are some tests for salivary secretion like sialometry, sialography, or salivary scintigraphy, which may be done only when necessary.
How do you Treat Dry Mouth?
Dryness of mouth usually resolves once the underlying cause is treated. Medications that cause dry mouth should be stopped or replaced by other drugs. However, this should be done only after consulting the treating physician.
Saliva substitutes or gels are available which may provide relief of symptoms of dry mouth. Sugar-free gum, candies or lozenges can stimulate salivary secretion. Drugs like pilocarpine or cevimeline may also be used to increase salivary secretion(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnosis and treatment of xerostomia (dry mouth)
Go to source, 6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnosis of salivary gland disease using ultrasound and sialography: a comparison
Go to source).
Since the patient is prone to mouth infections, antifungal drugs like local nystatin or lozenges containing clotrimazole may be used to prevent fungal infection.
Surgical procedure may be required for removal of salivary stone, to relieve obstruction to the flow of saliva.
How do you Prevent Dry Mouth?
Some ways in which you can prevent dry mouth are as follows:
- Drink plenty of water
- Chew sugarless gum if you take medications or suffer from illnesses that can cause dry mouth
- Avoid smoking and alcohol intake
Health Tips
Health tips for dry mouth include the following:
- Drink plenty of water
- Chew gum to maintain salivary secretion. Opt for sugarless gum to avoid excess sugar intake and tooth caries
- Rinse your mouth regularly to keep it clean and moist
- Take good care of your teeth. Make sure that you visit your dentist regularly to get oral hygiene tips and detect tooth decay at the earliest. Your dentist may prescribe fluoride to increase the strength of the teeth