- About Ebola virus disease - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001339.htm)
- Ebola virus disease - (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ebola_virus_disease)
About
Ebola is caused by a virus via direct contact with body fluids or infected blood.
Ebola virus disease, also known as Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a disease caused by a virus that gets its name from Ebola River, which flows near one of the villages in the Democratic Republic of Congo, the place where the disease first appeared.
Scientists have identified five types of Ebola virus, of which one is believed to be non-pathogenic to humans. The first outbreak of Ebola virus was seen in 1976, Zaire with 318 cases of the hemorrhagic disease, of which 280 died quickly. So far, this deadly disease has been found in parts of Africa and is known to infect monkeys and human beings.
The virus is known to be transmitted via contact with body fluids or blood from an infected person or through infected needles. However, due to the high mortality and quick death, the spread of the disease is limited. Laboratory personel who test the samples from patients are also at a high risk of infection.
Bats in the African forests have known to be reservoirs of the Ebola virus, although they remain asymptomatic. The infected bats may drop partially eaten fruits and pulp, which are picked up by terrestrial mammals such as gorillas, who in turn catch the virus. Fruit bats are also eaten by people in parts of West Africa, followed by the virus then spreading from person to person, within families, hospitals, communities and even during mortuary rituals.

Once a person catches the virus, its incubation period is 4 to 16 days. The virus spreads through blood and damages blood vessels in vital organs. This eventually causes severe damage to the liver, kidneys, ovaries and testis, lymphatic system and other organs. The bleeding results from damage done to the platelets, linings of arteries, mucosal surfaces of the stomach, heart membrane and vagina.
Diagnosis is based on isolation of the virus and other blood tests. Treatment is symptomatic. It is necessary to take adequate preventive measures since the disease has a high fatality rate.
Ebola Facts
- The Ebola virus first appeared during two outbreaks in Africa, in 1976.
- The virus got its name from the Ebola River, which is near a village in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where the disease first appeared.
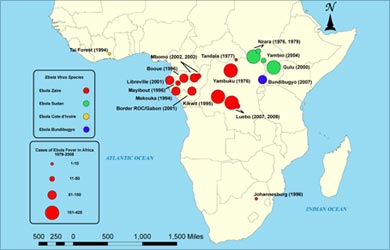
- The Philippines and the United States had reported another strain of Ebola virus, named Reston ebolavirus, and had no connection with the outbreaks in Africa.
- People don’t carry the Ebola virus. They get sick and the infected blood and bodily fluids infect others.
- There are five types of viruses that cause the disease. Four of them are known to be harmful to humans.
- Ebola virus can be transmitted to pigs which tend to develop the symptoms and are affected by the disease like humans.
- Bats and dogs are reservoirs of Ebola virus and transmit the virus, but remain asymptomatic themselves.
- Death in the infected person does not occur due to blood loss. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome due to low blood pressure, focal tissue necrosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation are the possible causes of death.
- The disease sometimes affects the central nervous system that presents as symptoms like headache, confusion, agitation, seizures and sometimes coma.

- There is no known treatment of Ebola yet. Clinical management of symptoms and prevention is the only way to survive the Ebola virus.
- Some scientists suspect that the Plague of Athens, which wiped out almost one-third of the population during the Peloponnesian War, could have been an outbreak of Ebola.